Introduction
 In this new article, we will see how to connect Java to REST API using a simple connector. This ODBC driver allows connecting to REST API or a local file in Java using SQL queries. If you are familiar with SQL, you can easily access to REST API or JSON using simple SQL queries. This article mainly focus on JSON based REST API but techniques listed in this article is almost same for XML based API (e.g. SOAP Web Services).
In this new article, we will see how to connect Java to REST API using a simple connector. This ODBC driver allows connecting to REST API or a local file in Java using SQL queries. If you are familiar with SQL, you can easily access to REST API or JSON using simple SQL queries. This article mainly focus on JSON based REST API but techniques listed in this article is almost same for XML based API (e.g. SOAP Web Services).
Requirements
- First of all, we will require the JDBC Driver for SQL Server.
- Secondly, we will require ZappySys ODBC PowerPack.
- Also, we will require a Java IDE. We will use Java NetBeans for this.
Getting started
First of all, we will create an ODBC connection with a Gateway to the SQL Server connector and then we will connect with Java code.
Add ZappySys ODBC Driver to connect to REST API
The ZappySys JSON Driver allows connecting to different resources like JSON files, REST API, OData, etc.
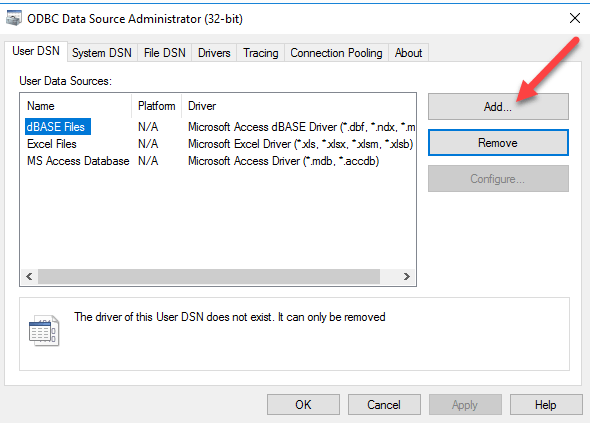
- First of all, in the ODBC Data Source Administrator, press add to add a new System Data Source:
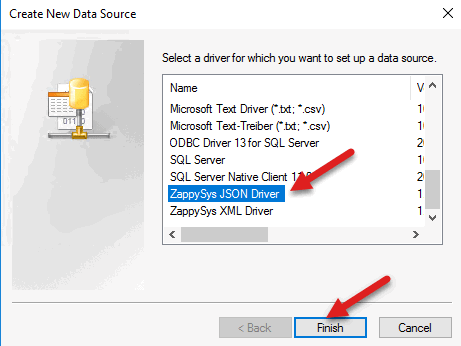
- Secondly, select the ZappySys JSON Driver:
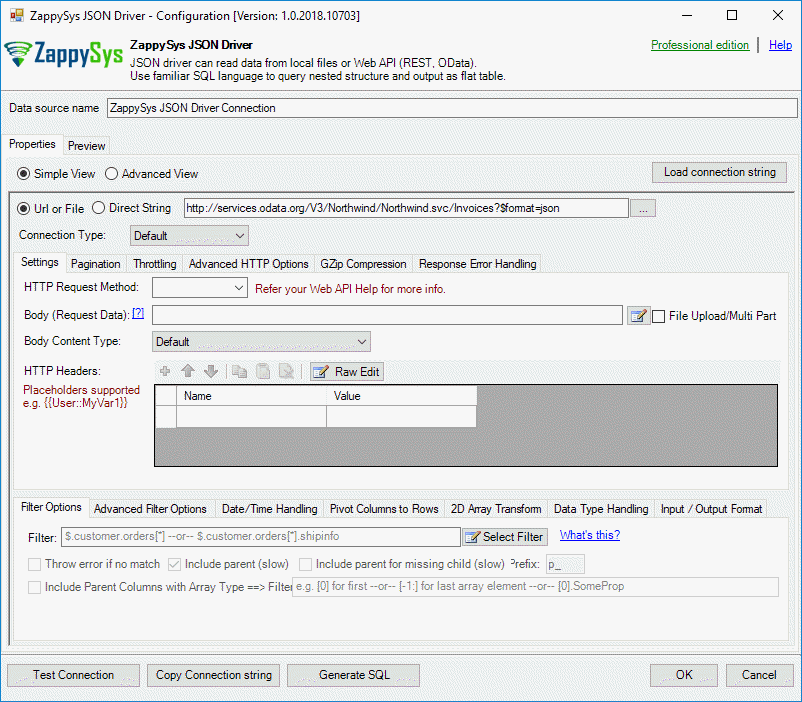
- Also, add this URL to the ZappySys JSON Driver:
1https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svc/Invoices?$format=json
ZappySys Gateway to connect Java to REST API
In order to connect Java to REST API, we will use a Gateway that is installed with the ZappySys ODBC PowerPack. This gateway uses a SQL Server connection. Let’s take a look at the steps.
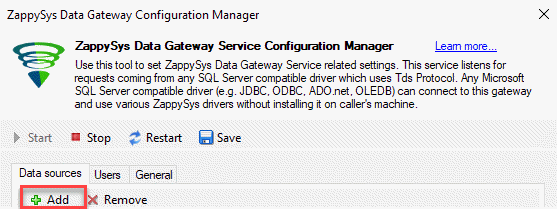
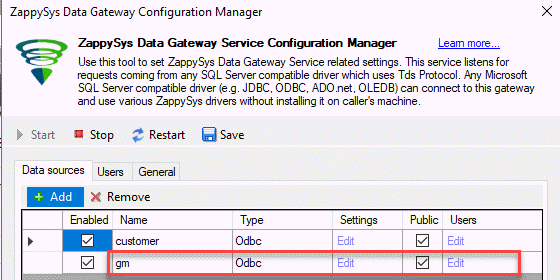
- First of all, open the ZappysSys Data Gateway Configuration.
- Secondly, press the add button and create a new data source named customer:
- Also, enable the custom data source and make sure to check the public option.
- In addition, press the Edit and add the ODBC Data Source created in the Add ZappySys ODBC Driver to connect to REST API section:
1<strong>NOTE:</strong> Whenever possible use native driver option for better performance / security and ease of use.
Zappysys ODBC driver
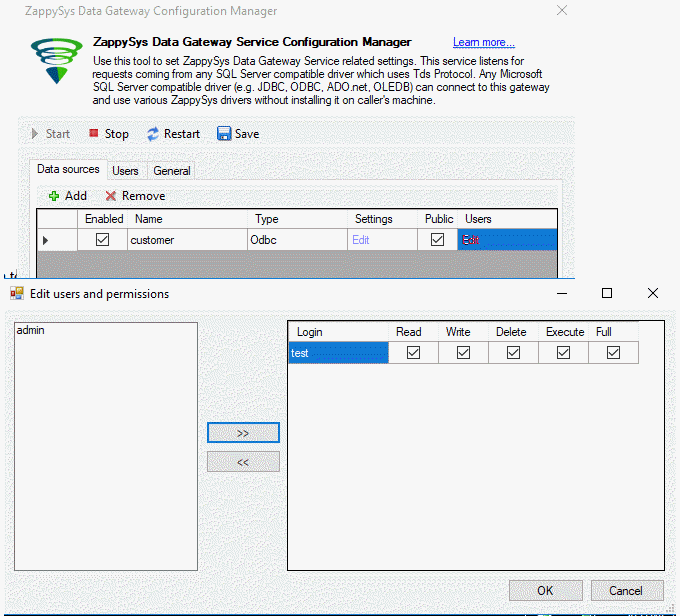
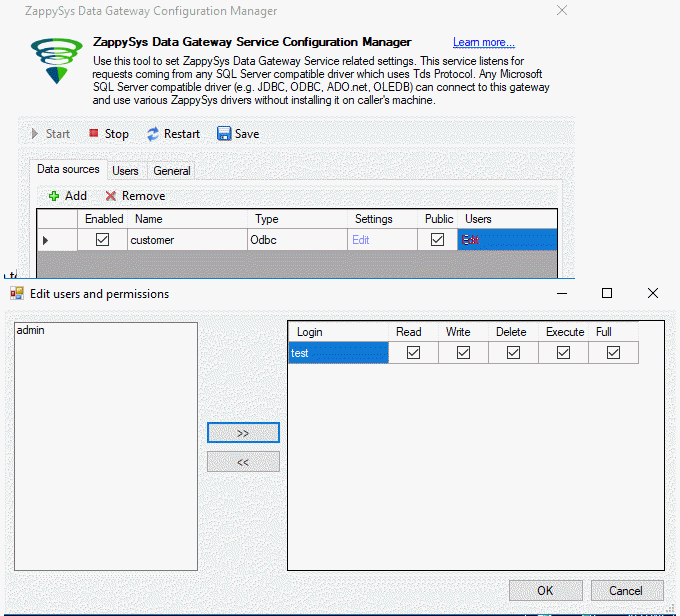
- Additionally, we will add a new user:
- Also, add the user to the data source:
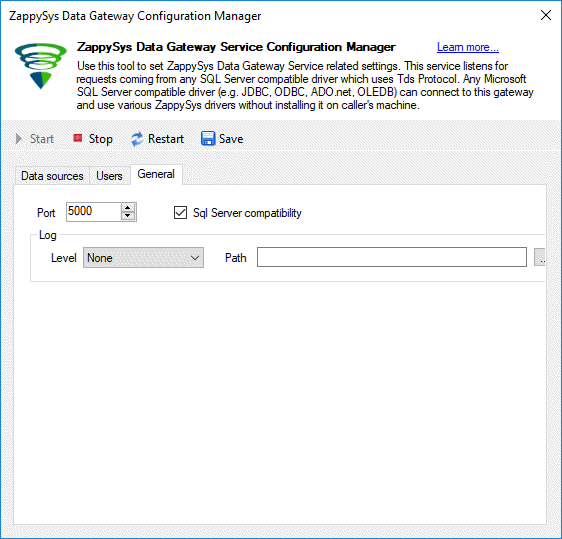
- Finally, check the default port in the general tab. By default this value is 5000:
Connect Java to REST API
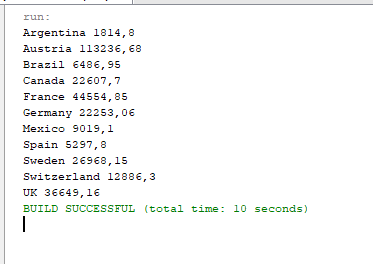
- First of all, we will first try to connect to the following URL:
1https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svc/Invoices?$format=json - Secondly, we will get the countries and the sum or quantity orders using the following code:
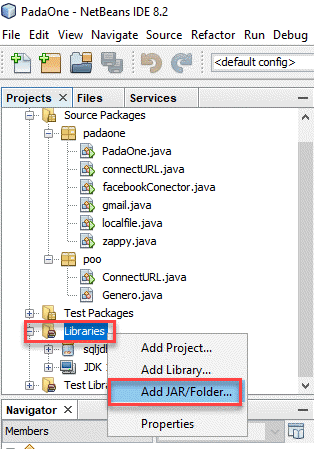
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647package padaone;import java.sql.*;public class zappy {public static void main(String[] args) {// Create a variable for the connection string.String connectionUrl = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:5000;databasename=customer;user=test;password=test";// Declare the JDBC objects.Connection con = null;Statement stmt = null;ResultSet rs = null;try {// Establish the connection.Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");con = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl);// Create and execute an SQL statement that returns some data.String SQL = "SELECT Country , SUM(UnitPrice * Quantity) Total "+ "FROM value "+ "GROUP BY Country "+ "WITH (SRC='https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svc/Invoices?$format=json')";stmt = con.createStatement();rs = stmt.executeQuery(SQL);// Iterate through the data in the result set and display it.while (rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getString(1) + " " + rs.getString(2));}}// Handle any errors that may have occurred.catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {if (rs != null) try { rs.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (stmt != null) try { stmt.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (con != null) try { con.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}}}} - In addition, in the project, go to libraries, right click and select the option to add JAR or folder and select the sqljdbc42.jar. This jar file is used to connect to SQL Server. The ZappySys ODBC PowerPack uses the SQL Server JDBC connector with a gateway to connect to REST API or JSON files:
- Also, we will need to add the sqljdb4.2.jar and the sqljdbc_auth.dll in the C:/Windows/System32 and the path where the JDK is installed (in this example C:/Program Files/Java/jdk1.8.0_171/bin).
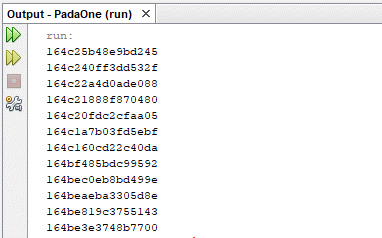
- Finally, run the code and you will visualize the query results of the REST API:
