Azure DevOps Connector for SSAS : Query work items via SQL


Learn how to query work items using the Azure DevOps Connector for SSAS. This connector enables you to read and write Azure DevOps (Cloud or On-Premises) data effortlessly. Integrate, manage, and automate work items, projects, and teams — almost no coding required. We'll walk you through the exact setup.
Let's dive in!
Create data source using Azure DevOps ODBC Driver
-
Download and install ODBC PowerPack (if you haven't already).
-
Search for
odbcand open the ODBC Data Sources (64-bit):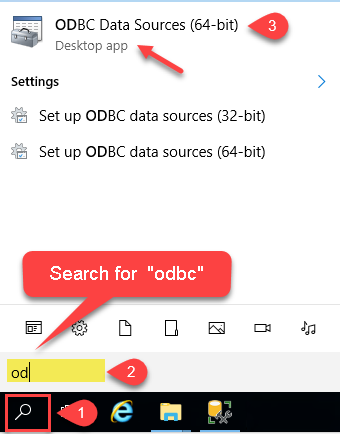
-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on the ZappySys API Driver driver:
ZappySys API Driver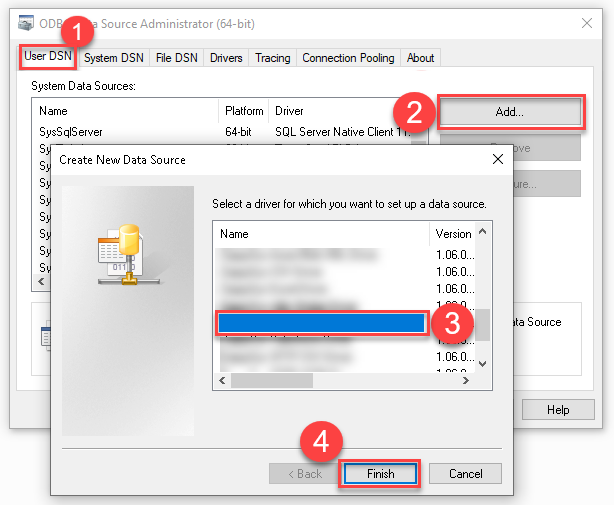
- Create and use a User DSN if the client application runs under a User Account. This is the ideal option at design time (e.g., when developing in Visual Studio). Use it for both types of applications (64-bit and 32-bit).
- Create and use a System DSN if the client application runs under a System Account (e.g., as a Windows Service). This is usually the required option in a production environment. If your Windows Service is a 32-bit application, you must use the 32-bit ODBC Data Source Administrator to configure this
-
When the Configuration window appears give your data source a name if you haven't done that already, then select "Azure DevOps" from the list of Popular Connectors. If "Azure DevOps" is not present in the list, then click "Search Online" and download it. Then set the path to the location where you downloaded it. Finally, click Continue >> to proceed with configuring the DSN:
AzureDevopsDSNAzure DevOps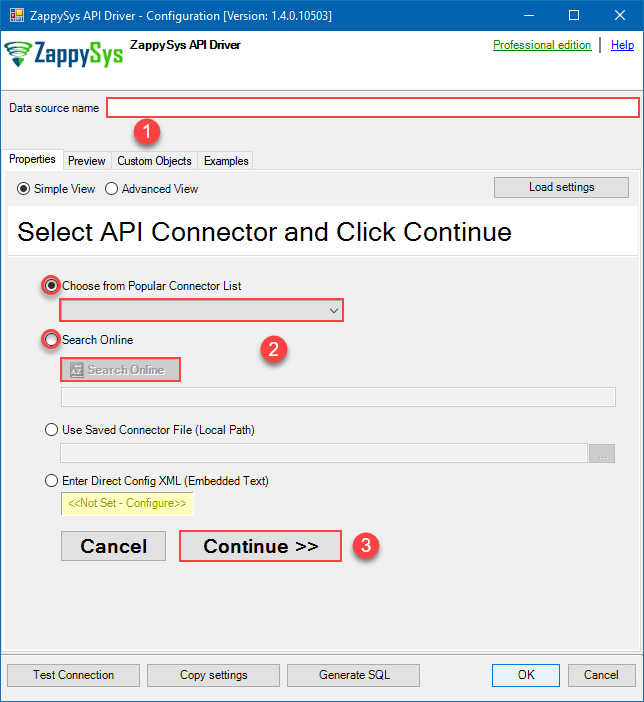
-
Now it's time to configure the Connection Manager. Select Authentication Type, e.g. Token Authentication. Then select API Base URL (in most cases, the default one is the right one). More info is available in the Authentication section.
Azure DevOps authentication
Delegated access using OAuth authorization code flow. Users sign in with their Azure AD account. [API reference]
Follow these simple steps below to create Microsoft Entra ID application with delegated access:
WARNING: To automate your company's processes, make sure you use a system/generic account (e.g.automation@my-company.com). When you use a personal account which is tied to a specific employee profile and that employee leaves the company, the token may become invalid and any automated processes using that token will start to fail.- Navigate to the Azure Portal and log in using your credentials.
- Access Microsoft Entra ID.
-
Register a new application by going to
App registrations
and clicking on New registration button:
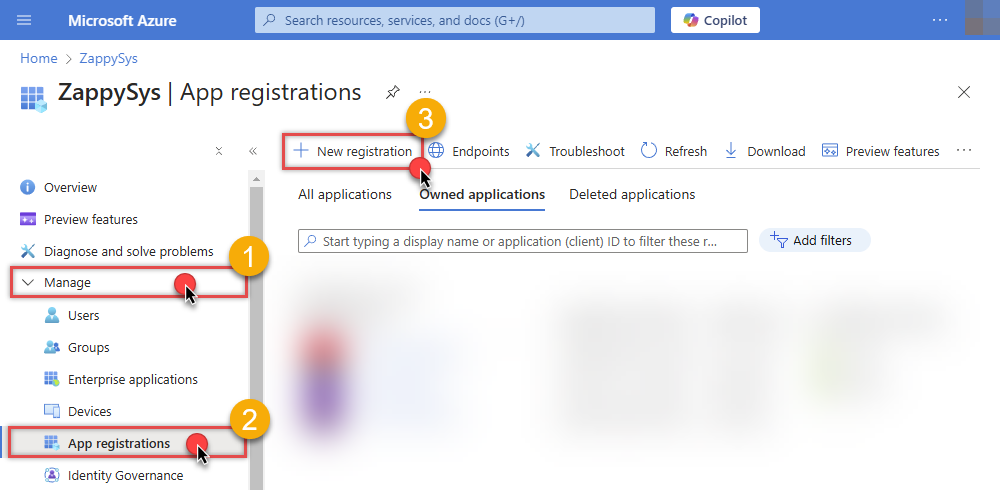 INFO: Find more information on how to register an application in Graph API reference.
INFO: Find more information on how to register an application in Graph API reference. -
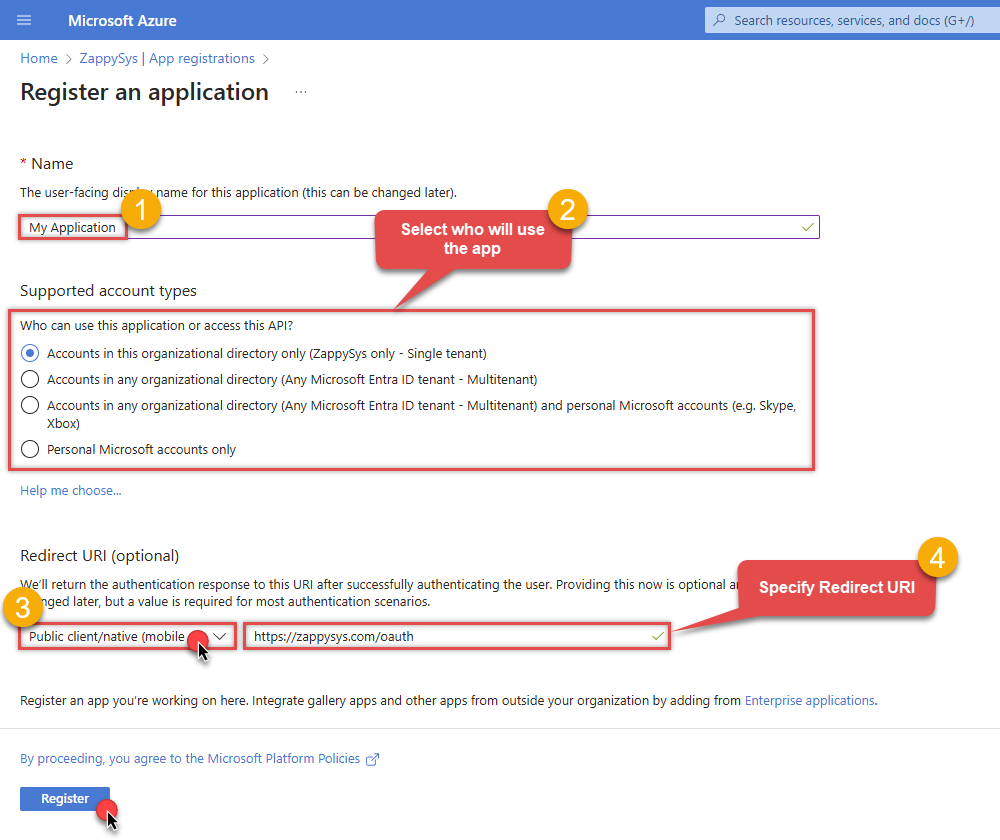
When configuration window opens, configure these fields:
-
Supported account type
- Use
Accounts in this organizational directory only, if you need access to data in your organization only.
