Salesforce Connector for SQL Server
Salesforce Connector can be used to extract/load large amount of data from/in Salesforce.com without any programming. You can use simple Table mode or Query mode with full SOQL query language support (SOQL=Salesforce.com Object Query Language).
In this article you will learn how to quickly and efficiently integrate Salesforce data in SQL Server without coding. We will use high-performance Salesforce Connector to easily connect to Salesforce and then access the data inside SQL Server.
Let's follow the steps below to see how we can accomplish that!
Salesforce Connector for SQL Server is based on ZappySys Salesforce Driver which is part of ODBC PowerPack. It is a collection of high-performance ODBC drivers that enable you to integrate data in SQL Server, SSIS, a programming language, or any other ODBC-compatible application. ODBC PowerPack supports various file formats, sources and destinations, including REST/SOAP API, SFTP/FTP, storage services, and plain files, to mention a few.
Video Tutorial - Integrate Salesforce data in SQL Server
This video covers the following topics and more, so please watch carefully. After watching the video, follow the steps outlined in this article:
- How to download and install the required PowerPack for Salesforce integration in SQL Server
- How to configure the connection for Salesforce
- Features of the ZappySys Salesforce Driver (Authentication / Query Language / Examples / Driver UI)
- How to use the Salesforce in SQL Server
Create Data Source in Data Gateway based on ZappySys Salesforce Driver
In this section we will create a data source for Salesforce in Data Gateway. Let's follow these steps to accomplish that:
-
Download and install ODBC PowerPack.
-
Search for
gatewayin Windows Start Menu and open ZappySys Data Gateway Configuration: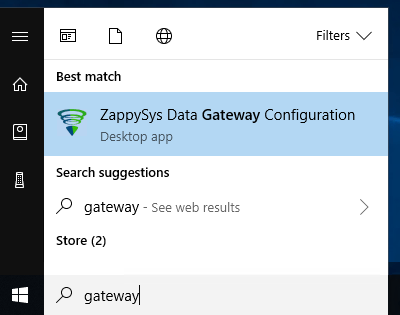
-
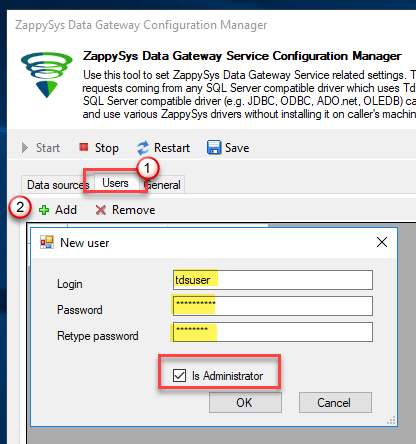
Go to Users tab and follow these steps to add a Data Gateway user:
- Click Add button
-
In Login field enter username, e.g.,
john - Then enter a Password
- Check Is Administrator checkbox
- Click OK to save
-
Now we are ready to add a data source:
- Click Add button
- Give Datasource a name (have it handy for later)
- Then select Native - ZappySys Salesforce Driver
- Finally, click OK
SalesforceDSNZappySys Salesforce Driver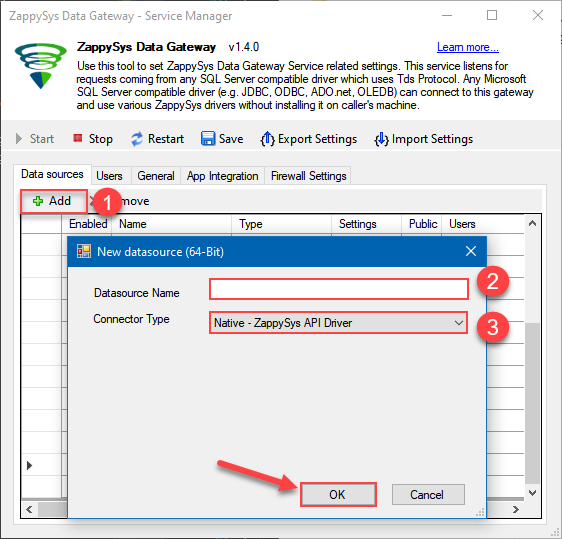
-
Now, we need SalesForce Connection. Lets create it.