Explanation of the code to Connect Java to REST API
Previously, we run the code to query REST API data in Java. Now we will explain the code.
- First of all, we will import the java.sql to connect to SQL Server using Java:
1import java.sql.*; - Secondly, we will create a connection to the ZappySys Gateway. Using the port 5000 and we are using the data source and user created in the Add ZappySys ODBC Driver to connect to REST API:
12String connectionUrl = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:5000;databasename=customer;user=test;password=test"; - Also, we will set the variables to null to initialize them:
123Connection con = null;Statement stmt = null;ResultSet rs = null; - In addition, we will connect to the JDBC SQL driver:
12Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");con = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl); - Additionally, we will send a query to the URL and get the country and the sum of price multiplied by quantity, group by country:
123456String SQL = "SELECT Country , SUM(UnitPrice * Quantity) Total "+ "FROM value "+ "GROUP BY Country "+ "WITH (SRC='https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svc/Invoices?$format=json')";stmt = con.createStatement();rs = stmt.executeQuery(SQL); - Next, we will print the results of the query:
123while (rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getString(1) + " " + rs.getString(2));} - Finally, we will close all the connections:
12345finally {if (rs != null) try { rs.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (stmt != null) try { stmt.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (con != null) try { con.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}}
How to connect to multiple JSON files
The ZappySys ODBC PowerPack can be used to easily read local JSON files in Java and query using SQL with SELECT, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING and other SQL clauses. For more information, refer to this link.
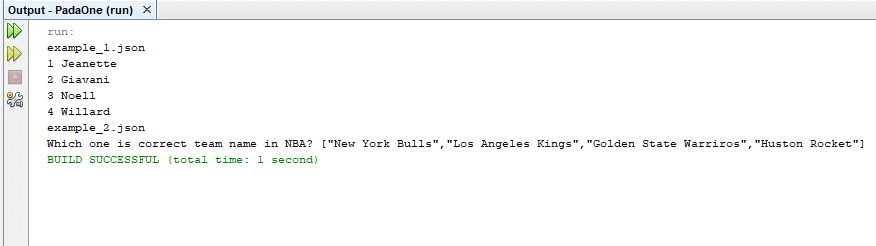
- The following code will list the files and the content of the JSON files:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768package padaone;import java.io.File;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.Statement;public class localfile {public static void main(String[] args) {File directory = new File ("C:\\temp");File[] list = directory.listFiles();printNames(list);}private static void printNames(File[] list) {for(int i =0;i<list.length;i++){if(list[i].isFile()){System.out.println(list[i].getName());showContent(list[i]);}}}private static void showContent(File file) {// Create a variable for the connection string.String connectionUrl = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:5000;databasename=customer;user=test;password=test";// Declare the JDBC objects.Connection con = null;Statement stmt = null;ResultSet rs = null;try {// Establish the connection.Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");con = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl);// Create and execute an SQL statement that returns some data.String SQL = "SELECT * FROM $ WITH (SRC='C:\\temp\\"+file.getName()+"')";stmt = con.createStatement();rs = stmt.executeQuery(SQL);// Iterate through the data in the result set and display it.while (rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getString(1) + " " + rs.getString(2));//+ " " + rs.getString(3)+ " " + rs.getString(4)+ " " + rs.getString(5)+ " " + rs.getString(6));}}// Handle any errors that may have occurred.catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {if (rs != null) try { rs.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (stmt != null) try { stmt.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (con != null) try { con.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}}}} - The JSON files are the following:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172example_1.json[{"id": 1,"first_name": "Jeanette","last_name": "Penddreth","email": "jpenddreth0@census.gov","gender": "Female","ip_address": "26.58.193.2"}, {"id": 2,"first_name": "Giavani","last_name": "Frediani","email": "gfrediani1@senate.gov","gender": "Male","ip_address": "229.179.4.212"}, {"id": 3,"first_name": "Noell","last_name": "Bea","email": "nbea2@imageshack.us","gender": "Female","ip_address": "180.66.162.255"}, {"id": 4,"first_name": "Willard","last_name": "Valek","email": "wvalek3@vk.com","gender": "Male","ip_address": "67.76.188.26"}]example_2.json{"quiz": {"sport": {"q1": {"question": "Which one is correct team name in NBA?","options": ["New York Bulls","Los Angeles Kings","Golden State Warriros","Huston Rocket"],"answer": "Huston Rocket"}},"maths": {"q1": {"question": "5 + 7 = ?","options": ["10","11","12","13"],"answer": "12"},"q2": {"question": "12 - 8 = ?","options": ["1","2","3","4"],"answer": "4"}}}} - Finally, if everything is fine, you will be able to see the file names
and the content:
How to connect Java to REST API Gmail
Connect Java to Google, Facebook, OneDrive or other REST API tools is a straightforward process using the ZappySys ODBC Driver. You just need to create the Data Source in ODBC and then create a ZappySys Gateway, the rest is simple in Java. Let’s take a look at an example.