- Use
-
Supported account type
-
Redirect URI:
- Set the type to
Public client/native (mobile & desktop). - Use
https://zappysys.com/oauthas the URL.
- Set the type to
-
After registering the app, copy the Application (client) ID for later:
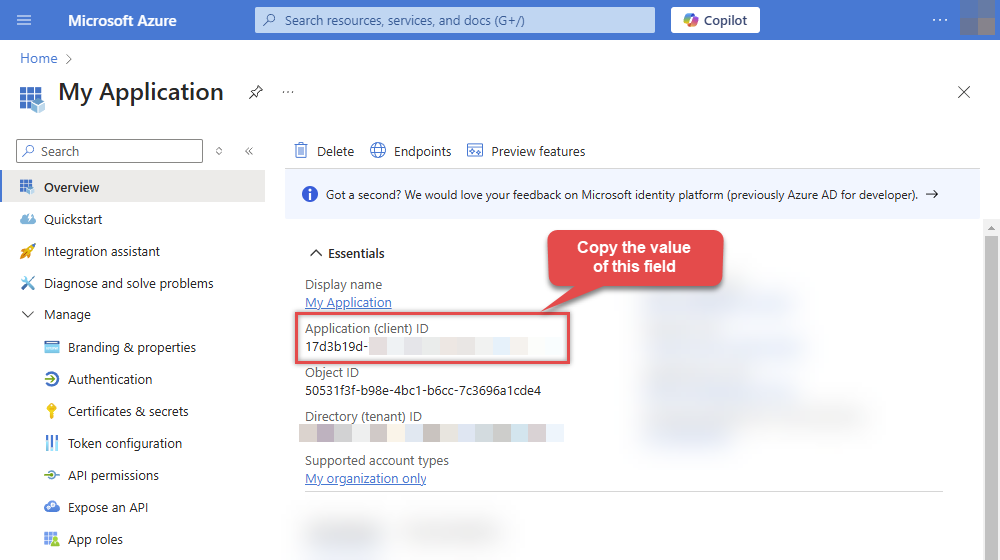
-
Then copy OAuth authorization endpoint (v2) & OAuth token endpoint (v2) URLs to use later in the configuration:
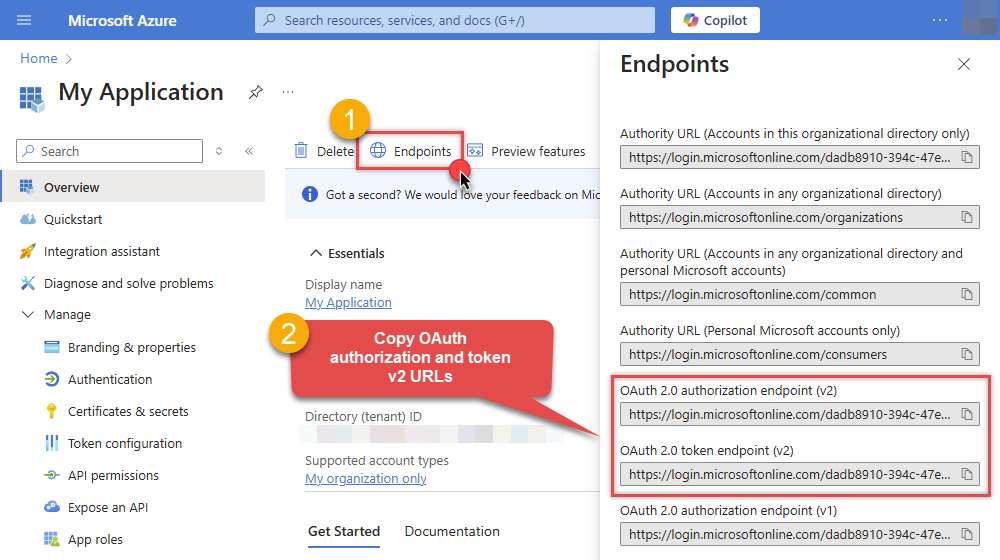
-
Now go to SSIS package or ODBC data source and use the copied values in User Credentials authentication configuration:
- In the Authorization URL field paste the OAuth authorization endpoint (v2) URL value you copied in the previous step.
- In the Token URL field paste the OAuth token endpoint (v2) URL value you copied in the previous step.
- In the Client ID field paste the Application (client) ID value you copied in the previous step.
-
In the Scope field use the default value or select individual scopes, e.g.:
-
vso.project -
vso.work_full
-
- Press Generate Token button to generate Access and Refresh Tokens.
- Optional step. Choose Default Drive Id from the drop down menu.
- Click Test Connection to confirm the connection is working.
- Done! Now you are ready to use the API Connector!
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
User Credentials [OAuth] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Press Generate Token button to generate the tokens.
- Finally, hit OK button:
AzureDevopsDSNAzure DevOpsUser Credentials [OAuth]https://dev.azure.comRequired Parameters Authorization URL Fill-in the parameter... Token URL Fill-in the parameter... Client ID Fill-in the parameter... Organization name or Id (e.g. mycompany) Fill-in the parameter... Return URL Fill-in the parameter... Scopes (Must match with App Registration) Fill-in the parameter... API Version Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters Client Secret Refresh Token File Path Default Project Name (Choose after Generating Token) RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True 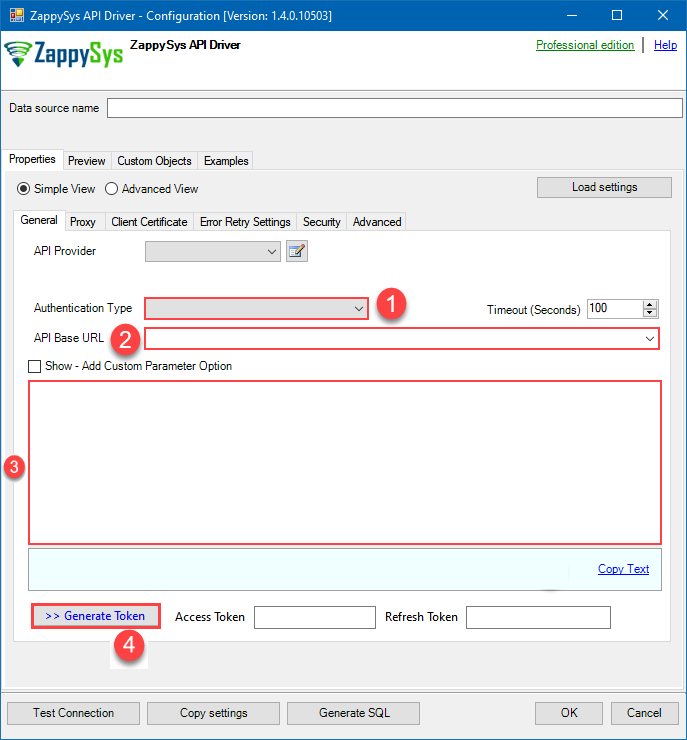
Azure DevOps authentication
Use Azure AD service principal credentials (client id + secret) with the client credentials flow. Recommended for automated server-to-server access instead of PAT or delegated OAuth. [API reference]
Step 1: Register the App in Microsoft Entra ID (AAD)
- Go to the Azure Portal > Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations and click New registration:

- Name it (e.g., ZS-AzureDevOps-AppCred).
- Set Supported account types to "Accounts in this organizational directory only" (Single Tenant):

- Leave Redirect URI blank (it's not used for Client Credentials).
- Click Register.
Step 2: Create a Client Secret
- In your new app, go to Certificates & secrets.
- Click New client secret, give it a name, and set an expiration.
- Copy the Secret Value immediately. You will never see it again once you leave the page:

Step 3: Set Permissions and Admin Consent
- Go to API permissions > Add a permission.
- Select Azure DevOps and click Delegated permissions.
- Check the necessary scopes (e.g.,
vso.project,vso.work_full). - Crucial: Click Grant admin consent for [Your Tenant]. Without this, the app cannot authenticate in the background.
Step 4: Map the App to Azure DevOps Organization
- Copy your Application (client) ID from the App Overview page.
- Go to your Azure DevOps Organization Settings > Users.
- Click Add users, paste the Application (client) ID in the search box, and select the App.
- Assign an Access level (usually Basic) and add it to the relevant Projects.
Step 5: Connection Settings
In your SSIS package or ODBC data source, use the following in the App Credentials configuration:
- In the Token URL field, paste the OAuth token endpoint (v2) URL from the Azure Portal 'Endpoints' tab.
- In the Client ID field, paste the Application (client) ID.
- In the Client Secret field, paste the Secret Value copied in Step 2.
- In the Scope field, use:
https://app.vssps.visualstudio.com/.default
Step 6: Finalize Connection
- Press Generate Token button to fetch the token using the Client Secret.
- Click Test Connection to confirm the setup.
- Done! You are ready to use the API Connector!
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
Azure App Credentials [OAuth] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
AzureDevopsDSNAzure DevOpsAzure App Credentials [OAuth]https://dev.azure.comRequired Parameters Token URL Fill-in the parameter... Client ID Fill-in the parameter... Client Secret Fill-in the parameter... Scopes (Use .default for App Credentials) Fill-in the parameter... Organization name or Id Fill-in the parameter... API Version Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters Default Project Name RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True 
Azure DevOps authentication
Same as Application Credentials but uses a client certificate instead of a secret. [API reference]
Step 1: Register the App in Microsoft Entra ID (AAD)
- Go to the Azure Portal > Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations and click New registration:

- Name it (e.g., ZS-AzureDevOps-CertAuth).
- Set Supported account types to "Accounts in this organizational directory only" (Single Tenant):

- Leave Redirect URI blank (it's not used for Client Credentials flows).
