JSON File Connector for MS Excel
JSON File Connector can be used to extract and output JSON data stored in local files or direct JSON String (variables or DB columns). JSON Connector also supports JSONPath to filter data from nested array/sub-documents. This Connector is optimized to work with very large files.
In this article you will learn how to quickly and efficiently integrate JSON File data in MS Excel without coding. We will use high-performance JSON File Connector to easily connect to JSON File and then access the data inside MS Excel.
Let's follow the steps below to see how we can accomplish that!
JSON File Connector for MS Excel is based on ZappySys JSON Driver which is part of ODBC PowerPack. It is a collection of high-performance ODBC drivers that enable you to integrate data in SQL Server, SSIS, a programming language, or any other ODBC-compatible application. ODBC PowerPack supports various file formats, sources and destinations, including REST/SOAP API, SFTP/FTP, storage services, and plain files, to mention a few.
Create ODBC Data Source (DSN) based on ZappySys JSON Driver
Step-by-step instructions
To get data from JSON File using MS Excel we first need to create a DSN (Data Source) which will access data from JSON File. We will later be able to read data using MS Excel. Perform these steps:
-
Download and install ODBC PowerPack.
-
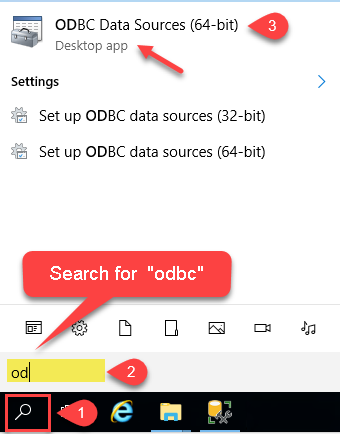
Open ODBC Data Sources (x64):
-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on ZappySys JSON Driver:
ZappySys JSON Driver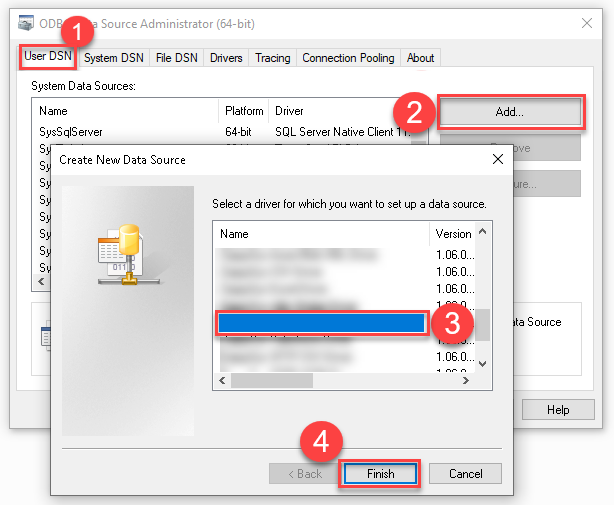
-
Create and use User DSN
if the client application is run under a User Account.
This is an ideal option
in design-time , when developing a solution, e.g. in Visual Studio 2019. Use it for both type of applications - 64-bit and 32-bit. -
Create and use System DSN
if the client application is launched under a System Account, e.g. as a Windows Service.
Usually, this is an ideal option to use
in a production environment . Use ODBC Data Source Administrator (32-bit), instead of 64-bit version, if Windows Service is a 32-bit application.
-
Create and use User DSN
if the client application is run under a User Account.
This is an ideal option
-
You can use pass single file or multiple file path using wildcard pattern in path and you can use select single file by clicking [...] path button or multiple file using wildcard pattern in path.
Note: If you want to operation with multiple files then use wild card pattern as below (when you use wild card pattern in source path then system will treat target path as folder regardless you end with slash) C:\SSIS\Test\reponse.json (will read only single reponse.json file) C:\SSIS\Test\j*.json (all files starting with file name) C:\SSIS\Test\*.json (all files with .json Extension and located under folder subfolder)
-
Now enter JSONPath expression in Array Filter textbox to extract only specific part of JSON file as below ($.value[*] will get content of value attribute from JSON document. Value attribute is array of JSON documents so we have to use [*] to indicate we want all records of that array)
NOTE: Here, We are using our desired filter, but you need to select your desired filter based on your requirement.