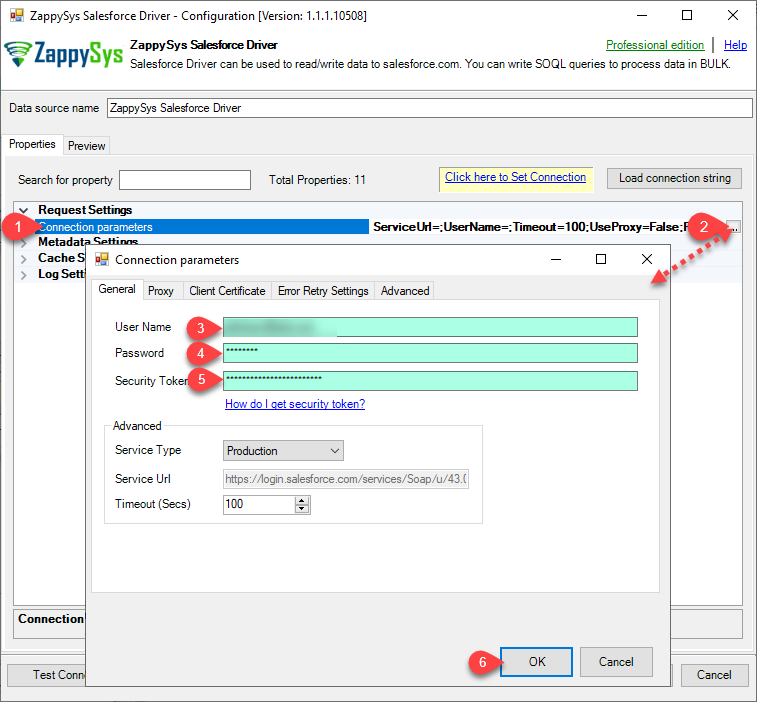
-
Now, When you see DSN Config Editor with zappysys logo first thing you need to do is change default DSN Name at the top and Click on Preview Tab, Select Table from Tables Dropdown or you can enter or modify a SOQL query and click on Preview Data.
This example shows how to write simple SOQL query (Salesforce Object Query Language). It uses WHERE clause. For more SOQL Queries click here.
SOQL is similar to database SQL query language but much simpler and many features you use in database query may not be supported in SOQL (Such as JOIN clause not supported). But you can use following Queries for Insert, Update, Delete and Upsert(Update or Insert record if not found).SELECT * FROM Account WHERE Name like '%Oil%'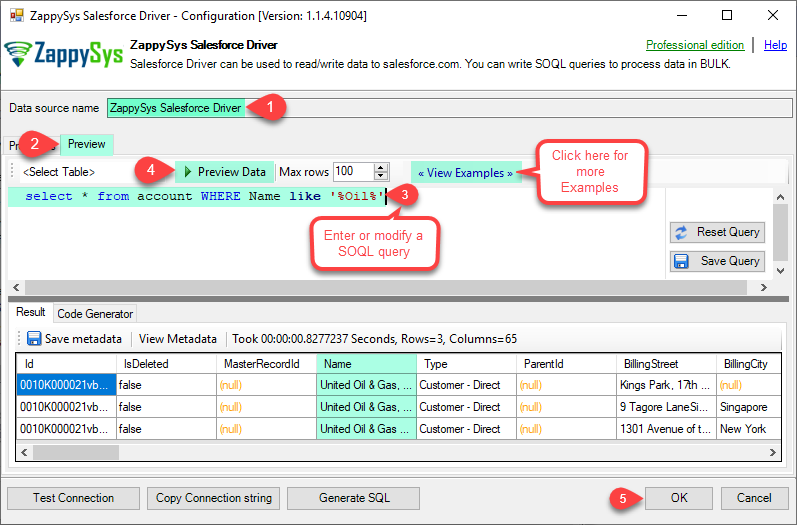
-
Click OK to finish creating the data source
-
Very important step. Now, after creating or modifying the data source make sure you:
- Click the Save button to persist your changes.
- Hit Yes, once asked if you want to restart the Data Gateway service.