- Click Register.
Step 2: Upload Client Certificate
- In your new app, go to Certificates & secrets.
- Click the Certificates tab, then click Upload certificate.
- Upload your public key certificate (.cer, .pem, or .crt). Keep the private key secure on your system.
- Copy the Thumbprint for your configuration:

Step 3: Set Permissions and Admin Consent
- Go to API permissions > Add a permission.
- Select Azure DevOps and click Delegated permissions.
- Select the required scopes (e.g.,
vso.project,vso.work_full). - Crucial: Click Grant admin consent for [Your Tenant]. Without this, the background service cannot acquire a token.
Step 4: Map the App to Azure DevOps Organization
- Copy your Application (client) ID from the App Overview page.
- Go to your Azure DevOps Organization Settings > Users.
- Click Add users and paste the Application (client) ID in the search box to find the App.
- Assign an Access level (usually Basic) and add it to the relevant Projects.
Step 5: Connection Settings
In your SSIS package or ODBC data source, use the following in the Client Certificate configuration:
- In the Token URL field, paste the OAuth token endpoint (v2) URL from the Azure Portal 'Endpoints' tab.
- In the Client ID field, paste the Application (client) ID.
- Configure your Certificate Path or Thumbprint in the Client Certificate tab of the connector.
- In the Scope field, use:
https://app.vssps.visualstudio.com/.default
Step 6: Finalize Connection
- Press Generate Token. The connector will sign the request using your certificate to fetch a token.
- Click Test Connection to confirm the setup.
- Done! Your certificate-based connection is ready!
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
Azure App Credentials with Certificate (Sign JWT with Private Key) [OAuth] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
AzureDevopsDSNAzure DevOpsAzure App Credentials with Certificate (Sign JWT with Private Key) [OAuth]https://dev.azure.comRequired Parameters Token URL Fill-in the parameter... Client ID Fill-in the parameter... Certificate: *** Configure [Client Certificate] Tab *** Fill-in the parameter... Scopes (Must match with App Registration) Fill-in the parameter... Organization name or Id Fill-in the parameter... API Version Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters Default Project Name RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True 
Azure DevOps authentication
**DEPRECATED:** this OAuth-based user credential flow is legacy; for new integrations prefer the Azure App Credentials options below. Connecting to your Azure DevOps data requires you to authenticate your REST API access. Follow the instructions below:- Go to https://app.vsaex.visualstudio.com/app/register to register your app.
-
Fill in your application and company's information as required, and then select the scopes that your application needs.
This should typically be Project and team (read and write) and Work items (read and write).
Your selected scopes when registering your app must match the scopes you enter here on the connector screen. If they don't match, the connector will not be able to work with your Azure DevOps account!If you need further information about the scopes used in Azure DevOps, or need to see what to enter into the connector screen to match up with your selected scopes, visit https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/integrate/get-started/authentication/oauth?view=azure-devops.
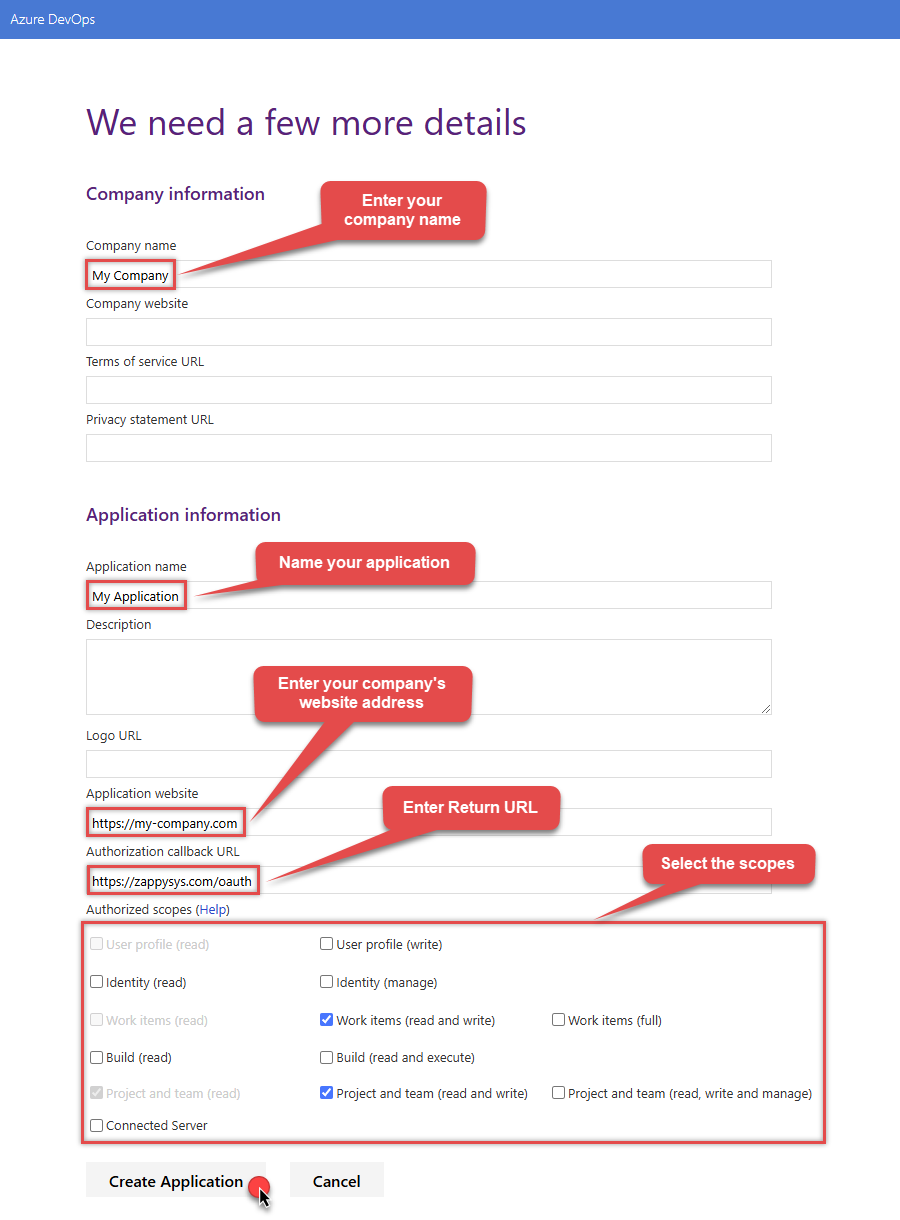
NOTE: For Authorization callback URL use your company's OAuth Redirect URL (if IT administrator provides you one) or you can use
https://zappysys.com/oauth(it's safe). - Select Create Application and then the Application Settings page will be displayed.
-
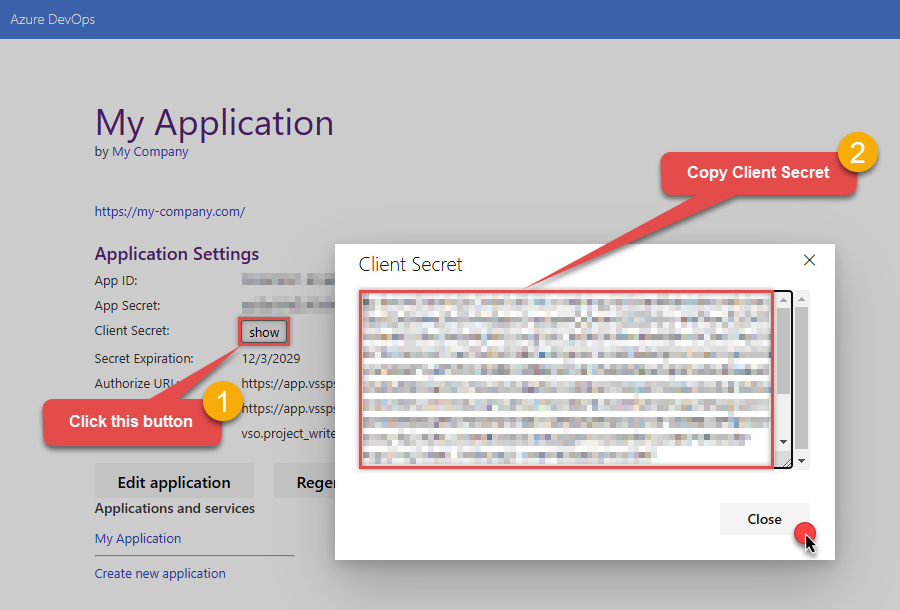
Record the App ID for us to use later:
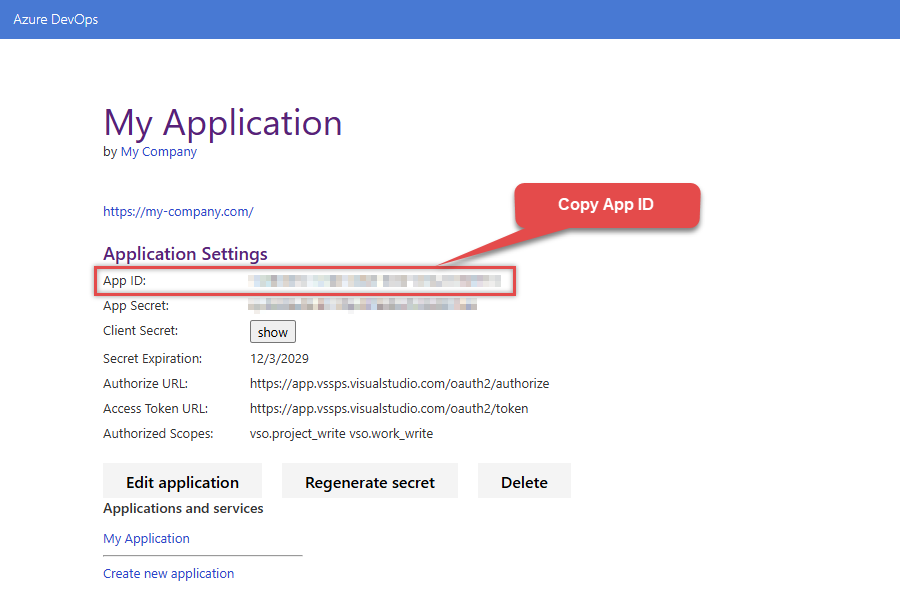
-
And do the same with Client Secret:
- Then go to https://aex.dev.azure.com and select relevant organization on the left.