Click on Test Connection button to view whether the Test Connection is SUCCESSFUL or Not.$.value[*]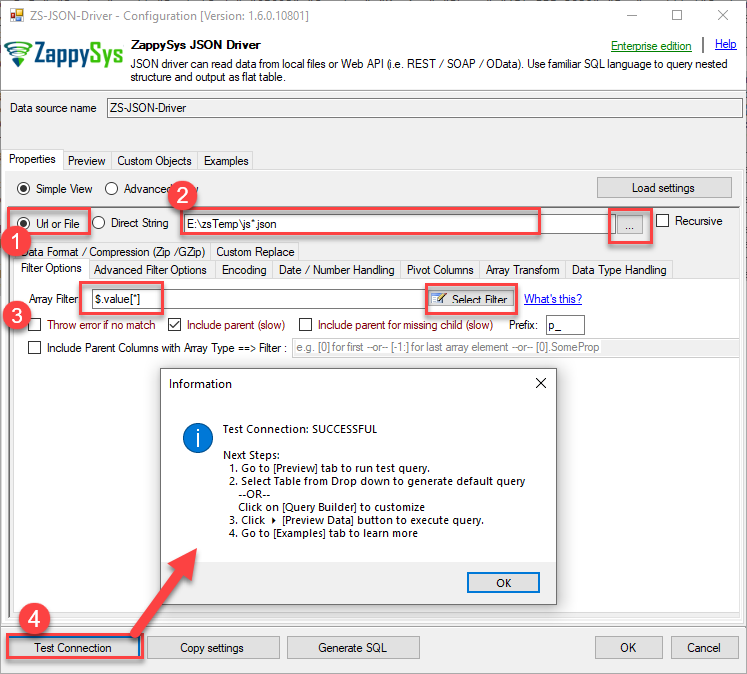
-
Once you configured a data source, you can preview data. Hit Preview tab, and use similar settings to preview data:
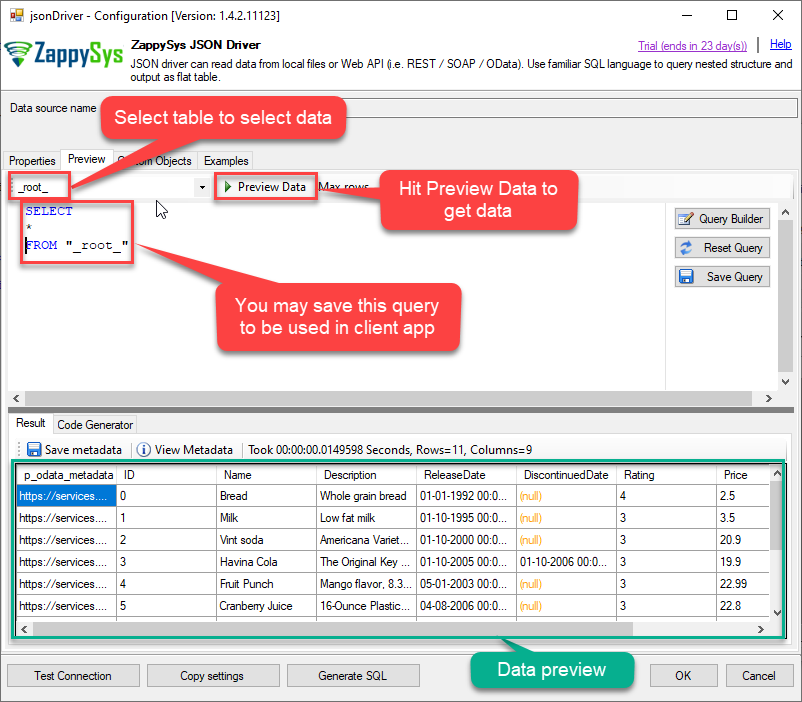
-
Click OK to finish creating the data source
-
That's it; we are done. In a few clicks we configured the call to JSON File using ZappySys JSON File Connector
Video Tutorial
Read data in Excel from the DSN
-
In Excel click Data, then select Get Data, proceed with From Other Sources and choose From ODBC item. This will get data from ODBC data source we created:
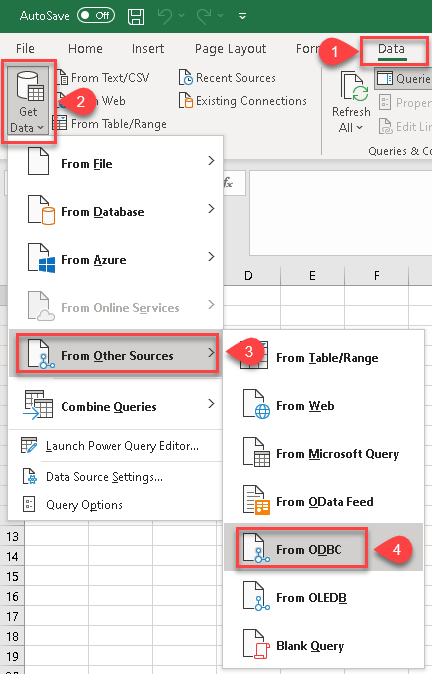
-
A small window opens, then simply select the data source you created in previous steps:
JsonFileDSN
-
Most likely, you will be asked to authenticate to a newly created DSN. Just select Windows authentication option together with Use my current credentials option:
JsonFileDSN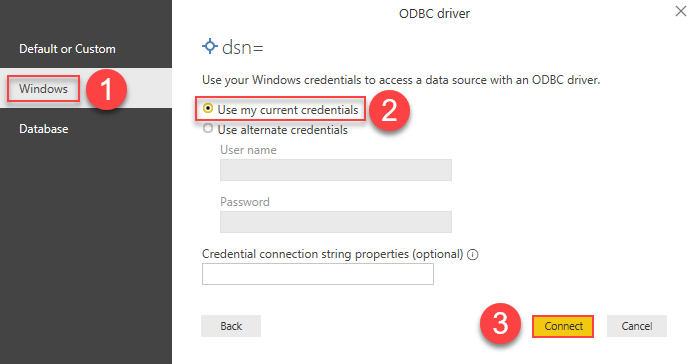
-
Finally, you will be asked to select a table or view to get data from. Select one and load the data!
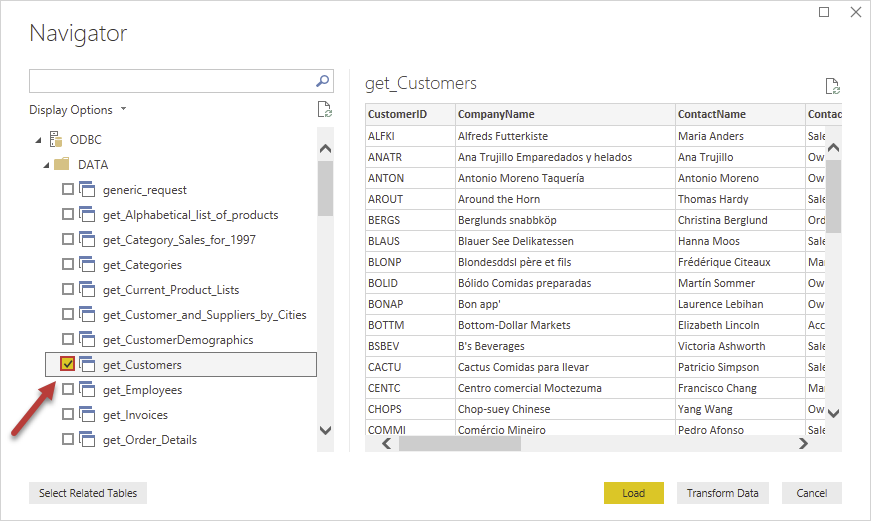
-
Finally, finally, use data extracted from JSON File API in an Excel worksheet:
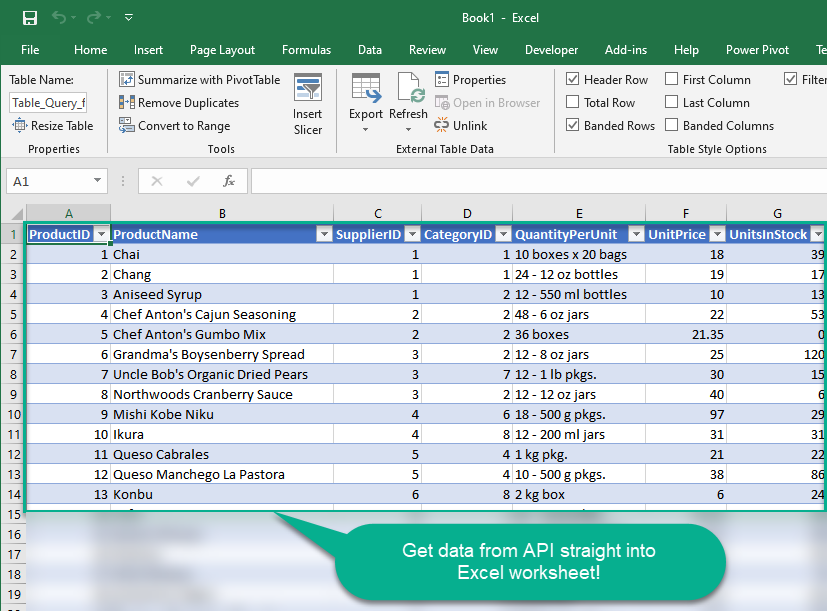
Refresh data source in Excel
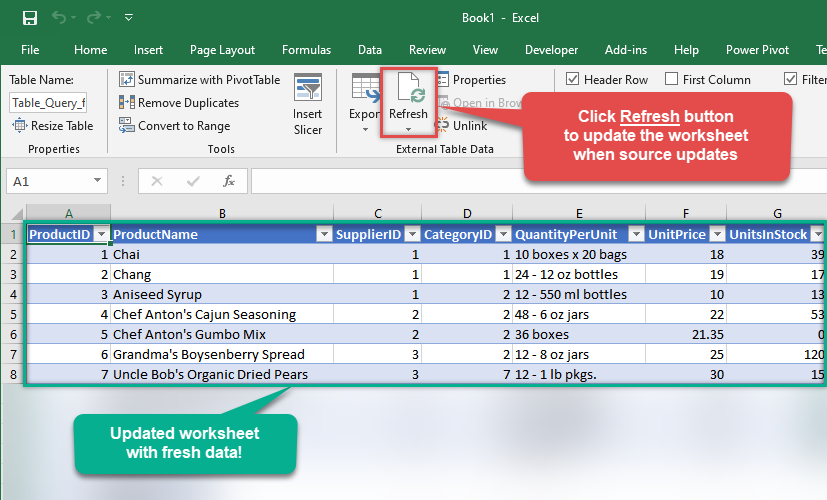
When data updates in JSON File, it is not automatically refreshed in Excel. To update the worksheet, go to Data or Table Design tab and click the Refresh button:
Centralized data access via Data Gateway
In some situations, you may need to provide JSON File data access to multiple users or services. Configuring the data source on a Data Gateway creates a single, centralized connection point for this purpose.
This configuration provides two primary advantages:
-
Centralized data access
The data source is configured once on the gateway, eliminating the need to set it up individually on each user's machine or application. This significantly simplifies the management process.
-
Centralized access control
Since all connections route through the gateway, access can be governed or revoked from a single location for all users.
| Data Gateway |
Local ODBC
data source
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Simple configuration | ||
| Installation | Single machine | Per machine |
| Connectivity | Local and remote | Local only |
| Connections limit | Limited by License | Unlimited |