This will ensure all changes are properly applied:
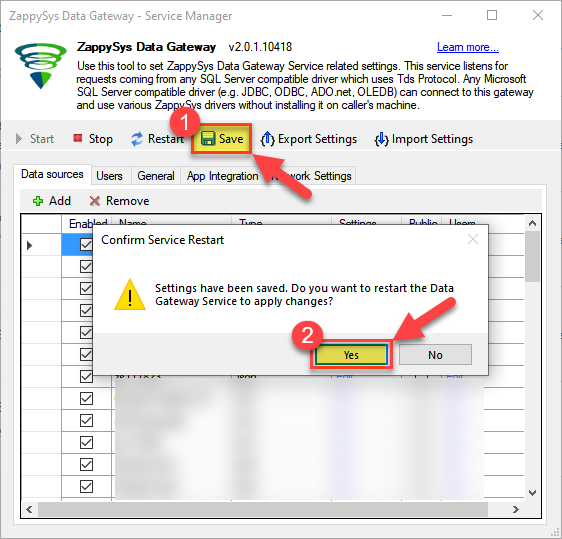 Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Read data in SQL Server via Data Gateway
After configuring your data source using the ZappySys ODBC Driver, the next mandatory step to read that data in SQL Server is to create a Linked Server. SQL Server requires a Linked Server definition to access any ODBC-based source through the ZappySys Data Gateway, allowing the source driver data to be queried using standard T-SQL.
There are two ways to create the Linked Server:- Method 1: Using a SQL Script automatically generated by the Data Gateway
- Method 2: Using SQL Server UI (SSMS) to manually configure the Linked Server
Method 1: Using a SQL Script automatically generated by the Data Gateway
The fastest and most reliable way to create the Linked Server is to use the SQL Script generated by the Data Gateway. This ensures all settings are applied correctly with minimal manual steps.
In the Data Gateway, open the App Integration tab.
Update the prefilled Linked Server Name if you want to use a custom name.
Select the SalesforceDSN data source which we created earlier as the Database.
-
Choose the correct SQL Server version for your environment.
- SQL 2019 or Lower (
@provider='SQLNCLI11') - SQL 2022 or Higher (
@provider='MSOLEDBSQL')
- SQL 2019 or Lower (
Click Generate Code.
-
In the generated script scroll down to 4. Attach Gateway login with linked server step, enter your Data Gateway admin username and password.
'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY'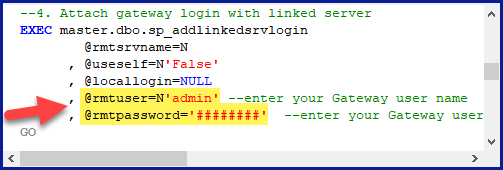
-
Press Ctrl + A and Ctrl + C to copy the entire script.
LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAYSalesforceDSN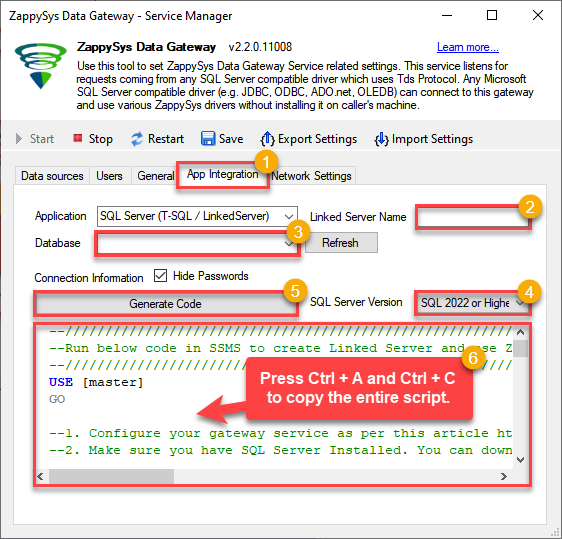
-
Paste the script into SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and run it.