-
Then copy Organization's host name part (e.g.
acmeinc, if full host name isacmeinc.visualstudio.com), save it to a file, and click it: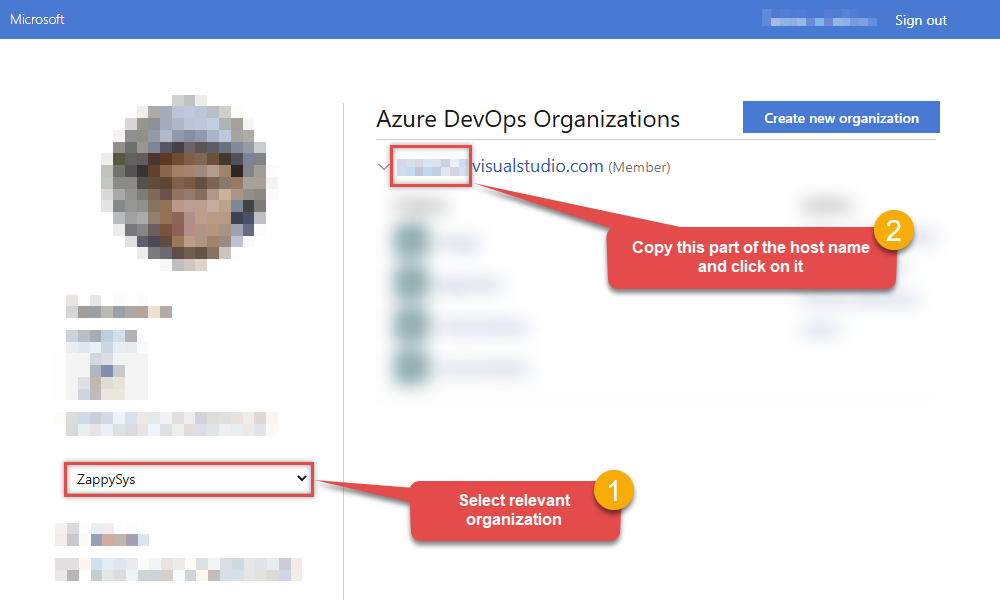
- Back at the connector screen, enter the App ID into the Client Id (App ID) field that was recorded in the previous step.
- Enter the Client Secret that was recorded in the previous step into the Client Secret field. In order to edit the text in this field, select the ellipses (...) button that appears when the textbox is clicked, and edit the Client Secret with the dialog box that appears.
- Enter the organization that was recorded in step 5 into the Organization name or Id for url field.
- Click Generate Token. If proper authentication occurs, you will see a notice saying so. You can click Yes to save a backup file of your generated tokens.
- Select the project you want to connect to by default from the Default Project (Choose after Generating Token) field.
- Select the Security tab.
-
Enter
https://auditservice.dev.azure.com,https://almsearch.dev.azure.cominto the Additional Trusted Domains field. - Select the Test Connection button at the bottom of the window to verify proper connectivity with your Azure DevOps account.
- If the connection test succeeds, select OK.
-
To edit previously created app you can visit
https://app.vsaex.visualstudio.com/meand see Applications and services section. Click on your desired app name.
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
(Cloud) OAuth App - User Credentials (DEPRECATED) [OAuth] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Press Generate Token button to generate the tokens.
- Finally, hit OK button:
AzureDevopsDSNAzure DevOps(Cloud) OAuth App - User Credentials (DEPRECATED) [OAuth]https://dev.azure.comRequired Parameters Client Id (App ID) Fill-in the parameter... Client Secret Fill-in the parameter... Organization name or Id (e.g. mycompany) Fill-in the parameter... Return URL Fill-in the parameter... Scopes (Use .default for App Credentials) Fill-in the parameter... API Version Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters Default Project Name (Choose after Generating Token) RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True 
Azure DevOps authentication
**DEPRECATED:** Personal Access Tokens are still supported but the new Azure App Credentials auth is recommended for security and automation. To connect to Azure DevOps using a Personal Access Token (PAT), you must first create a valid PAT:- Start by going to https://aex.dev.azure.com and selecting relevant organization on the left.
-
Then copy Organization's host name part (e.g.
acmeinc, if full host name isacmeinc.visualstudio.com), save it to a file, and click it:
-
Next, click User settings icon and then click Personal access tokens:
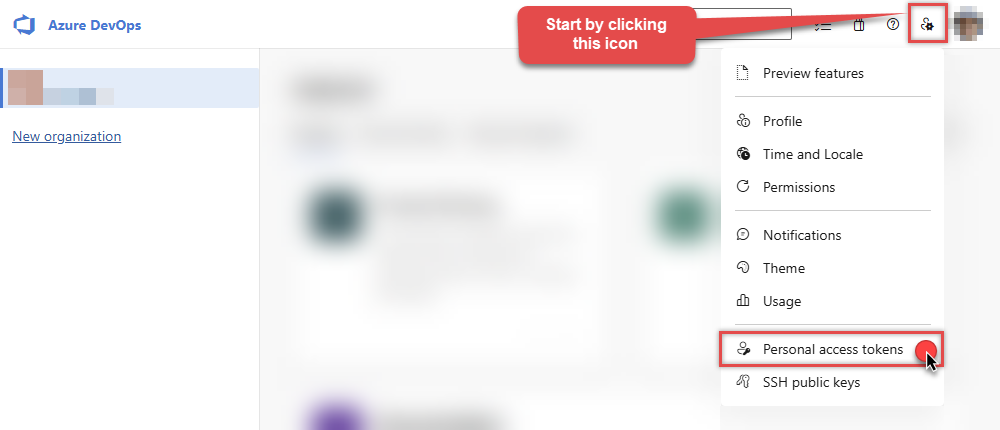
-
Then click New Token button to create a new personal access token:
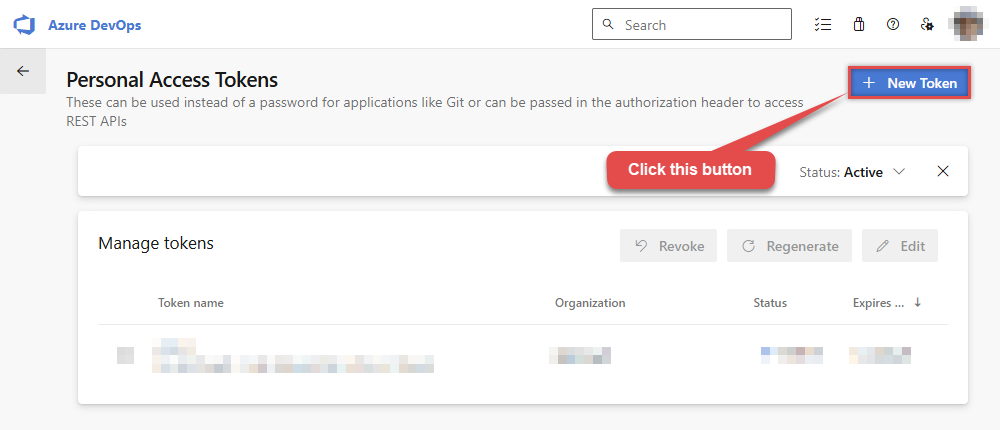
-
Continue by...
- naming your token
- selecting the right Organization
- setting token's Expiration date (it's recommended to use
Custom definedoption and make it expire after one year or later) - and setting the Scopes:
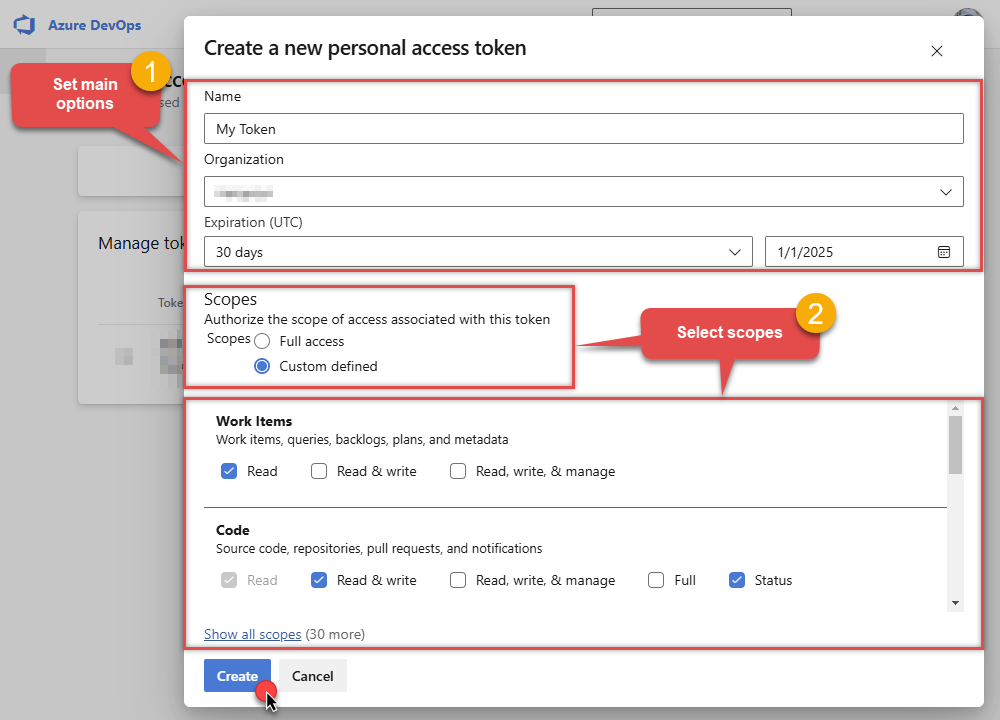
NOTE: You may be restricted from creating full-scoped PATs. If so, your Azure DevOps administrator in Azure AD has enabled a policy which limits you to a specific custom defined set of scopes.