| Central data access | ||
| Central access control | ||
| More flexible cost |
If you need any of these requirements, you will have to create a data source in Data Gateway to connect to JSON File, and to create an ODBC data source to connect to Data Gateway in MS Excel.
Let's not wait and get going!
Creating JSON File data source in Gateway
In this section we will create a data source for JSON File in Data Gateway. Let's follow these steps to accomplish that:
-
Search for
gatewayin Windows Start Menu and open ZappySys Data Gateway Configuration:
-
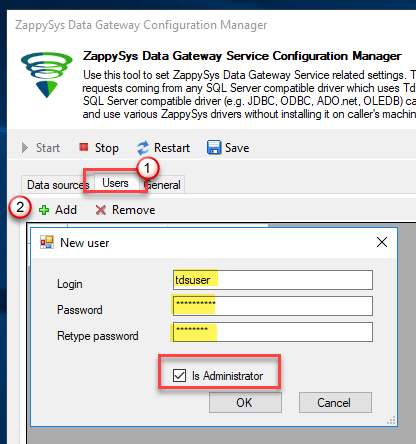
Go to Users tab and follow these steps to add a Data Gateway user:
- Click Add button
-
In Login field enter username, e.g.,
john - Then enter a Password
- Check Is Administrator checkbox
- Click OK to save
-
Now we are ready to add a data source:
- Click Add button
- Give Datasource a name (have it handy for later)
- Then select Native - ZappySys JSON Driver
- Finally, click OK
JsonFileDSNZappySys JSON Driver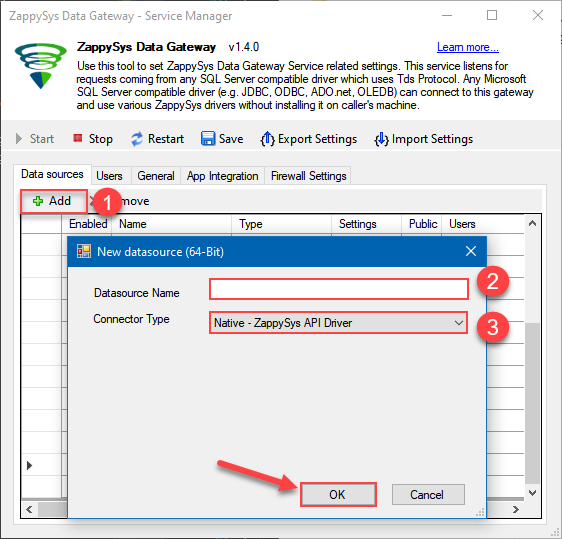
-
When the ZappySys JSON Driver configuration window opens, configure the Data Source the same way you configured it in ODBC Data Sources (64-bit), in the beginning of this article.