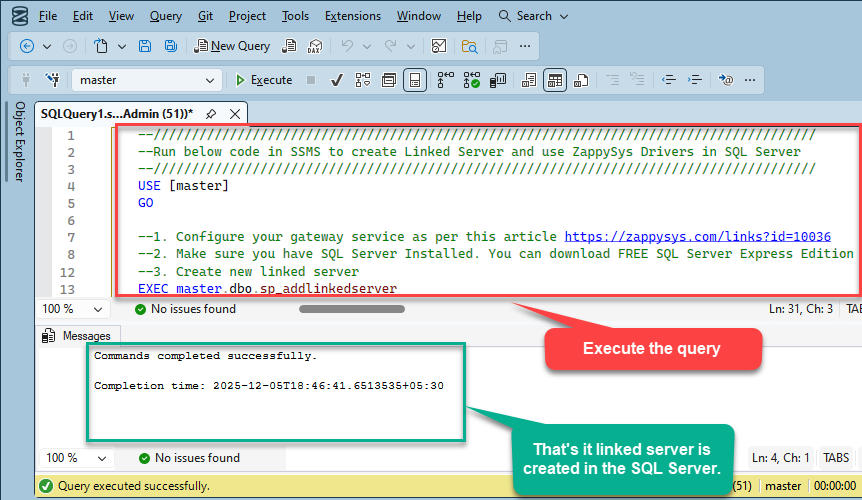
That's it linked server is created in the SQL Server.
-
Finally, open a new query and execute a query we saved in one of the previous steps:
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY], 'SELECT * FROM Orders')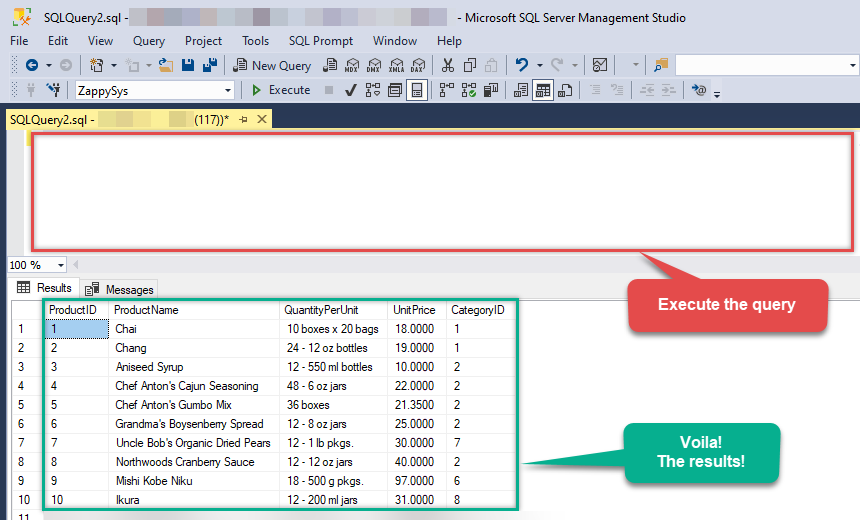
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY], 'SELECT * FROM Orders')
Sample SQL Script for Creating a Linked Server in SQL Server
USE [master]
GO
--///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
--Run below code in SSMS to create Linked Server and use ZappySys Drivers in SQL Server
--///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
-- Replace YOUR_GATEWAY_USER, YOUR_GATEWAY_PASSWORD
-- Replace localhost with IP/Machine name if ZappySys Gateway Running on different machine other than SQL Server
-- Replace Port 5000 if you configured gateway on a different port
--1. Configure your gateway service as per this article https://zappysys.com/links?id=10036
--2. Make sure you have SQL Server Installed. You can download FREE SQL Server Express Edition from here if you dont want to buy Paid version https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/sql-server/sql-server-editions-express
--Uncomment below if you like to drop linked server if it already exists
--EXEC master.dbo.sp_dropserver @server=N'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', @droplogins='droplogins'
--3. Create new linked server
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver
@server = N'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY' --Linked server name (this will be used in OPENQUERY sql
, @srvproduct=N''
---- For MSSQL 2012, 2014, 2016, 2017, and 2019 use below (SQL Server Native Client 11.0)---
, @provider=N'SQLNCLI11'
---- For MSSQL 2022 or higher use below (Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server)---
--, @provider=N'MSOLEDBSQL'
, @datasrc=N'localhost,5000' --//Machine / Port where Gateway service is running
, @provstr=N'Network Library=DBMSSOCN;'
, @catalog=N'SalesforceDSN' --Data source name you gave on Gateway service settings
--4. Attach gateway login with linked server
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
@rmtsrvname=N'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY' --linked server name
, @useself=N'False'
, @locallogin=NULL
, @rmtuser=N'YOUR_GATEWAY_USER' --enter your Gateway user name
, @rmtpassword='YOUR_GATEWAY_PASSWORD' --enter your Gateway user's password
GO
--5. Enable RPC OUT (This is Optional - Only needed if you plan to use EXEC(...) AT YourLinkedServerName rather than OPENQUERY
EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'rpc', true;
EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'rpc out', true;
--Disable MSDTC - Below needed to support INSERT INTO from EXEC AT statement
EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'remote proc transaction promotion', false;
--Increase query timeout if query is going to take longer than 10 mins (Default timeout is 600 seconds)
--EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'query timeout', 1200;
GOMethod 2: Using SQL Server UI (SSMS) to manually configure the Linked Server
You can also create the Linked Server manually through SSMS if you prefer a visual setup. This method lets you configure the provider, data source, and security interactively.