-
Now click Copy button and save the newly created token into a file for quick access later:
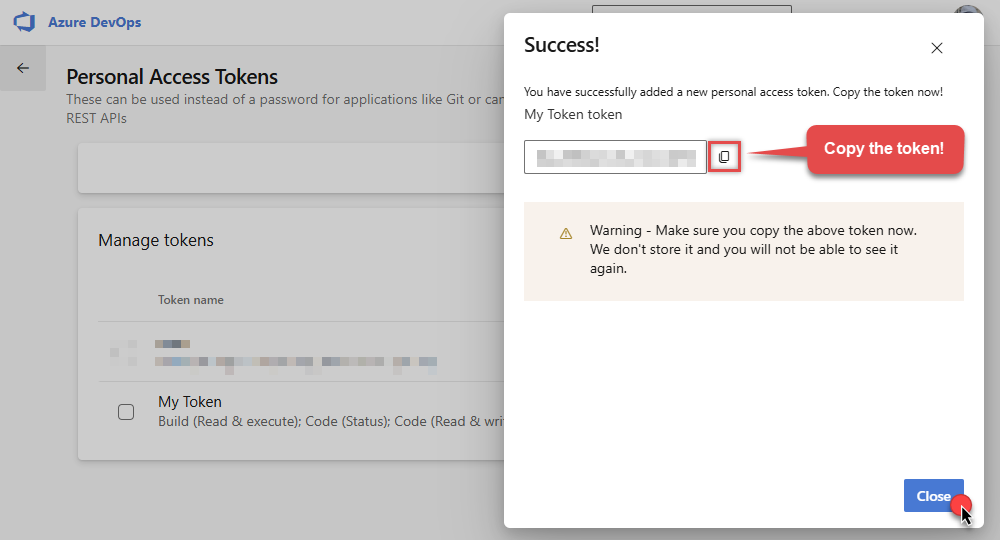
- Go back to the connector screen, input the token you saved in a previous step into the Personal Access Token (PAT) field.
- Then enter the Organization host name part that you noted recorded in previous step into Organization name or Id for url field.
- Enter the name or Id of the project you want to connect to by default in the Default Project (Choose after above fields) field.
- Select the Security tab.
- Enter
https://auditservice.dev.azure.com,https://almsearch.dev.azure.com,https://analytics.dev.azure.cominto the Additional Trusted Domains field. - Select the Test Connection button at the bottom of the window to verify proper connectivity with your Azure DevOps account.
- Done!
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
(Cloud) Personal Access Token (PAT) (DEPRECATED) [Http] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
AzureDevopsDSNAzure DevOps(Cloud) Personal Access Token (PAT) (DEPRECATED) [Http]https://dev.azure.comRequired Parameters Personal Access Token (PAT) Fill-in the parameter... Organization name or Id for url Fill-in the parameter... API Version Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters AuthScheme Bearer AuthHeader Authorization Default Project Name RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True 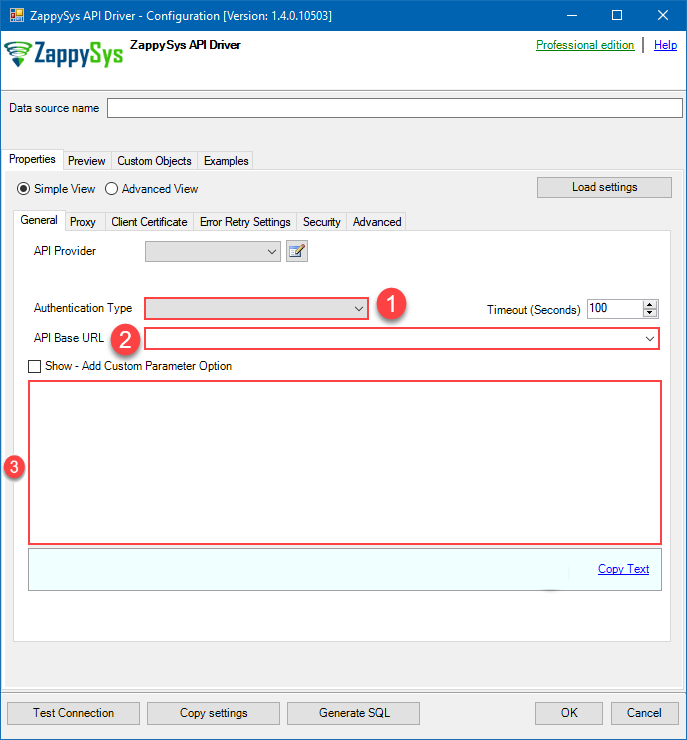
Azure DevOps authentication
**DEPRECATED:** On-premises PAT method is legacy; consider Azure App Credentials if your server supports Azure AD apps. To connect to Azure DevOps On-Premises Server using a Personal Access Token (PAT), you must first create a valid PAT:-
Start by navigating to your on-premises Azure DevOps Server URL.
NOTE: The screenshots shown below are from the cloud version, so your interface may look slightly different depending on which on-premises Azure DevOps Server version you’re using — however, the overall concepts and steps are very similar between the cloud and on-premises editions. -
Now open any project and capture Collection Name from the URL. For example if your URL is
https://tfs.mycompany.local/tfs/MyCollection/MyProject/
then your collection name is MyCollection usually after /tfs/. Copy this collection name and later we will enter on Connection UI. -
Next, click User settings icon and then click Personal access tokens:

-
Then click New Token button to create a new personal access token:

-
Continue by...
- naming your token
- selecting the right Organization
- setting token's Expiration date (it's recommended to use
Custom definedoption and make it expire after one year or later) - and setting the Scopes:

NOTE: You may be restricted from creating full-scoped PATs. If so, your Azure DevOps administrator in Azure AD has enabled a policy which limits you to a specific custom defined set of scopes.
-
Now click Copy button and save the newly created token into a file for quick access later:

- Go back to the connector screen, input the token you saved in a previous step into the Personal Access Token (PAT) field.
- Then enter the Organization host name part that you noted recorded in previous step into Organization name or Id for url field.
- Enter the name or Id of the project you want to connect to by default in the Default Project (Choose after above fields) field.
- Select the Security tab.
- Enter
https://auditservice.dev.azure.com,https://almsearch.dev.azure.com,https://analytics.dev.azure.cominto the Additional Trusted Domains field. - Select the Test Connection button at the bottom of the window to verify proper connectivity with your Azure DevOps account.
- Done!
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
(On-Premises) Personal Access Token (PAT) (DEPRECATED) [Http] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
AzureDevopsDSNAzure DevOps(On-Premises) Personal Access Token (PAT) (DEPRECATED) [Http]https://dev.azure.comRequired Parameters Personal Access Token (PAT) Fill-in the parameter... Collection name (e.g. MyCollection) Fill-in the parameter... API Version Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters AuthScheme Bearer AuthHeader Authorization Default Project Name RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True 
-
Then go to Preview tab to start building a SQL query.