- First of all, we will create a new Data source in the Windows ODBC Data
Source Administrator. We will create a new ZappySys JSON Driver and add the following link:
1https://www.googleapis.com/gmail/v1/users/me/messages/ - Secondly, select the OAuth connection type and $.messages[*] in the
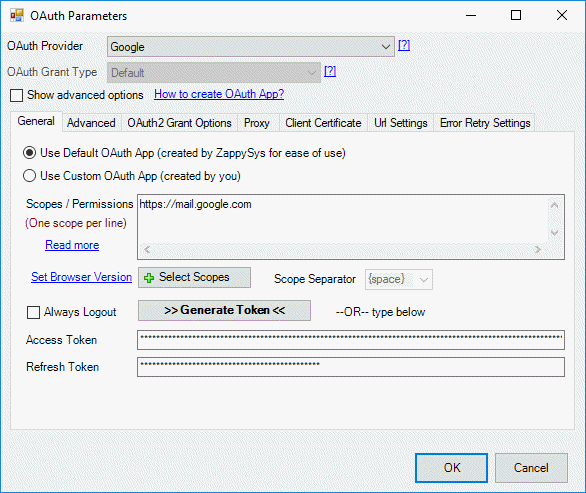
filter and press the Click to Configure link: - Also, in the OAuth parameters link, select the Google OAuth Provider.
- In addition in scopes write the scope https://mail.google.com:
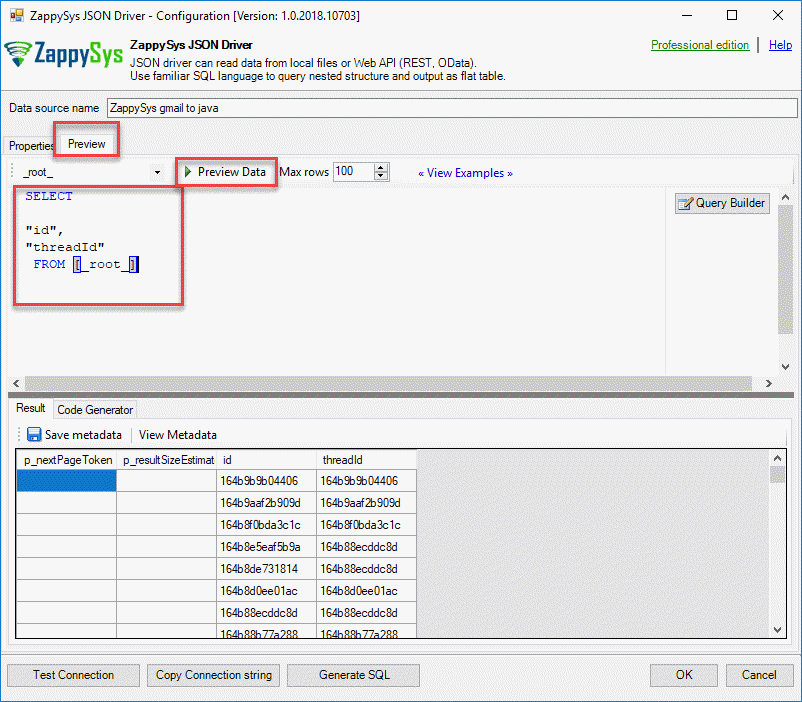
- Additionally, in the preview tab, you can generate your queries and save
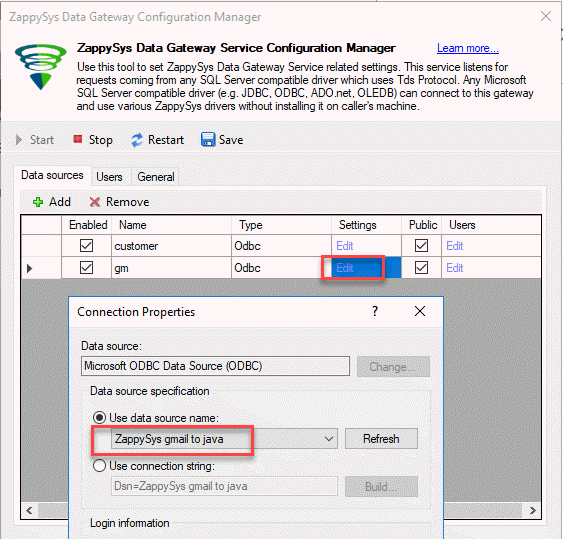
your Data Source: - Next, open your ZappySys Data Gateway. We will create a new Data Source
named gm: - Also, we will associate the ODBC Data Source with the Gateway Data Source. Make sure to add the test user to the Gateway data source:
- Finally, you can run this code. The code in Java will connect to the Gateway data source using the port 5000 and the Gateway user and password. The query will show the Gmail message ids:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647package padaone;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.Statement;public class gmail {public static void main(String[] args) {// Create a variable for the connection string.String connectionUrl = "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:5000;databasename=gm;user=test;password=test";// Declare the JDBC objects.Connection con = null;Statement stmt = null;ResultSet rs = null;try {// Establish the connection.Class.forName("com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver");con = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl);// Create and execute an SQL statement that returns some data.String SQL = "SELECT id FROM [_root_]";stmt = con.createStatement();rs = stmt.executeQuery(SQL);// Iterate through the data in the result set and display it.while (rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getString(1));}}// Handle any errors that may have occurred.catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {if (rs != null) try { rs.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (stmt != null) try { stmt.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}if (con != null) try { con.close(); } catch(Exception e) {}}}} - You can find your message id in Google by clicking your messages:
ZappySys JSON /REST API Driver Query Examples
Reading from XML files or API can be done using the same way as previous sections except you have to use ZappySys XML Driver. Read help file here to see json query examples.
ZappySys XML / SOAP Driver Query Examples
Reading from XML files or API can be done using the same way as previous sections except you have to use ZappySys XML Driver. Read help file here to see xml query examples.
Calling XML SOAP Web Service in JAVA
So far we have looked at examples to consume data using JSON driver. Now lets look at an example, to call XML SOAP Web Service in JAVA.
What is SOAP Web Service?
If you are new to SOAP Web Service sometimes referred as XML Web Service then please read some concept about SOAP Web service standard from this link There are two important aspects in SOAP Web service.- Getting WSDL file or URL
- Knowing exact Web Service URL
What is WSDL
In very simple term WSDL (often pronounced as whiz-dull) is nothing but a document which describes Service metadata (e.g. Functions you can call, Request parameters, response structure etc). Some service simply give you WSDL as xml file you can download on local machine and then analyze or sometimes you may get direct URL (e.g. http://api.mycompany.com/hr-soap-service/?wsdl )Example SQL Query for SOAP API call using ZappySys XML Driver
Here is an example SQL query you can write to call SOAP API. If you not sure about many details then check next few sections on how to use XML Driver User Interface to build desired SQL query to POST data to XML SOAP Web Service without any coding.SELECT * FROM $
WITH(
Src='http://www.holidaywebservice.com/HolidayService_v2/HolidayService2.asmx'
,DataConnectionType='HTTP'
,CredentialType='Basic' --OR SoapWss
,SoapWssPasswordType='PasswordText'
,UserName='myuser'
,Password='pass$$w123'
,Filter='$.soap:Envelope.soap:Body.GetHolidaysAvailableResponse.GetHolidaysAvailableResult.HolidayCode[*]'
,ElementsToTreatAsArray='HolidayCode'
,RequestMethod='POST'
,Header='Content-Type: text/xml;charset=UTF-8 || SOAPAction: "http://www.holidaywebservice.com/HolidayService_v2/GetHolidaysAvailable"'
,RequestData='
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:hol="http://www.holidaywebservice.com/HolidayService_v2/">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<hol:GetHolidaysAvailable>
<!--type: Country - enumeration: [Canada,GreatBritain,IrelandNorthern,IrelandRepublicOf,Scotland,UnitedStates]-->
<hol:countryCode>UnitedStates</hol:countryCode>
</hol:GetHolidaysAvailable>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>'
)
Now let's look at steps to create SQL query to call SOAP API. Later we will see how to generate code for your desired programming language (e.g. C# or SQL Server)
Video Tutorial - Introduction to SOAP Web Service and SoapUI tool
Before we dive into details about calling SOAP API using ZappySys XML Driver, lets first understand what is SOAP API and how to create SOAP requests using SoapUI tool. You will learn more about this process in the later section. The video contains some fragment about using SOAP API in SSIS but just ignore that part because we will be calling Soap API using ZappySys ODBC Driver rather than SSIS Components.Using SoapUI to test SOAP API call / Create Request Body XML
Assuming you have downloaded and installed SoapUI from here, now we are ready to use WSDL for your SOAP Web Service Calls. If you do not have WSDL file or URL handy then contact your API provider (sometimes you just have to add ?wsdl at the end of your Service URL to get WSDL so try that. Example: http://mycompany/myservice?wsdl ). If you don't know what is WSDL then in short, WSDL is Web service Description Language (i.e. XML file which describes your SOAP Service). WSDL helps to craft SOAP API request Body for ZappySys XML Driver. So Let's get started.- Open SoapUI and click SOAP button to create new SOAP Project
- Enter WSDL URL or File Path of WSDLFor example WSDL for our sample service can be accessed via this URL
http://www.dneonline.com/calculator.asmx?wsdl
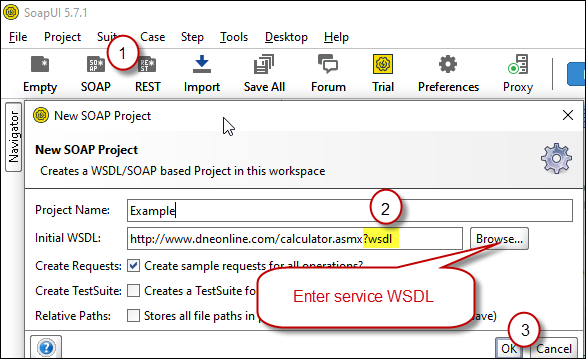 Create new SOAP API Project in SoapUI tool for SOAP API Testing
Create new SOAP API Project in SoapUI tool for SOAP API Testing - Once WSDL is loaded you will see possible operations you can call for your SOAP Web Service.