-
First, let's open SQL Server Management Studio, create a new Linked Server, and start configuring it:
LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAYMicrosoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Serverlocalhost,5000SalesforceDSNSalesforceDSN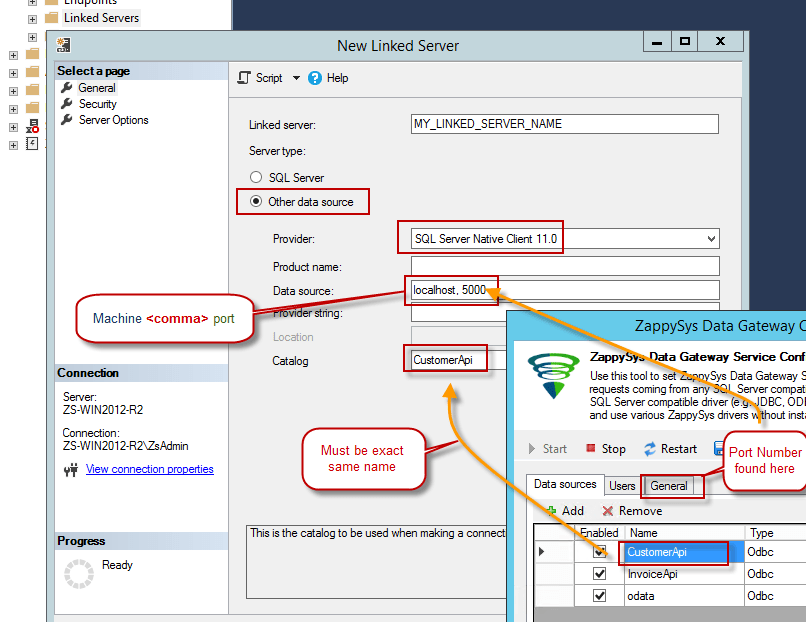
- For SQL Server 2012, 2014, 2016, 2017, and 2019, choose SQL Server Native Client 11.0 as the provider.
- For SQL Server 2022 or higher, choose Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server as the provider.
-
Then click on Security option and configure username we created in ZappySys Data Gateway in one of the previous steps, e.g.
john: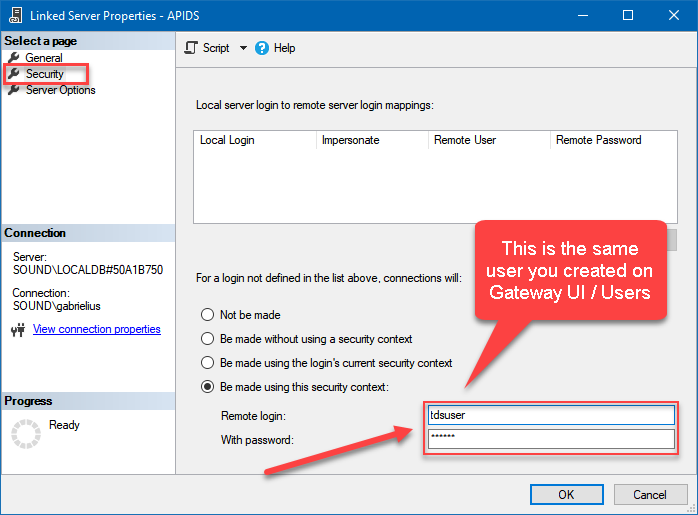
-
Optional step. Under the Server Options, Enable RPC and RPC Out and Disable Promotion of Distributed Transactions(MSDTC).