-
Once you do that, proceed by opening Query Builder:
ZappySys API Driver - Azure DevOpsRead and write Azure DevOps (Cloud or On-Premises) data effortlessly. Integrate, manage, and automate work items, projects, and teams — almost no coding required.AzureDevopsDSN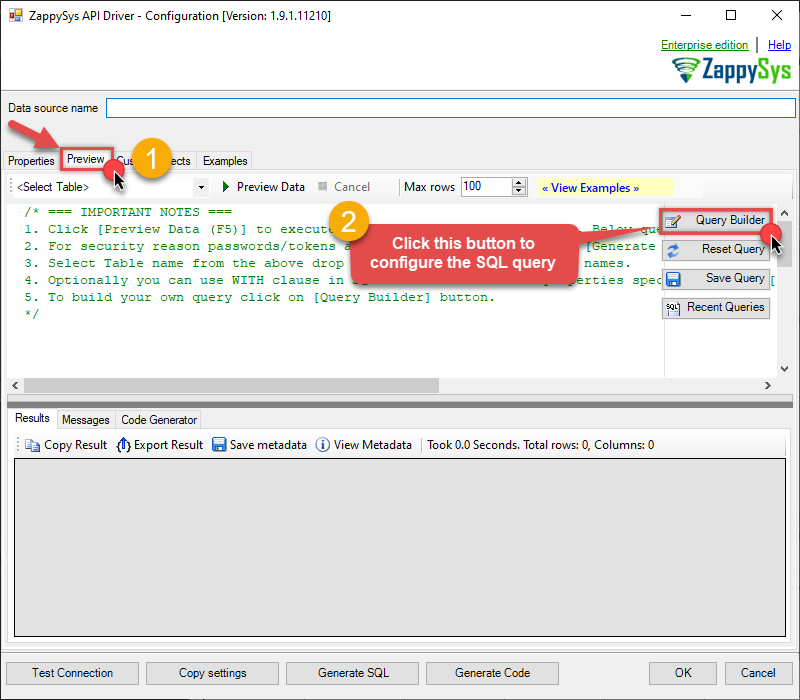
-
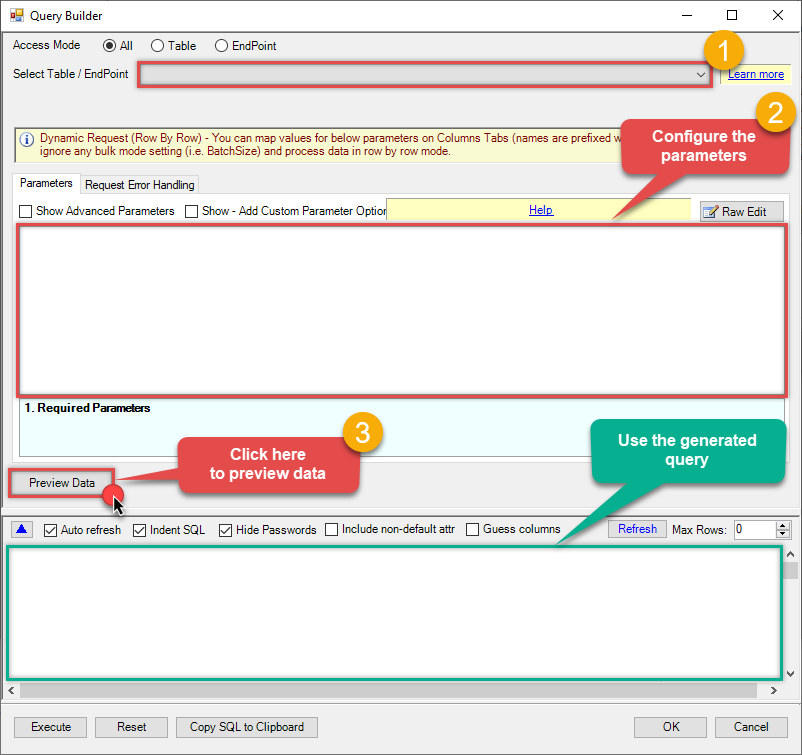
Then simply select the Query Work Items endpoint (action).
-
Continue by configuring the Required parameters. You can also set optional parameters too.
-
Move on by hitting Preview Data button to preview the results.
-
If you see the results you need, simply copy the generated query:
-
Click OK to use built SQL query and close the Query Builder.
-
Now hit Preview Data button to preview the data using the generated SQL query. If you are satisfied with the result, use this query in SSAS:
 ZappySys API Driver - Azure DevOpsRead and write Azure DevOps (Cloud or On-Premises) data effortlessly. Integrate, manage, and automate work items, projects, and teams — almost no coding required.AzureDevopsDSN
ZappySys API Driver - Azure DevOpsRead and write Azure DevOps (Cloud or On-Premises) data effortlessly. Integrate, manage, and automate work items, projects, and teams — almost no coding required.AzureDevopsDSNSELECT * FROM WorkItems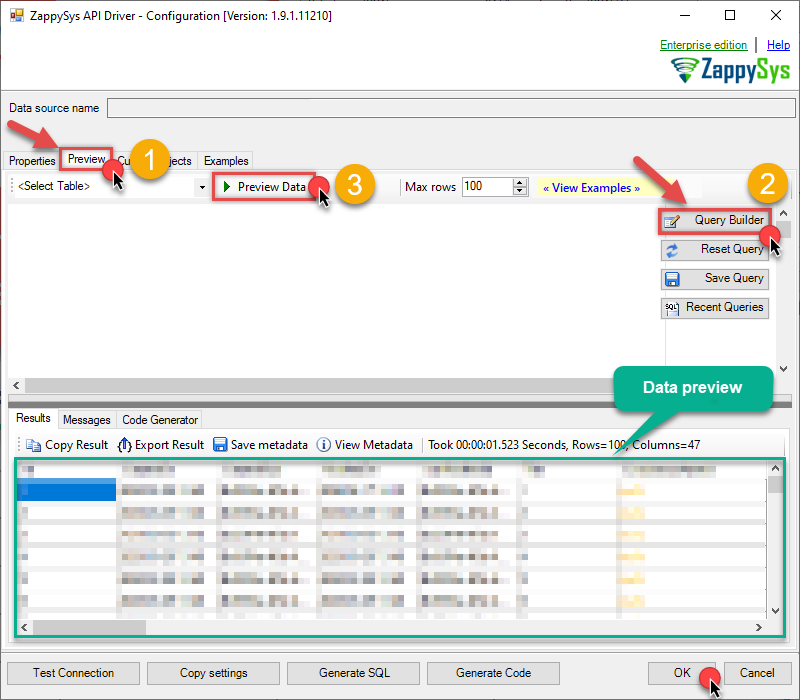 You can also access data quickly from the tables dropdown by selecting <Select table>.A
You can also access data quickly from the tables dropdown by selecting <Select table>.AWHEREclause,LIMITkeyword will be performed on the client side, meaning that thewhole result set will be retrieved from the Azure DevOps API first, and only then the filtering will be applied to the data. If possible, it is recommended to use parameters in Query Builder to filter the data on the server side (in Azure DevOps servers).
Let's not stop here and explore SQL query examples, including how to use them in Stored Procedures and Views (virtual tables) in the next steps.
Azure DevOps SQL query examples
Use these SQL queries in your SSAS data source:
List work items (default project)
Returns work items from the default project specified in the connection (or the project you set in the WITH clause). Use this as the baseline list; you can filter by ID, state, or other columns in the WHERE clause, or pass a WIQL query in WITH to filter on the server.
SELECT * FROM WorkItemsList work items for a project
Lists work items for a specific project by supplying the project name in the WITH clause. Use this when your connection default is one project but you need to query another. You can combine with a WHERE clause or a WIQL query in WITH to narrow results.
SELECT * FROM WorkItems WITH (Project='ProductTesting')List work items with ParentId
By default, relation fields such as ParentId are not returned so that list queries stay fast. When you need parent-child or other link information, set Expand='Relations' in the WITH clause. The result set will then include ParentId and other relation columns so you can join or filter by hierarchy.
SELECT * FROM WorkItems WITH(Expand='Relations')Query work items by WIQL (filters and date range)
Use a WIQL (Work Item Query Language) query to filter work items by project, ID range, changed/created dates, work item type, state, priority, and more. The query runs on the server and returns only matching rows. This example shows typical filters: project, ID range, date variables like @Today and @StartOfYear, and ordering by changed date.
For full syntax and operators, see WIQL syntax and query operators and variables.
SELECT * FROM WorkItems WITH (Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems
WHERE [System.Id] > 2000 AND [System.Id] < 7050
AND [System.TeamProject]=''ProductTesting''
AND [System.ChangedDate] < @Today
AND [System.CreatedDate] > @StartOfYear
AND [System.WorkItemType]=''Task''
AND [System.State]=''Resolved''
AND [Microsoft.VSTS.Common.Priority] >= 1
ORDER BY [System.ChangedDate] DESC
')Query work items modified after a date (dynamic)
Use placeholder functions (e.g. monthstart, today, yearend) and arithmetic (e.g. monthstart-1d) to build dynamic dates in your WIQL query so the same statement always reflects the intended period without manual date changes. The placeholder is evaluated before the query is sent to Azure DevOps.
For placeholder syntax and options see placeholder functions. For WIQL see WIQL syntax.
SELECT * FROM WorkItems WITH (Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems
WHERE [System.TeamProject]=''ProductTesting''
AND [System.ChangedDate] >= ''<<monthstart-1d,FUN_TO_DATE>>''
ORDER BY [System.ChangedDate] DESC
')Query work items by WIQL in a project
Runs a WIQL query in a specific project by passing both the project name and the query in the WITH clause. Use this when the connection default is different from the project you want to query, or when you need to target one project explicitly. The query can filter by ID, state, type, or any other WIQL criteria.
SELECT * FROM WorkItems WITH (Project='PosProject', Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.Id] = 2819')Query work items by type (e.g. Task)
Returns work items of a given type (e.g. Task, Bug, User Story) by filtering with a WIQL query on System.WorkItemType. Use this to list all tasks, all bugs, or any other type. You can combine with other WIQL conditions (state, project, dates) in the same query string.
SELECT * FROM WorkItems WITH (Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.WorkItemType] = ''Task''')Query work items using WIQL
Run a WIQL query to filter work items by project and criteria; the query is passed in the WITH clause and executed on the server. You can select specific columns (e.g. Id, Title, Description, CreatedDate, Url) or use * to return all columns. WIQL supports project, ID, state, work item type, dates, and more.
For syntax and operators see WIQL syntax.
SELECT
Id
, Title
, Description
, CreatedDate
, Url
FROM WorkItems
--WHERE Id=5283490 -- uncomment to get just one WorkItem
WITH(Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.TeamProject]=''ProductTesting'' and [System.Id]=6455 ORDER BY [System.Id] DESC')Query sprint hours by team member (estimated vs completed)
Returns aggregated original estimate, remaining work, and completed work per team member for a sprint (iteration path). Useful for sprint burndown or capacity reporting. The query groups by iteration path and assignee; the WITH clause filters to a specific sprint and state (e.g. Resolved, Closed).
This only gives meaningful results if your team updates Original Estimate and Completed Work on work items as they progress. You can change the iteration path in the query to cover other sprints or the whole product.