-
Very important step. Now, after creating or modifying the data source make sure you:
- Click the Save button to persist your changes.
- Hit Yes, once asked if you want to restart the Data Gateway service.
This will ensure all changes are properly applied:
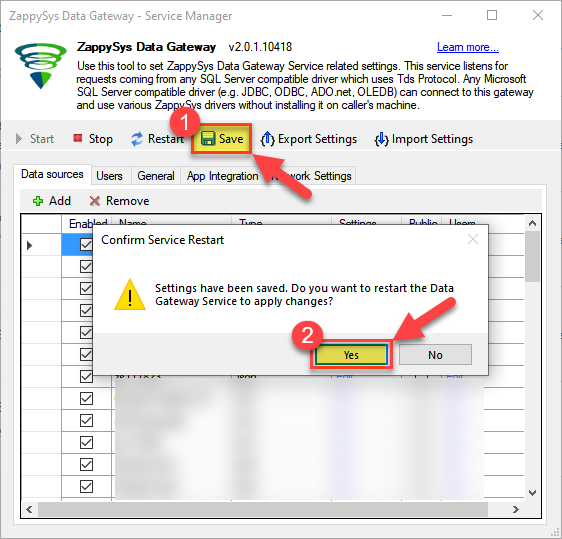 Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Creating ODBC data source for Data Gateway
In this part we will create ODBC data source to connect to Data Gateway from MS Excel. To achieve that, let's perform these steps:
-
Open ODBC Data Sources (x64):

-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server:
ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server If you don't see ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version driver.
If you don't see ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version driver. -
Then set a Name of the data source (e.g.
Gateway) and the address of the Data Gateway:GatewayDSNlocalhost,5000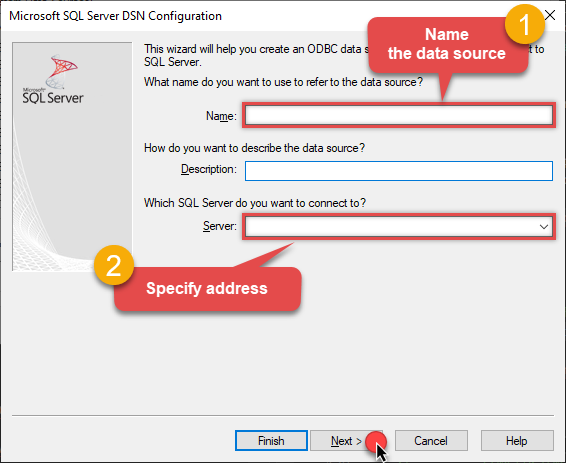 Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.
Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.localhost,5000. -
Proceed with authentication part:
- Select SQL Server authentication
-
In Login ID field enter the user name you used in Data Gateway, e.g.,
john - Set Password to the one you configured in Data Gateway
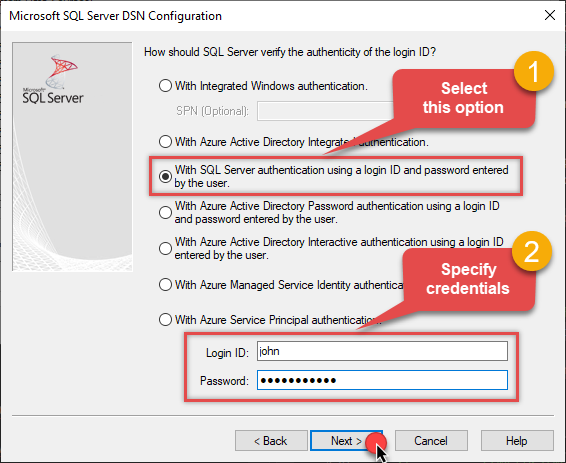
-
Then set the default database property to
JsonFileDSN(the one we used in Data Gateway):JsonFileDSN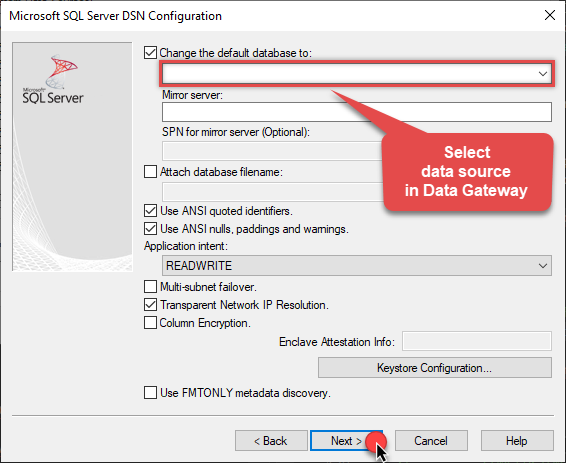
-
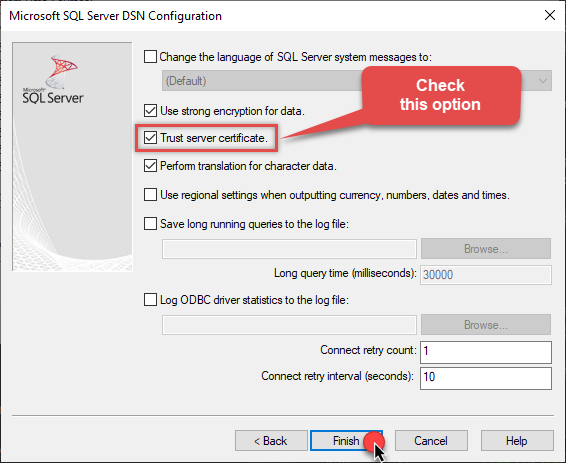
Continue by checking Trust server certificate option:
-
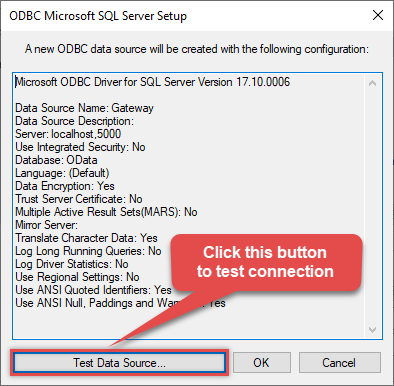
Once you do that, test the connection:
-
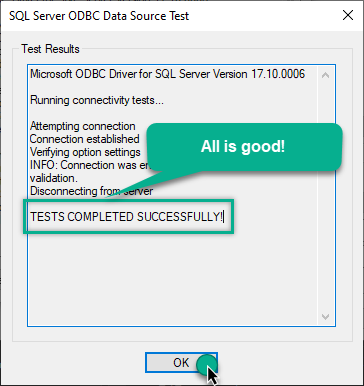
If connection is successful, everything is good:
-
Done!
We are ready to move to the final step. Let's do it!
Accessing data in MS Excel via Data Gateway
Finally, we are ready to read data from JSON File in MS Excel via Data Gateway. Follow these final steps:
-
Go back to MS Excel.
-
In Excel click Data, then select Get Data, proceed with From Other Sources and choose From ODBC item. This will get data from ODBC data source we created:

-
A small window opens, then simply select the data source you created in previous steps:
GatewayDSN
-
Read the data the same way we discussed at the beginning of this article.
-
That's it!
Now you can connect to JSON File data in MS Excel via the Data Gateway.
john and your password.
Conclusion
In this article we showed you how to connect to JSON File in MS Excel and integrate data without any coding, saving you time and effort.
We encourage you to download JSON File Connector for MS Excel and see how easy it is to use it for yourself or your team.
If you have any questions, feel free to contact ZappySys support team. You can also open a live chat immediately by clicking on the chat icon below.
Download JSON File Connector for MS Excel Documentation