- If your web service requires credentials then you have to configure it. There are two common credential types for public services (SOAP WSS or BASIC )
-
To use SOAP WSS Credentials select request node and enter UserId, Password, and WSS-PasswordType (PasswordText or PasswordHash)
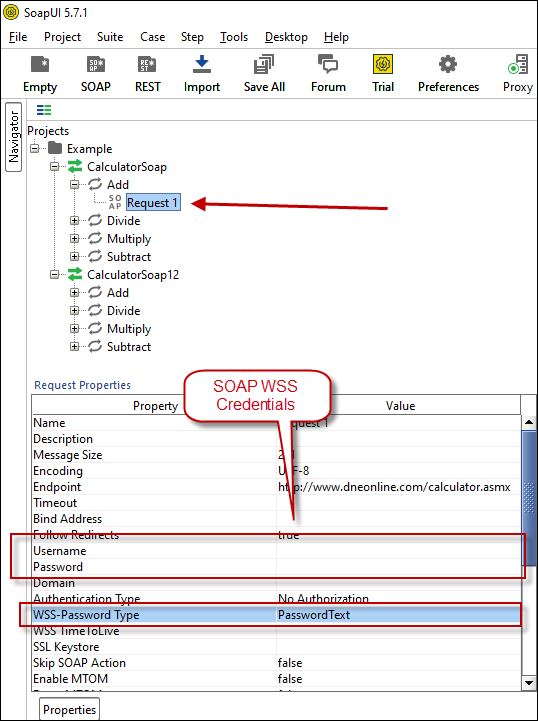 Configure SOAP WSS Credentials for SoapUI (SOAP API Testing Tool)
Configure SOAP WSS Credentials for SoapUI (SOAP API Testing Tool) - To use BASIC Auth Credentials select request node and double-click it. At the bottom click on Auth (Basic) and From Authorization dropdown click Add New and Select Basic.
 Configure Basic Authorization for SoapUI (SOAP API Testing Tool)
Configure Basic Authorization for SoapUI (SOAP API Testing Tool)
-
- Now you can test your request first Double-click on the request node to open request editor.
- Change necessary parameters, remove optional or unwanted parameters. If you want to regenerate request you can click on Recreate default request toolbar icon.
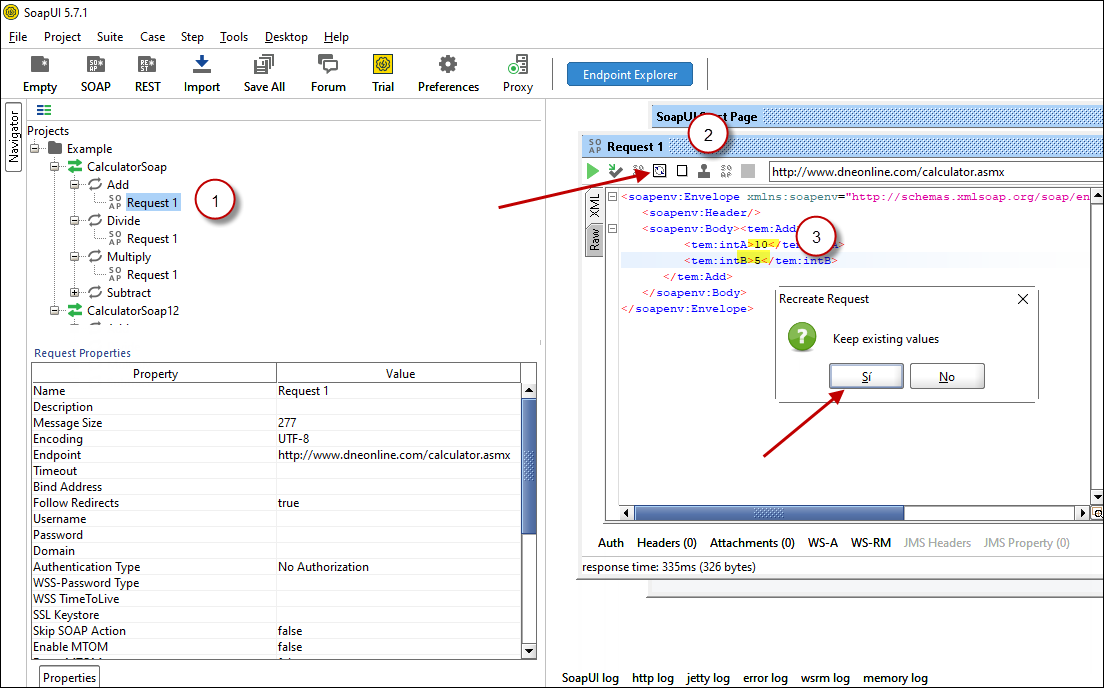 Create SOAP Request XML (With Optional Parameters)
Create SOAP Request XML (With Optional Parameters) - Once your SOAP Request XML is ready, Click the Play button in the toolbar to execute SOAP API Request and Response will appear in Right side panel.
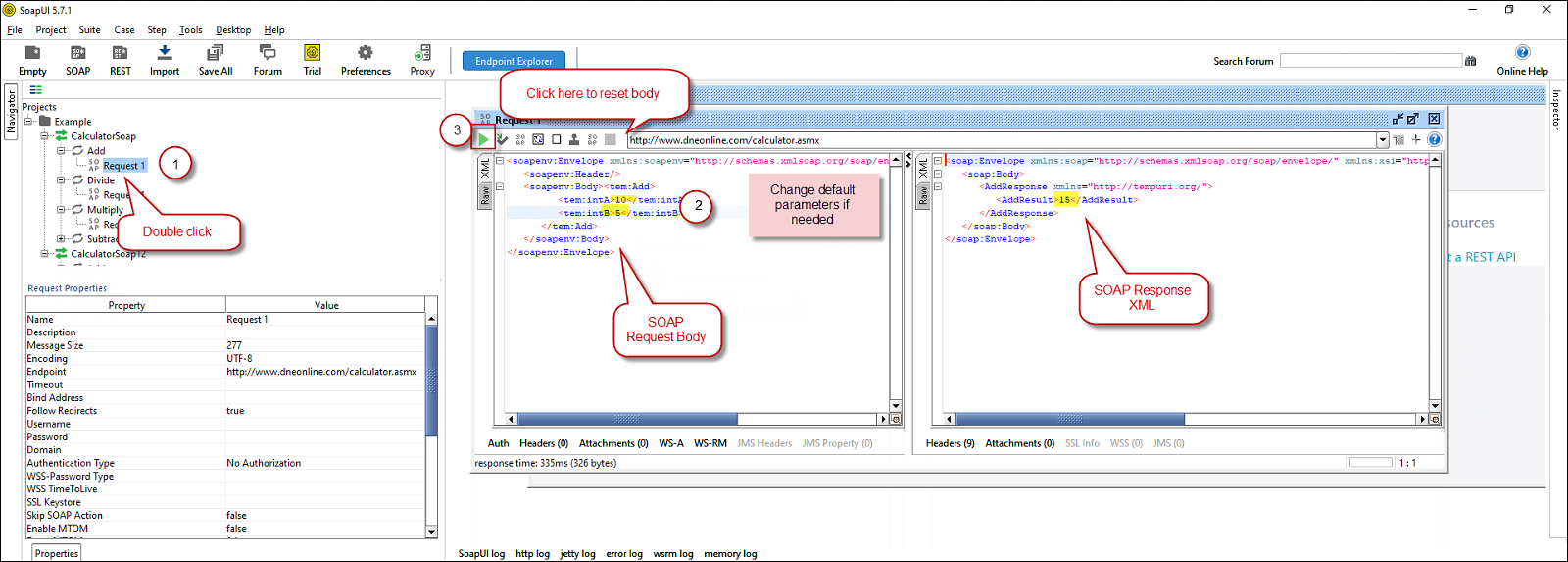 Test SOAP API using SoapUI Tool (Change Default XML Body / Parameters, Execute and See Response)
Test SOAP API using SoapUI Tool (Change Default XML Body / Parameters, Execute and See Response)
Create DSN using ZappySys XML Driver to call SOAP API