SELECT
IterationPath as Sprint
, AssignedToUniqueName as AssignedTo
, SUM(OriginalEstimate) as OriginalHours_Total
, SUM(RemainingWork) as RemainingWork_Total
, SUM(CompletedWork) as CompletedHours_Total
FROM WorkItems
GROUP BY IterationPath,AssignedToUniqueName
WITH(
Project='ProductTesting'
--//On Preview UI Change [Max Rows] to use more sample rows - else it will use only 100 rows
,Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.IterationPath] UNDER ''ProductTesting\Sprint 1'' and State IN(''Resolved'', ''Closed'')'
--Use below to query all sprints for this Product
--,Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.IterationPath] UNDER ''ProductTesting\'' and State IN(''Resolved'', ''Closed'')'
)Read more than 20000 work items (UNION ALL)
The Azure DevOps API returns at most 20000 work items per request. To read more, run multiple queries that each request a different ID range (e.g. 1–19999, 20000–39999) and combine the results. This example uses temp tables and UNION ALL so you get one result set; you can add more ranges by adding more SELECT INTO and UNION ALL lines.
Run the full script at once. Adjust the ID ranges and the number of temp tables to match your data size.
SELECT * INTO #t1 FROM WorkItems WITH(Project='ProductTesting', Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.Id]>=1 and [System.Id]<20000');
SELECT * INTO #t2 FROM WorkItems WITH(Project='ProductTesting', Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.Id]>=20000 and [System.Id]<40000');
SELECT * INTO #t3 FROM WorkItems WITH(Project='ProductTesting', Query='SELECT * FROM WorkItems WHERE [System.Id]>=40000 and [System.Id]<60000');
--//....
--//add more temp tables above and update UNION ALL too
SELECT * FROM #t1
UNION ALL
SELECT * FROM #t2
UNION ALL
SELECT * FROM #t3
;
query_workitems endpoint belongs to
WorkItems
table(s), and can therefore be used via those table(s).
Create SQL view in ODBC data source
ZappySys API Drivers support flexible Query language so you can override Default Properties you configured on Data Source such as URL, Body. This way you don't have to create multiple Data Sources if you like to read data from multiple EndPoints. However not every application support supplying custom SQL to driver so you can only select Table from list returned from driver.
If you're dealing with Microsoft Access and need to import data from an SQL query, it's important to note that Access doesn't allow direct import of SQL queries. Instead, you can create custom objects (Virtual Tables) to handle the import process.
Many applications like MS Access, Informatica Designer wont give you option to specify custom SQL when you import Objects. In such case Virtual Table is very useful. You can create many Virtual Tables on the same Data Source (e.g. If you have 50 URLs with slight variations you can create virtual tables with just URL as Parameter setting.
-
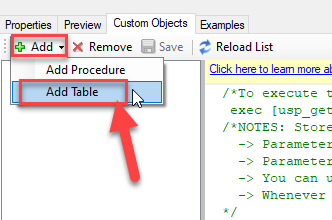
Go to Custom Objects Tab and Click on Add button and Select Add Table:
-
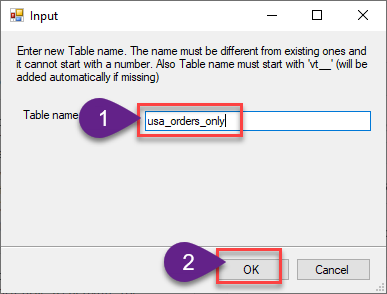
Enter the desired Table name and click on OK:
-
And it will open the New Query Window Click on Cancel to close that window and go to Custom Objects Tab.
-
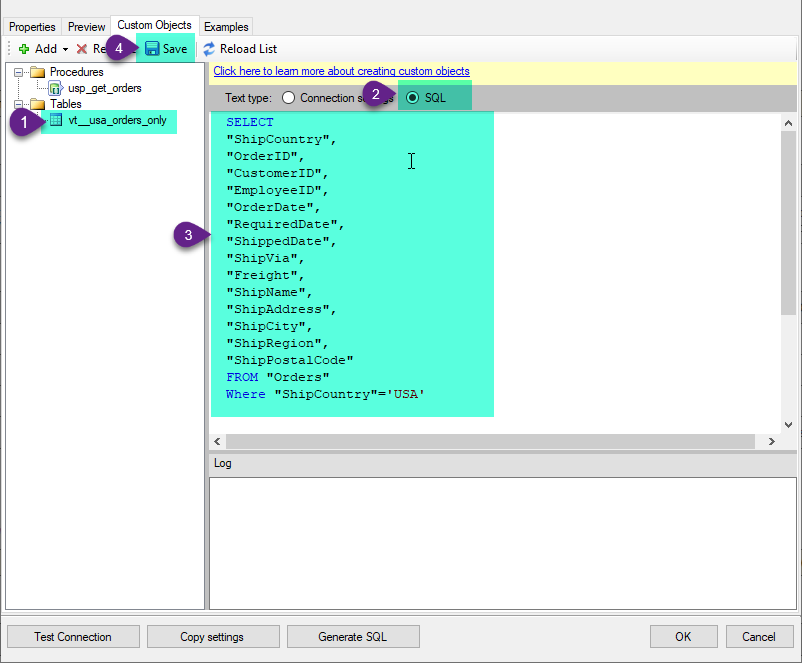
Select the created table, Select Text Type AS SQL and write the your desired SQL Query and Save it and it will create the custom table in the ZappySys Driver:
Here is an example SQL query for ZappySys Driver. You can insert Placeholders also. Read more about placeholders here
SELECT "ShipCountry", "OrderID", "CustomerID", "EmployeeID", "OrderDate", "RequiredDate", "ShippedDate", "ShipVia", "Freight", "ShipName", "ShipAddress", "ShipCity", "ShipRegion", "ShipPostalCode" FROM "Orders" Where "ShipCountry"='USA'
-
That's it now go to Preview Tab and Execute your custom virtual table query. In this example it will extract the orders for the USA Shipping Country only:
SELECT * FROM "vt__usa_orders_only"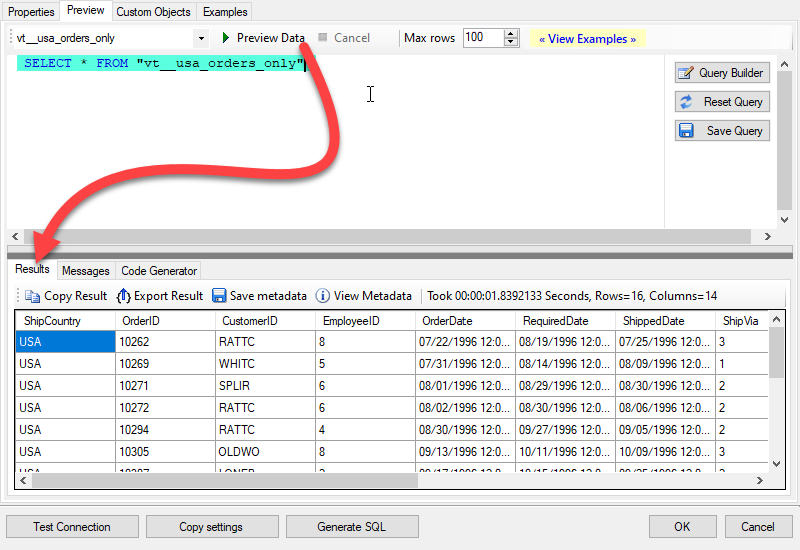
Query work items in SSAS via SQL view
-
Start by right-clicking on Data Source Views and then choosing New Data Source View...:
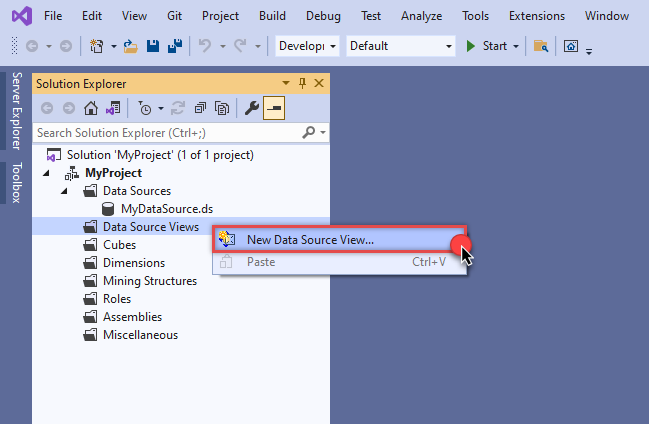
-
Select the previously created data source and click Next:
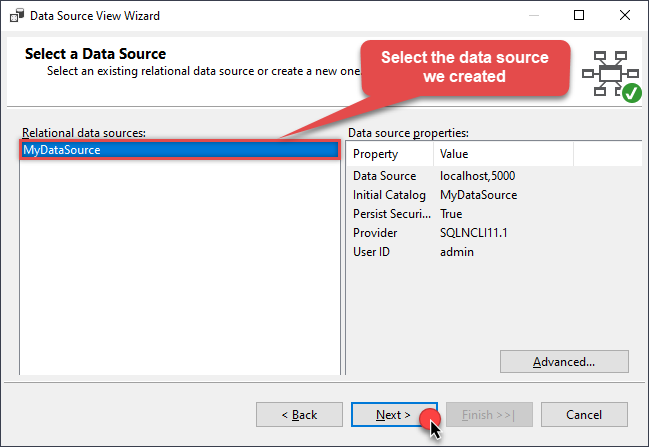
-
Ignore the Name Matching window and click Next.