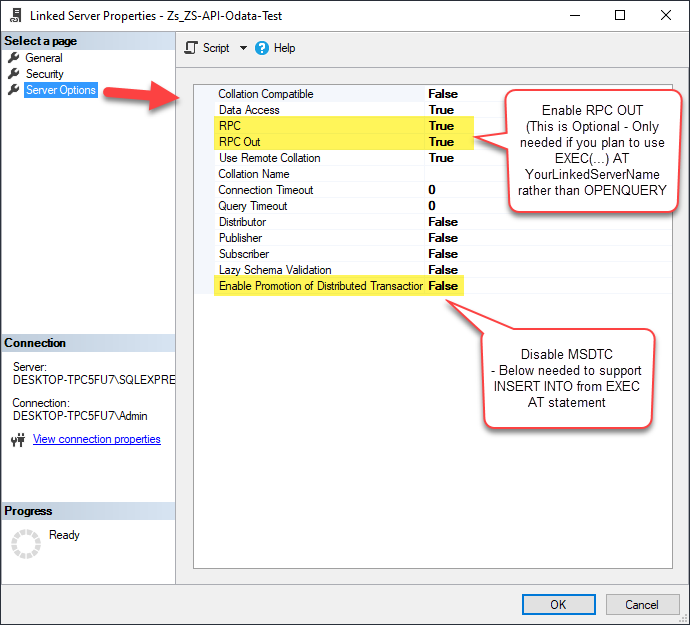
You need to enable RPC Out if you plan to use
EXEC(...) AT [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY]rather than OPENQUERY.
If don't enabled it, you will encounter theServer 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY' is not configured for RPCerror.Query Example:
DECLARE @MyQuery NVARCHAR(MAX) = 'SELECT * FROM Orders'; EXEC (@MyQuery) AT [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY];
If you plan to use
'INSERT INTO <TABLE> EXEC(...) AT [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY]'in that case you need to Disable Promotion of Distributed Transactions(MSDTC).
If don't disabled it, you will encounter theThe operation could not be performed because OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11" for linked server "MY_LINKED_SERVER_NAME" was unable to begin a distributed transaction.error.Query Example:
INSERT INTO dbo.Products DECLARE @MyQuery NVARCHAR(MAX) = 'SELECT * FROM Orders'; EXEC (@MyQuery) AT [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY]; -
Finally, open a new query and execute a query we saved in one of the previous steps:
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY], 'SELECT * FROM Orders')
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY], 'SELECT * FROM Orders')
Firewall settings
So far we have assumed that Gateway is running on the same machine as SQL Server. However there will be a case when ZappySys ODBC PowerPack is installed on a different machine than SQL Server. In such case you may have to perform additional Firewall configurations. On most computers firewall settings wont allow outside traffic to ZappySys Data Gateway. In such case perform following steps to allow other machines to connect to Gateway.
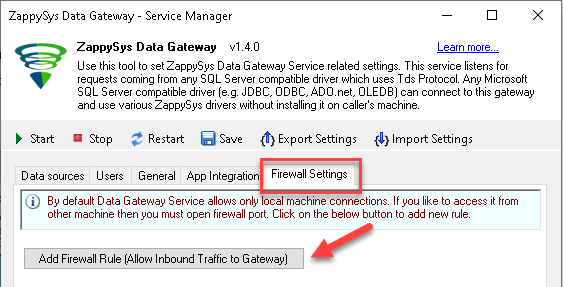
Method-1 (Preferred)If you are using newer version of ZappySys Data Gateway then adding firewall rule is just a single click.
- Search for gateway in start menu and open ZappySys Data Gateway.
-
Go to Firewall Tab and click Add Firewall Rule button like below. This will create Firewall rule to all Inbound Traffic on Port 5000 (Unless you changed it).