Once you have tested your SOAP API in SoapUI tool, we are ready to use ZappySys XML driver to call SOAP API in your preferred BI tool or Programming language.- First open ODBC Data Sources (search ODBC in your start menu or go under ZappySys > ODBC PowerPack > ODBC 64 bit)
- Goto System DSN Tab (or User DSN which is not used by Service account)
- Click Add and Select ZappySys XML Driver
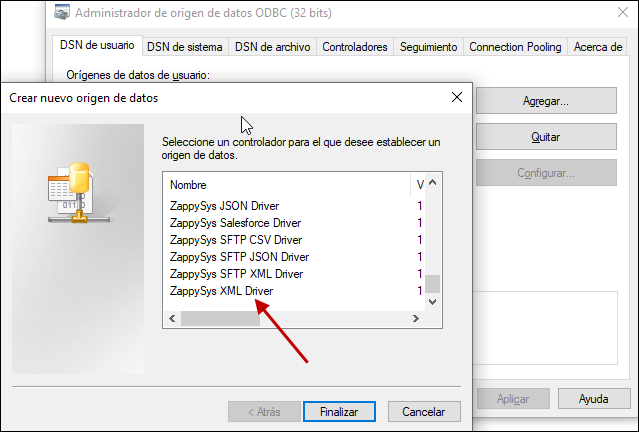 ZappySys ODBC Driver for XML / SOAP API
ZappySys ODBC Driver for XML / SOAP API - Configure API URL, Request Method and Request Body as below
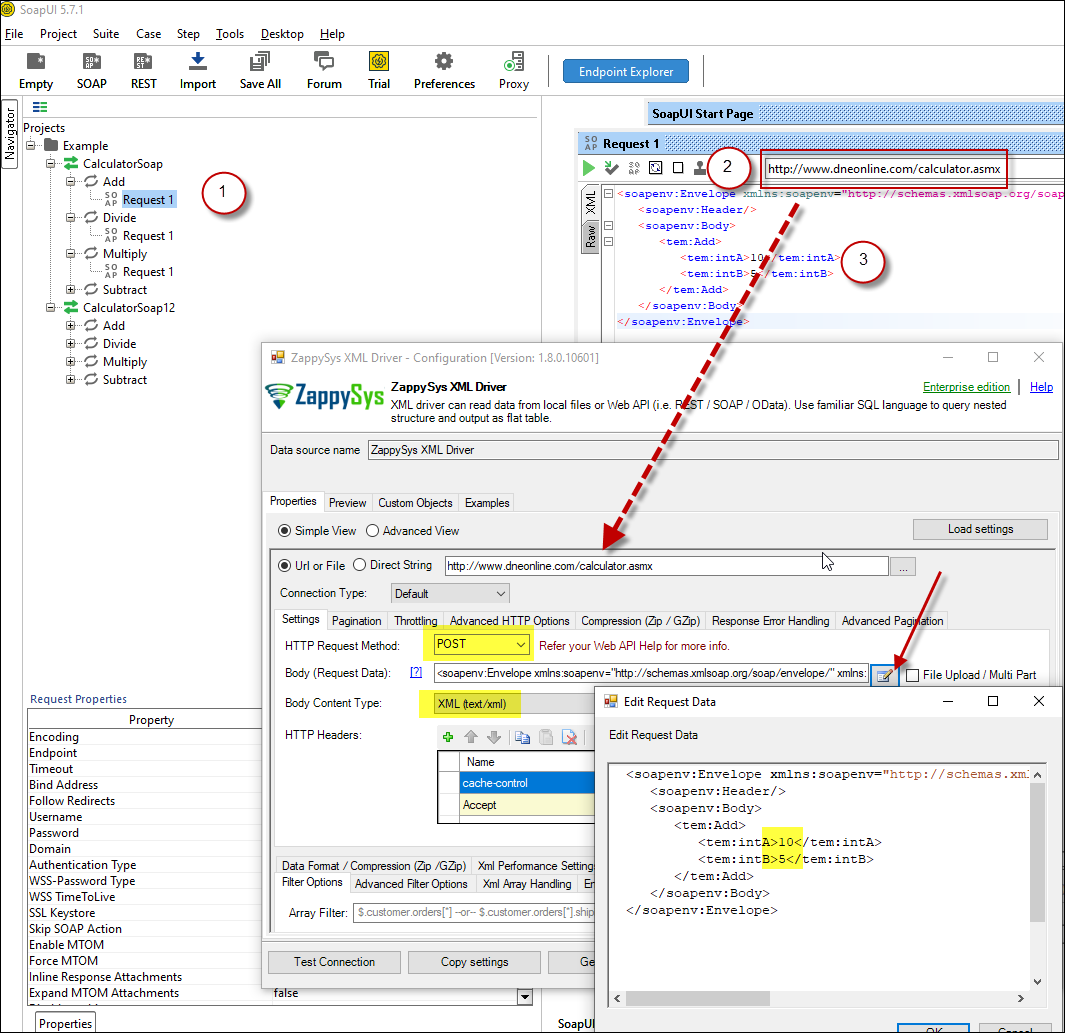 ZappySys XML Driver - Calling SOAP API - Configure URL, Method, Body
ZappySys XML Driver - Calling SOAP API - Configure URL, Method, Body - (This step is Optional) If your SOAP API requires credentials then Select Connection Type to HTTP and configure as below.
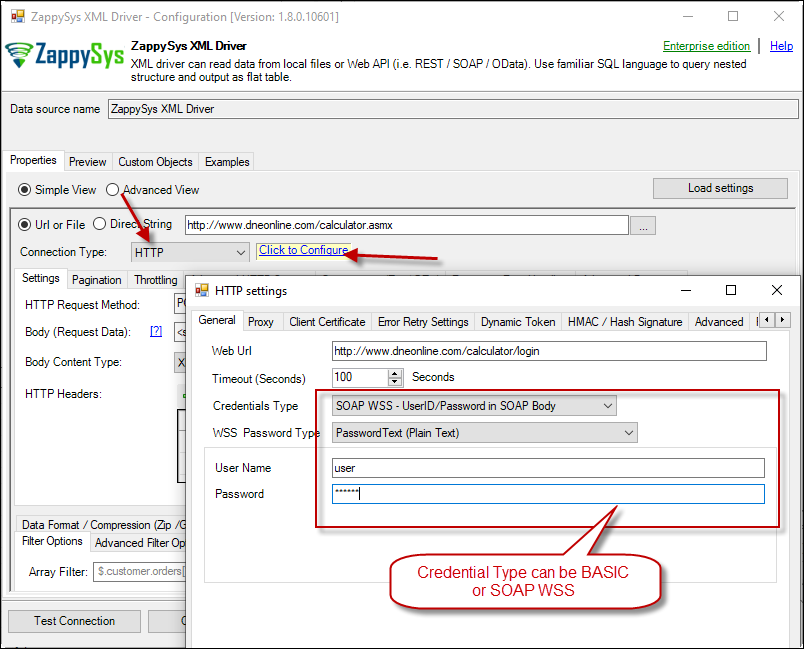 ZappySys XML Driver - Configure SOAP WSS Credentials or Basic Authorization (Userid, Password)
ZappySys XML Driver - Configure SOAP WSS Credentials or Basic Authorization (Userid, Password) - Configure-Request Headers as below (You can get it from Request > Raw tab from SoapUI after you test the request by clicking the Play button)
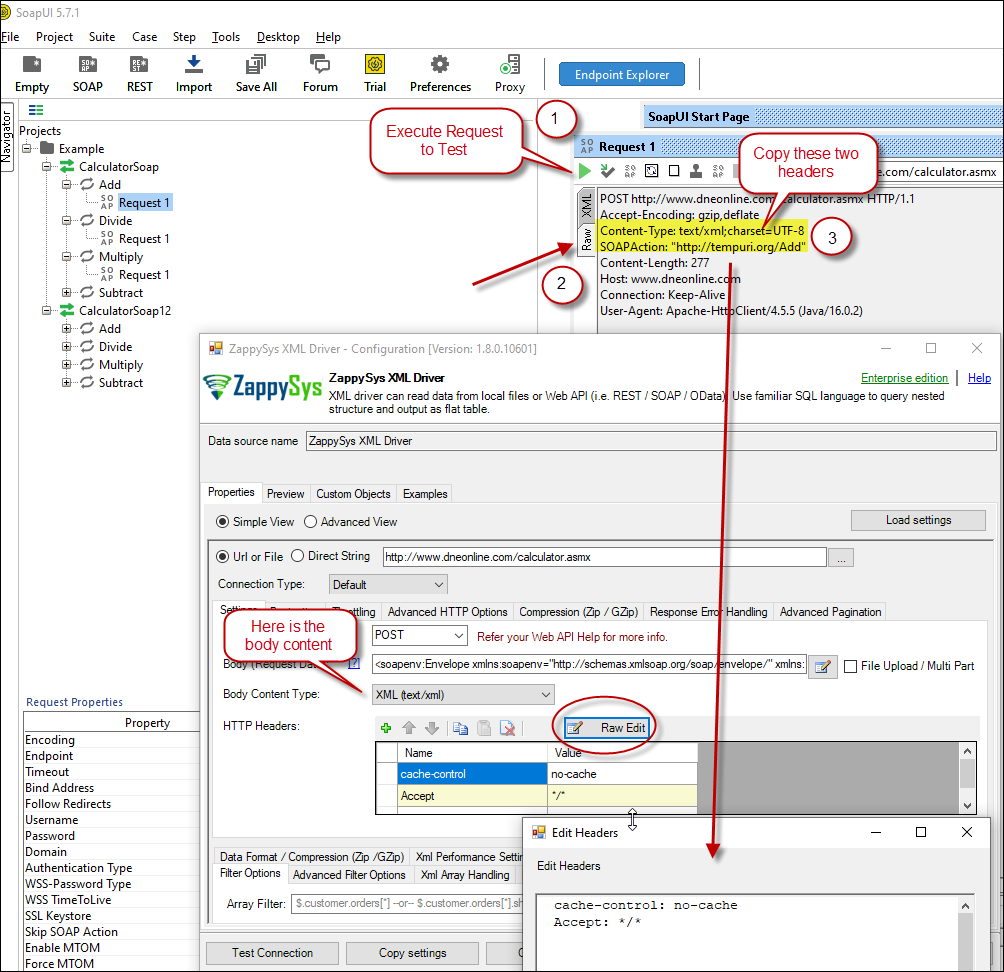 Configure SOAP API Request Headers - ZappySys XML Driver
Configure SOAP API Request Headers - ZappySys XML Driver - Once credentials entered you can select Filter to extract data from the desired node. Make sure to select array node (see special icon) or select the node which contains all necessary columns if you don't have array node.