-
Add the tables you will use in your SSAS cube:
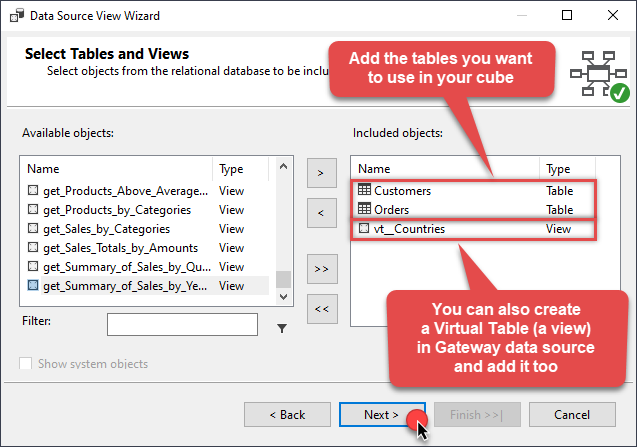 For cube dimensions, consider creating a Virtual Table in the Data Gateway's data source. Use the
For cube dimensions, consider creating a Virtual Table in the Data Gateway's data source. Use theDISTINCTkeyword in theSELECTstatement to get unique values from the facts table, like this:SELECT DISTINCT Country FROM CustomersFor demonstration purposes we are using sample tables which may not be available in Azure DevOps. -
Review your data source view and click Finish:
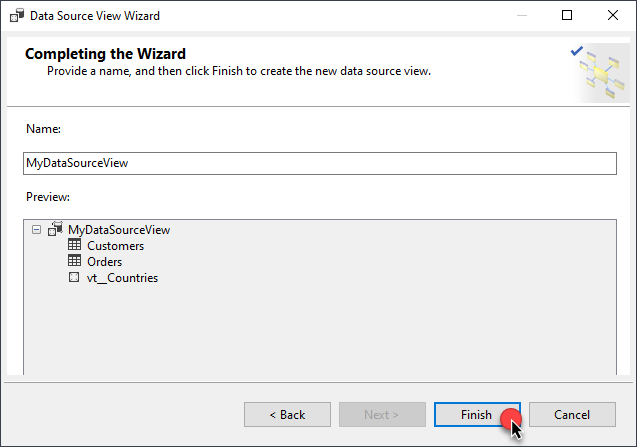
-
Add the missing table relationships and you're done!
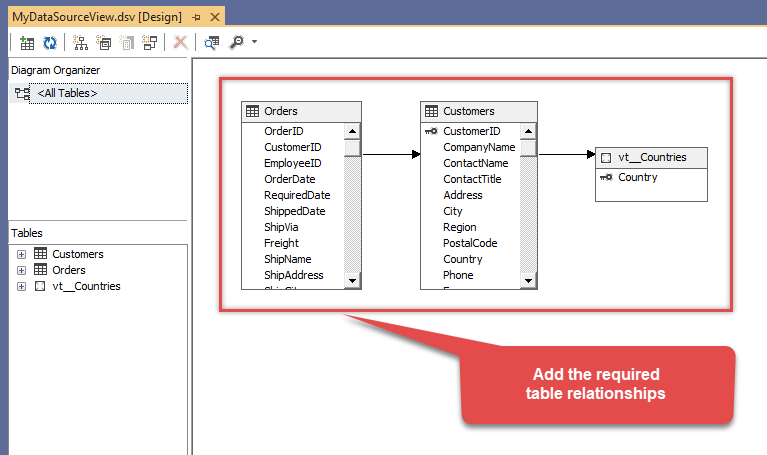
Advanced topics
Creating SQL stored procedures
You can create procedures to encapsulate custom logic and then only pass handful parameters rather than long SQL to execute your API call.
Steps to create Custom Stored Procedure in ZappySys Driver. You can insert Placeholders anywhere inside Procedure Body. Read more about placeholders here
-
Go to Custom Objects Tab and Click on Add button and Select Add Procedure:
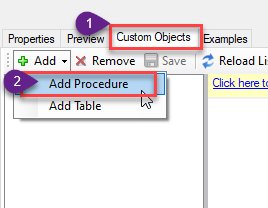
-
Enter the desired Procedure name and click on OK:
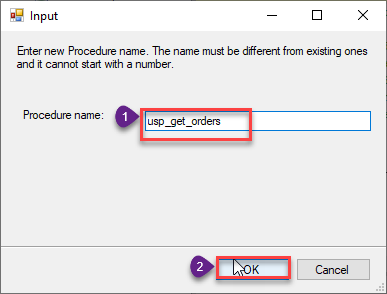
-
Select the created Stored Procedure and write the your desired stored procedure and Save it and it will create the custom stored procedure in the ZappySys Driver. Here is an example stored procedure for ZappySys Driver. You can insert Placeholders anywhere inside Procedure Body. Read more about placeholders here
CREATE PROCEDURE [usp_get_orders] @fromdate = '<<yyyy-MM-dd,FUN_TODAY>>' AS SELECT * FROM Orders where OrderDate >= '<@fromdate>';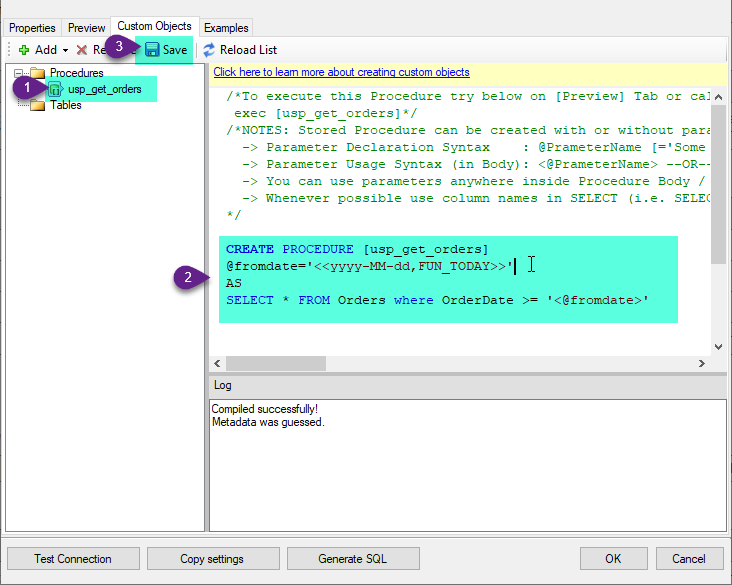
-
That's it now go to Preview Tab and Execute your Stored Procedure using Exec Command. In this example it will extract the orders from the date 1996-01-01:
Exec usp_get_orders '1996-01-01';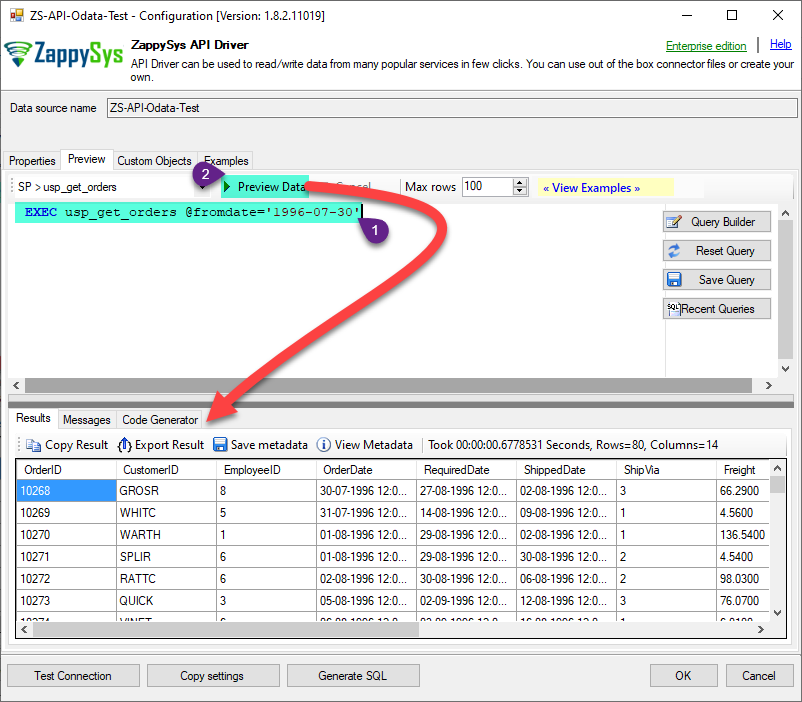
Conclusion
And there you have it — a complete guide on how to query work items in SSAS without writing complex code. All of this was powered by Azure DevOps ODBC Driver, which handled the REST API pagination and authentication for us automatically.
Download the trial now or ping us via chat if you have any questions or are looking for a specific feature (you can also reach out to us by submitting a ticket):
More actions supported by Azure DevOps Connector
Got another use case in mind? We've documented the exact setups for a variety of essential Azure DevOps operations directly in SSAS, so you can skip the trial and error. Find your next step-by-step guide below:
- Create Project
- Create Team
- Create Work Item
- Create Work Item Comment
- Delete Project
- Delete Team
- Delete Work Item
- Delete Work Item Comment
- Get List of Projects
- Get List of Queries
- Get List of Teams
- Get Project Details
- Get Query Fileds
- Get Team Details
- Get Team Iteration Capacities
- Get Team Iterations
- Get Team Members
- Get Work Item Column Fields
- Get Work Item Comment by Comment Id and Work Item Id
- Get Work Item Comments (by WorkItem Id)
- Get Work Item Types
- Get Work Items by Ids
- Get Work Items for Specified Query Id
- Query Work Item Comments
- Search for Work Items by Text
- Update Project
- Update Team
- Update Work Item
- Update Work Item Comment
- Make Generic REST API Request
- Make Generic REST API Request (Bulk Write)