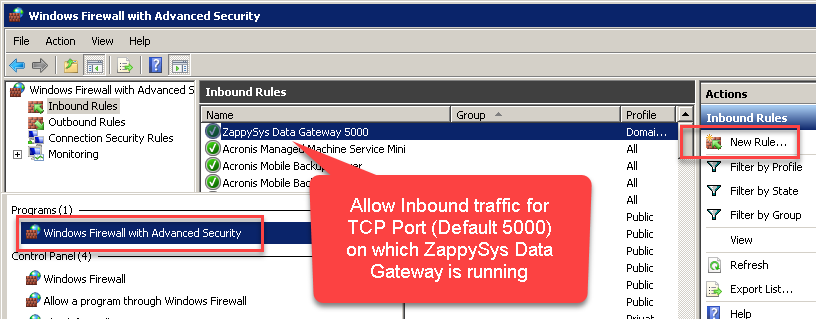
Here is another way to add / edit Inbound Traffic rule in windows firewall. Use below method if you choose to customize your rule (for advanced users).
- Search for Windows Firewall Advanced Security in start menu.
- Under Inbound Rules > Right click and click [New Rule] >> Click Next
- Select Port on Rule Type >> Click Next
- Click on TCP and enter port number under specified local port as 5000 (use different one if you changed Default port) >> Click Next
- Select Profile (i.e. Private, Public) >> Click Next
- Enter Rule name [i.e. ZappySys Data Gateway – Allow Inbound ] >> Click Next
- Click OK to save the rule
OPENQUERY vs EXEC (handling larger SQL text)
So far we have seen examples of using OPENQUERY. It allows us to send pass-through query at remote server. The biggest limitation of OPENQUERY is it doesn't allow you to use variables inside SQL so often we have to use unpleasant looking dynamic SQL (Lots of tick, tick …. and escape hell). Well there is good news. With SQL 2005 and later you can use EXEC(your_sql) AT your_linked_server syntax .
Disadvantage of EXEC AT is you cannot do SELECT INTO like OPENQUERY. Also you cannot perform JOIN like below in EXEC AT
SELECT a.*
FROM OPENQUERY([LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY],'SELECT * FROM Customers') AS A
JOIN OPENQUERY([LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY],'SELECT * FROM Orders') AS B
ON A.CustomerId = B.CustomerId;INSERT INTO SomeTable EXEC(…) AT your_linked_server. So table must exists when you do that way.
Here is how to use it. To use EXEC(..) AT {linked-server} you must turn on RPC OUT option. Notice how we used variable in SQL to make it dynamic. This is much cleaner than previous approach we saw.
USE [master]
GO
--Replace YOUR_GATEWAY_USER, YOUR_GATEWAY_PASSWORD
--Replace localhost with IP/Machine name if ZappySys Gateway Running on different machine other than SQL Server
--Create new linked server
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver
@server = N'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY' --Linked server name (this will be used in OPENQUERY sql)
, @srvproduct=N''
---- For MSSQL 2012, 2014, 2016, 2017, and 2019 use below (SQL Server Native Client 11.0)---
, @provider=N'SQLNCLI11'
---- For MSSQL 2022 or higher use below (Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server)---
--, @provider=N'MSOLEDBSQL'
, @datasrc=N'localhost,5000' --//Machine / Port where Gateway service is running
, @provstr=N'Network Library=DBMSSOCN;'
, @catalog=N'SalesforceDSN' --Data source name you gave on Gateway service settings
--Attach gateway login with linked server
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
@rmtsrvname=N'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY' --linked server name
, @useself=N'False'
, @locallogin=NULL
, @rmtuser=N'YOUR_GATEWAY_USER' --enter your Gateway user name
, @rmtpassword='YOUR_GATEWAY_PASSWORD' --enter your Gateway user's password
GO
--5. Enable RPC OUT (This is Optional - Only needed if you plan to use EXEC(...) AT YourLinkedServerName rather than OPENQUERY
EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'rpc', true;
EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'rpc out', true;
--Disable MSDTC - Below needed to support INSERT INTO from EXEC AT statement
EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'remote proc transaction promotion', false;
--Increase query timeout if query is going to take longer than 10 mins (Default timeout is 600 seconds)
--EXEC sp_serveroption 'LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY', 'query timeout', 1200;
GO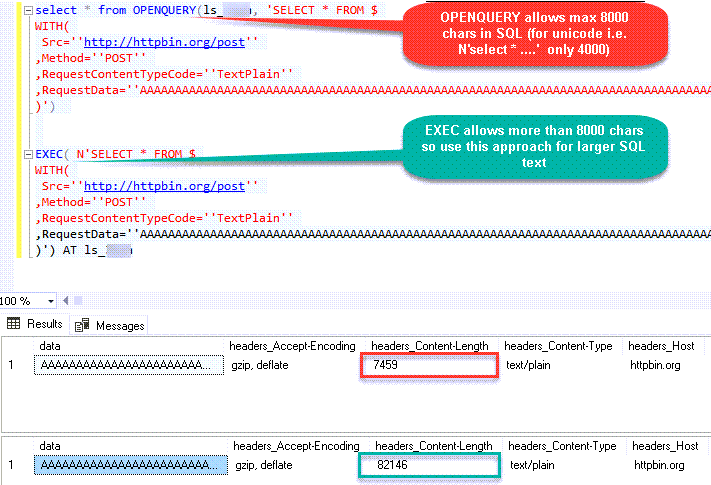