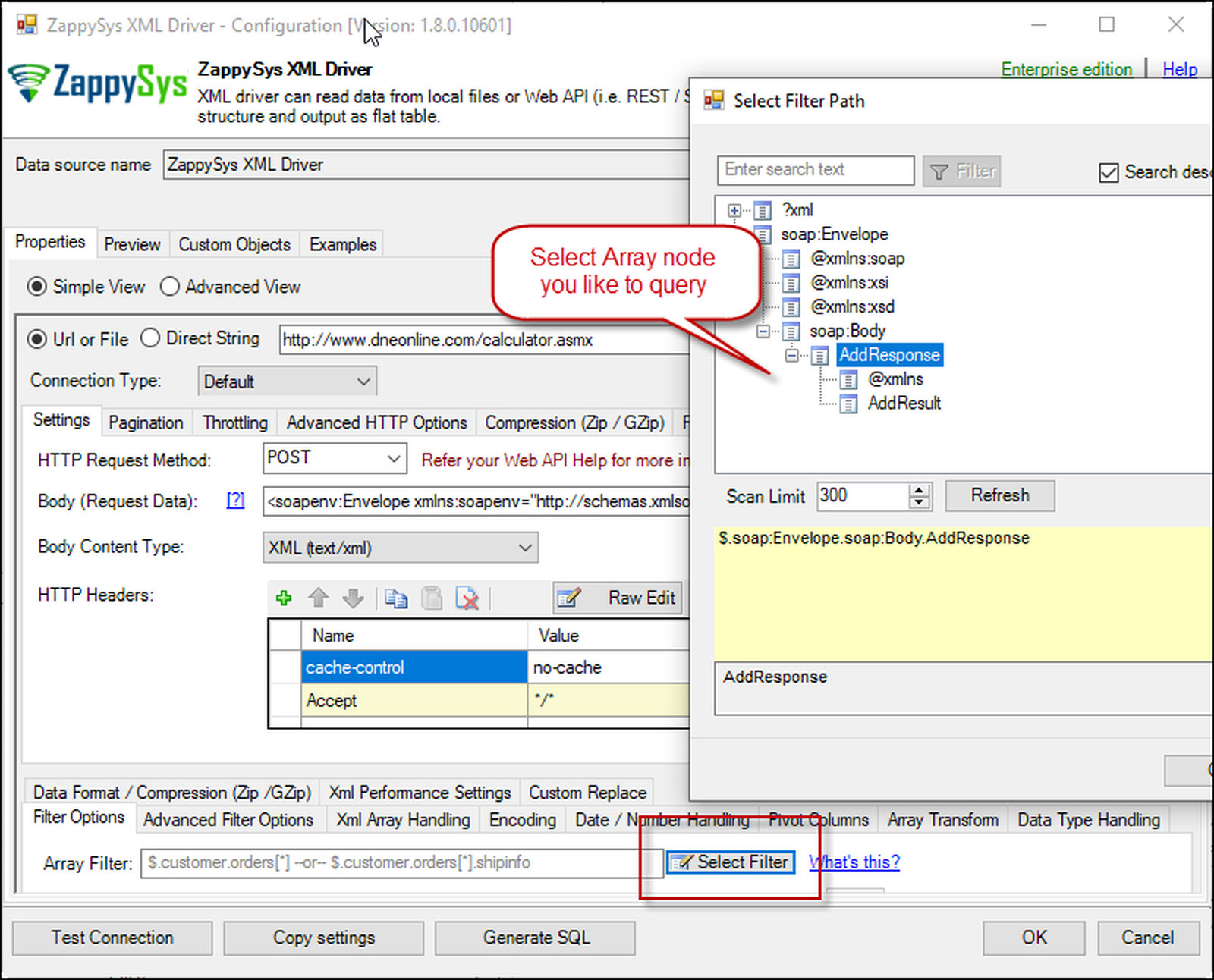 Select Filter - Extract data from nested XML / SOAP API Response (Denormalize Hierarchy)
Select Filter - Extract data from nested XML / SOAP API Response (Denormalize Hierarchy) - If prompted select yes to treat selected node as Array (This is helpful when you expect one or more record for selected node)
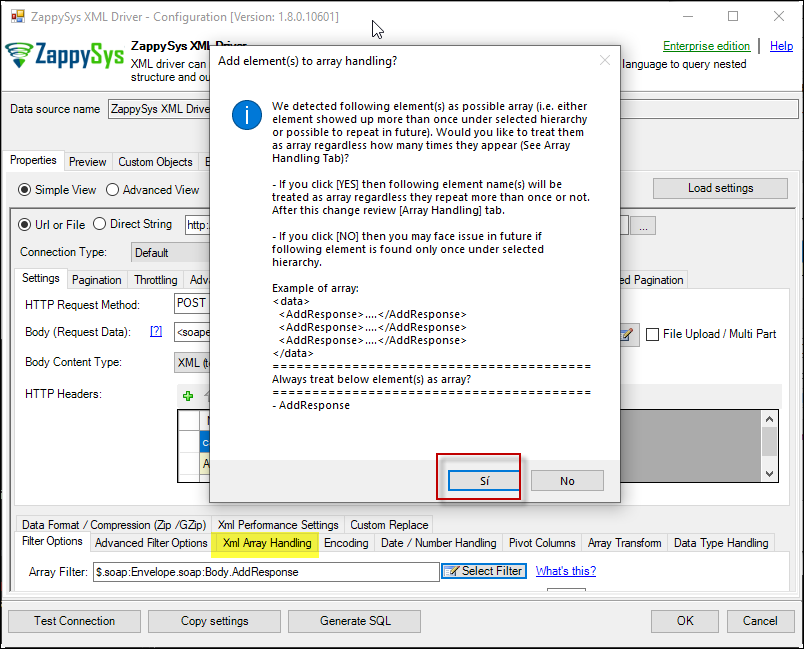 Treat selected node as XML Array Option for SOAP API Response XML
Treat selected node as XML Array Option for SOAP API Response XML
Preview SOAP API Response / Generate SQL Code for SOAP API Call
Once you configure settings for XML Driver now you can preview data or generate example code for desired language (e.g. C#, Python, Java, SQL Server). Go to Preview tab and you will see default query generated based on settings you entered in previous sections. Attributes listed in WITH clause are optional. If you omit attribute in WITH clause it will use it from Properties tab.Preview Data
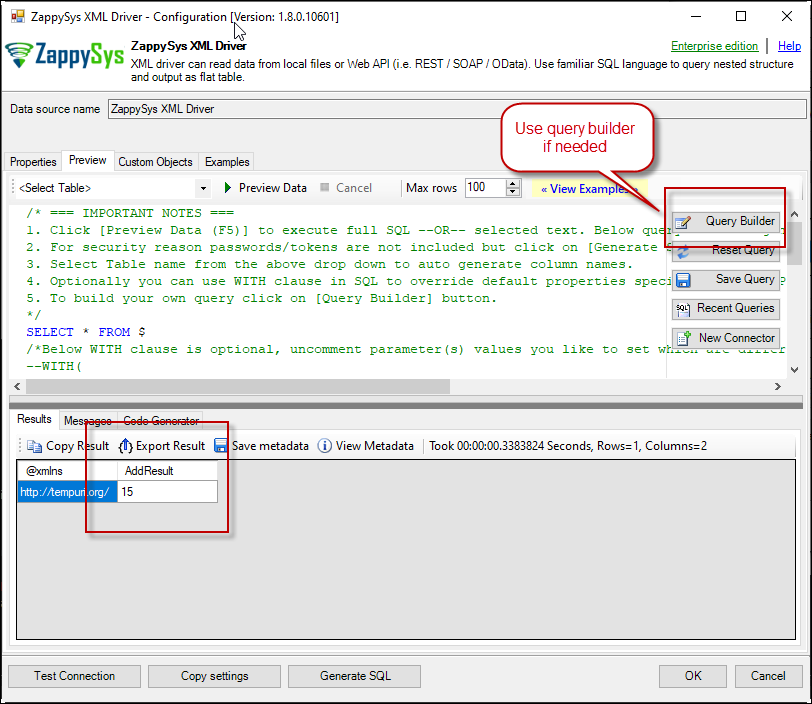 Preview SOAP API Response in ZappySys XML Driver
Preview SOAP API Response in ZappySys XML Driver
Generate Code Option
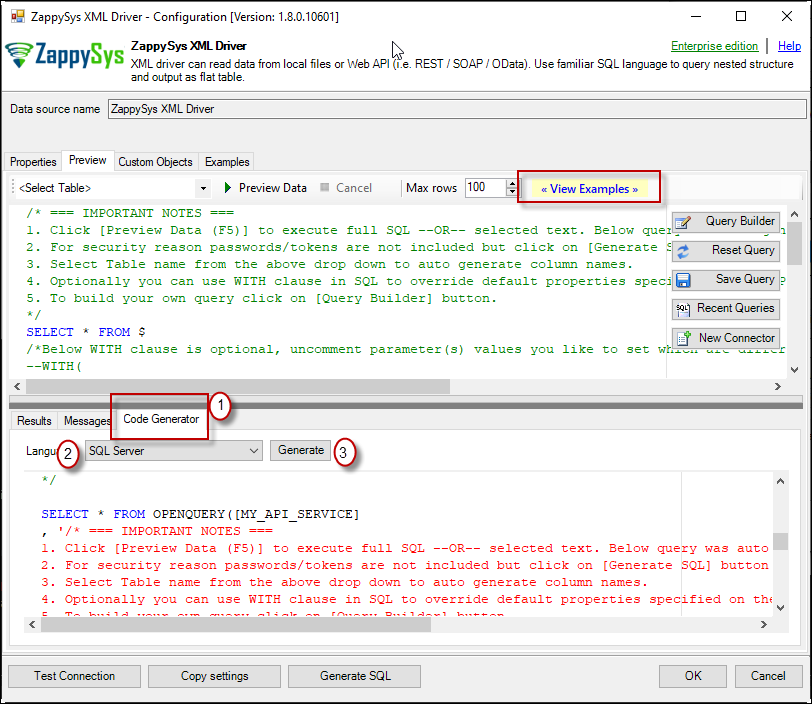
POST data to REST API URL from file in JAVA
Above example was POST data to API URL but what if your Request Body is large and you have saved that to file? Well here is the way to get your request body from a file (Use @ symbol before path).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
SELECT * FROM $ WITH (METHOD='POST' ,HEADER='Content-Type:text/plain || x-hdr1:AAA' ,SRC='http://httpbin.org/post' ,BODY='@c:\files\dump.xml' ,IsMultiPart='True' ) |
REST API Pagination in JAVA
Paginate by Response Attribute
This example shows how to paginate API calls where you need to paginate until the last page detected. In this example, next page is indicated by some attribute called nextlink (found in response). If this attribute is missing or null then it stops fetching the next page.SELECT * FROM $ WITH( SRC=@'https://zappysys.com/downloads/files/test/pagination_nextlink_inarray_1.json' ,NextUrlAttributeOrExpr = '$.nextlink' --keep reading until this attribute is missing. If attribute name contains dot then use brackets like this $.['my.attr.name'] )
Paginate by URL Parameter (Loop until certain StatusCode)
This example shows how to paginate API calls where you need to pass page number via URL. The driver keeps incrementing page number and calls next URL until the last page detected (401 error). There are few ways to indicate the last page (e.g. By status code, By row count, By response size). If you don't specify end detection then it will use the default (i.e. No records found).SELECT * FROM $ WITH ( SRC=@'https://zappysys.com/downloads/files/test/page-xml.aspx?page=1&mode=DetectBasedOnResponseStatusCode' ,PagingMode='ByUrlParameter' ,PagingByUrlAttributeName='page' ,PagingByUrlEndStrategy='DetectBasedOnResponseStatusCode' ,PagingByUrlCheckResponseStatusCode=401 ,IncrementBy=1 )
Paginate by URL Path (Loop until no record)
This example shows how to paginate API calls where you need to pass page number via URL Path. The driver keeps incrementing page number and calls next URL until the last page is detected. There are few ways to indicate the last page (e.g. By status code, By row count, By response size). If you don't specify end detection then it will use the default (i.e. No records found).SELECT * FROM $ WITH ( SRC=@'https://zappysys.com/downloads/files/test/cust-<%page%>.xml' ,PagingMode='ByUrlPath' ,PagingByUrlAttributeName='<%page%>' ,PagingByUrlEndStrategy='DetectBasedOnRecordCount' ,IncrementBy=1 )
Paginate by Header Link (RFC 5988)
API like GitHub / Wordpress use Next link in Headers (RFC 5988)SELECT * FROM $ LIMIT 25 WITH( Src='https://wordpress.org/news/wp-json/wp/v2/categories?per_page=10' ,PagingMode='ByResponseHeaderRfc5988' ,WaitTimeMs='200' --//wait 200 ms after each request )
Error Handling in REST API / SOAP
METHOD 1 - Using Error Handling Options
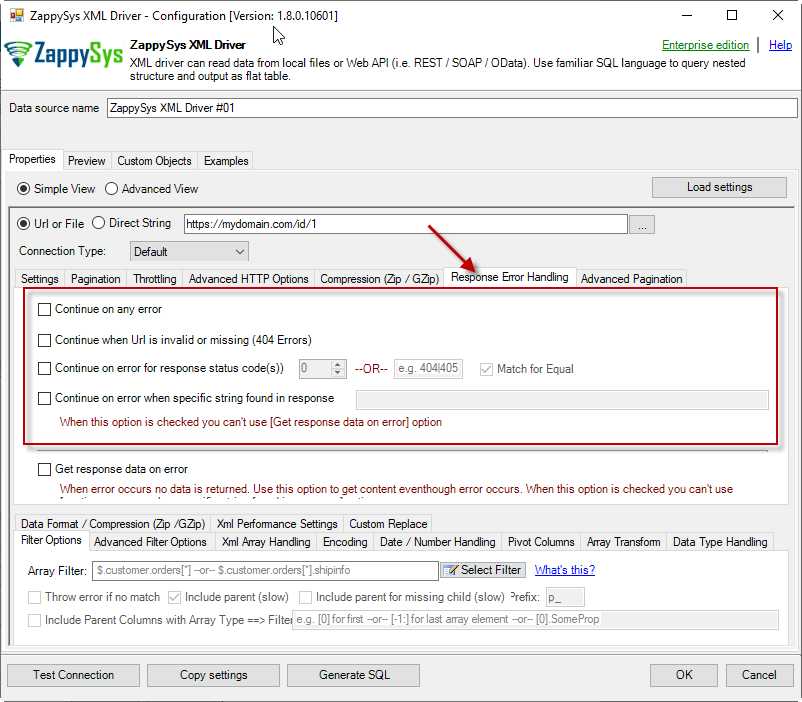
When to use?
You may want to use them when your source is a resource located on the Internet; e.g. a file on a website, a file on an FTP server or just a plain API HTTP response. By default, when a remote server returns an error, data retrieval is stopped, an error is raised and no data is given back to you. This might not be always desirable.Scenario 1
Imagine a scenario, that there is a web server which each day at 12 AM releases a new JSON file with that day's date as filename, e.g. http://www.some-server.com/data/2018-06-20.json. And, of course, you want to download it and use it daily in your Power BI report. But you have a problem: Power BI report data sources are refreshed each hour and you may get HTTP 404 status code (no file was found) when a file is not released yet. Which consequentially means other data sources won't be updated as well and you will see old and cached data on the report. That's where you could use Continue on any error or Continue when Url is invalid or missing (404 Errors) to avoid an error being raised and let other data sources to be updated.Scenario 2
Another scenario is when you expect a web server to raise some kind of HTTP error when accessing a URL. You don't want ODBC Data Source to raise an error but instead, you want to get response data. That's where you can use Continue on any error or alike together with Get response data on error to continue on an error and get the data: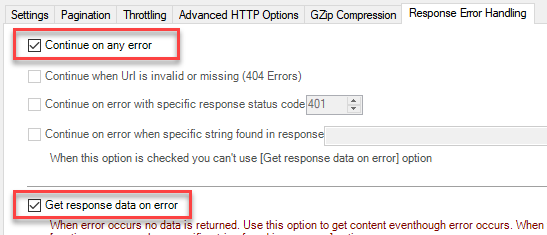
METHOD 2 - Using Connection [Retry Settings]
Another scenario you may run into is a buggy web server. You ask it to give you some file or data and it, like a snotty kid, just doesn't give it to you! You have to ask twice or thrice before it does its job. If that's the case, you have to retry HTTP requests using Connection: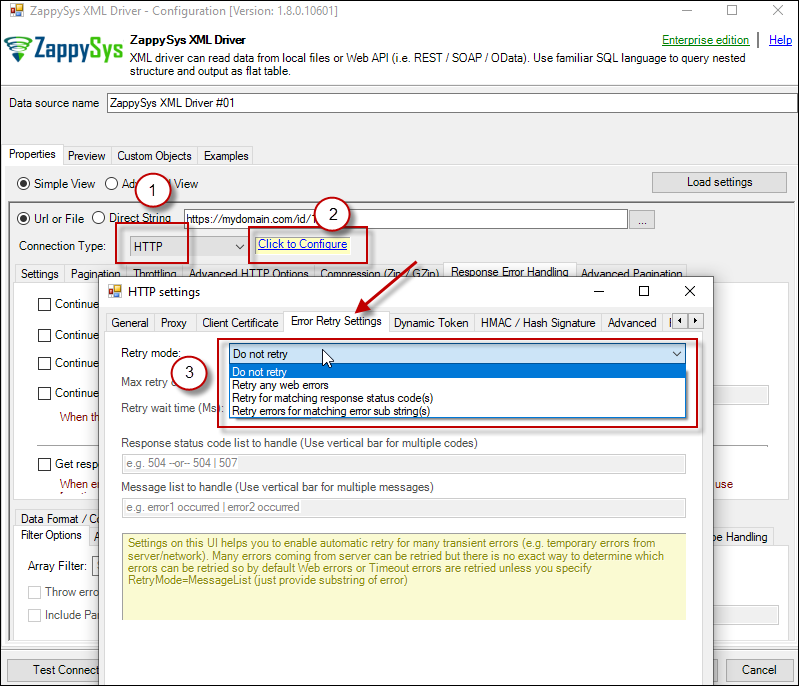
REST API / SOAP Connection Types in JAVA (OAuth / HTTP)
- HTTP
- OAuth
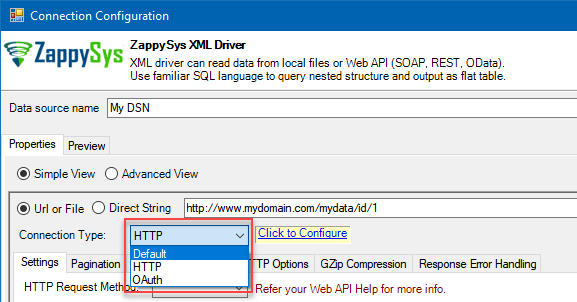
HTTP Connection
- SOAP WSS (when accessing a SOAP WebService)
- Static Token / API Key (when need to pass an API key in HTTP header)
- Dynamic Token (same as Static Token method except that each time you need to log in and retrieve a fresh API key)
- JWT Token (As per RFC 7519)
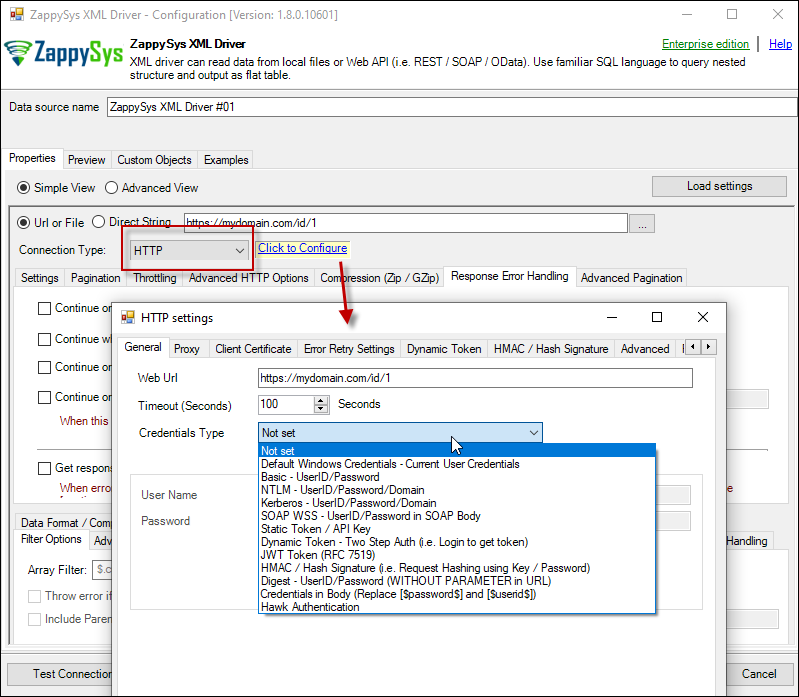
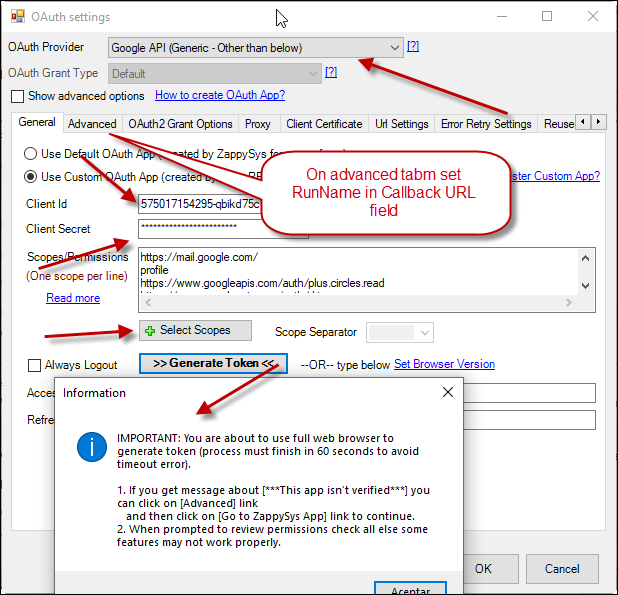
OAuth
If you are trying to access REST API resource, it is a huge chance, you will need to use OAuth Connection. Read this article to understand how OAuth authentication and authorization works and how to use it (article originally was written for SSIS PowerPack, but the concepts and UI stay the same):https://zappysys.com/blog/rest-api-authentication-with-oauth-2-0-using-ssis/
Performance consideration for Web API Calls
Use Server-side filtering if possible in URL or Body Parameters
Many API supports filtering your data by URL parameters or via Body. Whenever possible try to use such features. Here is an example of odata API, In the below query the first query is faster than the second query because in the first query we filter at the server.SELECT * FROM value WITH( Src='https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svc/Customers?$format=json&$filter=Country eq ''USA''' ,DataFormat='Odata' ) -- Slow query - Client-side filtering SELECT * FROM value WHERE Country ='USA' WITH( Src='https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svc/Customers?$format=json' ,DataFormat='Odata' )
Avoid Special features in SQL Query (e.g. WHERE, Group By, Order By)
ZappySys API engine triggers client-side processing if special features are used in Query. Following SQL Features will trigger Client-Side processing which is several times slower than server-side processing. So always try to use simple query (Select col1, col2 .... from mytable )- WHERE Clause
- GROUP BY Clause
- HAVING Clause
- ORDER BY
- FUNCTIONS (e.g. Math, String, DateTime, Regex... )
Consider using pre-generated Metadata / Cache File
Use META option in WITH Clause to use static metadata (Pre-Generated)There are two more options to speedup query processing time. Check this article for details.-
select * from value WITH( meta='c:\temp\meta.txt' ) --OR-- select * from value WITH( meta='my-meta-name' ) --OR-- select * from value WITH( meta='[ {"Name": "col1", "Type": "String", Length: 100}, {"Name": "col2", "Type": "Int32"} ...... ]' ) - Enable Data Caching Options (Found on Property Grid > Advanced Mode Only )
Consider using Metadata / Data Caching Option
ZappySys API drivers support Caching Metadata and Data rows to speed up query processing. If your data doesn't change often then you can enable this option to speed up processing significantly. Check this article for details how to enable Data cache / metadata cache feature for datasource level or query level. To define cache option at query level you can use like below.SELECT * FROM $ WITH ( SRC='https://myhost.com/some-api' ,CachingMode='All' --cache metadata and data rows both ,CacheStorage='File' --or Memory ,CacheFileLocation='c:\temp\myquery.cache' ,CacheEntryTtl=300 --cache for 300 seconds )
Use --FAST Option to enable Stream Mode
ZappySys JSON / XML drivers support --FAST suffix for Filter. By using this suffix after Filter driver enables Stream Mode, Read this article to understand how this works.SELECT * FROM $ LIMIT 10 --//add this just to test how fast you can get 10 rows WITH( Filter='$.LargeArray[*]--FAST' --//Adding --FAST option turn on STREAM mode (large files) ,SRC='https://zappysys.com/downloads/files/test/large_file_100k_largearray_prop.json.gz' --,SRC='c:\data\large_file.json.gz' ,IncludeParentColumns='False' --//This Must be OFF for STREAM mode (read very large files) ,FileCompressionType='GZip' --Zip or None (Zip format only available for Local files) )
Other considerations for Web API calls in JAVA
API Limit / Throttling
While calling public API or other external web services one important aspect you have to check, how many requests are allowed by your API. Especially when you use API pagination options to pull many records you have to slow down based on API limits. For example, your API may allow you only 5 requests per second. Use Throttling Tab on Driver UI to set delay after each request.2D Array Transformation
If you are using JSON or XML API Driver then possible you may have to transform your data using 2D array transformation feature. Check this link for more information.Conclusion
To conclude, in this tutorial, we learned how to access the REST API using Java. We created a ZappySys ODBC connection and then used a ZappySys Gateway to connect to it.
References
- ZappySys ODBC PowerPack
- Java example ZappySys ODBC PowerPack
- Add connection in Netbeans 8 to the SQL Server 2012 database.