Fetching Tables / Columns using metadata stored procs
ZappySys Data Gateway emulates certains system procs you might find in real SQL Server. You can call using below syntax using 4-Parts syntaxEXEC [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY].[SalesforceDSN].[DATA].sp_tablesEXEC [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY].[SalesforceDSN].[DATA].sp_columns_90 N'your-table-name'-- List all tables
EXEC [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY].[SalesforceDSN].[DATA].sp_tables
-- List all columns and its type for specified table
EXEC [LS_TO_SALESFORCE_IN_GATEWAY].[SalesforceDSN].[DATA].sp_columns_90 N'Account'Known Issues
Let's explore some common problems that can occur when using OPENQUERY or Data Gateway connectivity.
SQL Native Client 11.0 not visible in the Providers dropdown (Linked Server Creation)
If you are following some screenshots / steps from our article it might say use SQL Native Client to create Linked Server to ZappySys Gateway but for some users they dont see that driver entry in the dropdown. This is due to the fact that Microsoft has deprecated SQL Native Client OLEDB Driver (SQLNCLI and SQLNCLI11) going forward after SQL 2022. So you need to use [Microsoft OLE DB Driver for SQL Server] instead (MSOLEDBSQL). Please follow all other instructions except the driver type selection, use new suggested driver instead if you dont see SQL Native Client.
Error: The data is invalid
There will be a time when, you may encounter unexpected errors like the ones listed below. These can include:
OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11" for linked server "Zs_Csv" returned message "Deferred prepare could not be completed.". OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11" for linked server "Zs_Csv" returned message "Communication link failure". Msg 13, Level 16, State 1, Line 0 Session Provider: The data is invalid.Possible Cause:
There are few reasons for such error but below are two main reasons
-
If the query length exceeds 2000 characters, as shown below, you might encounter this error.
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(LS, '--some really long text more than 2000 chars--') -
If a query contains multiple OPENQUERY statements for JOINs or UNIONs, as shown below, it might fail due to a MARS compatibility issue where the gateway doesn't support parallel queries on a single connection.
SELECT a.id, b.name from OPENQUERY(LS, 'select * from tbl1') a join OPENQUERY(LS, 'select * from tbl2') b on a.id=b.id
There are few ways to fix above error based on reason why you getting this error (i.e. Query Length issue OR JOIN/UNION in the same statement)
-
If your query has long SQL (more than 2000 chars ) then reduce SQL length using different techniques
- e.g. use SELECT * FROM MyTable rather than SELECT col1,col2… FROM MyTable
- Use Meta Option in WITH clause if you must use column name. (e.g. SELECT * FROM MyTable WITH(META=’c:\meta.txt’) this way you can define column in Meta file rather than SELECT query. Check this article
- Consider using EXECT (….) AT [Linked_Server_name] option rather than OPENQUERY so you can use very long SQL (See next section on EXEC..AT usecase)
-
Consider
using Virtual Table / Stored Proc
to wrap long SQL so your call is very small (where usp_GetOrdersByYear is custom proc created on ZappySys Driver UI)
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(LS, 'EXEC usp_GetOrdersByYear 2021')
-
If your query uses JOIN / UNION with multiple OPENQUERY in same SQL then use multiple Linked servers (one for each OPENQUERY clause) as below.
select a.id, b.name from OPENQUERY(LS_1, 'select * from tbl1') a join OPENQUERY(LS_2, 'select * from tbl2') b on a.id=b.id
Error: Unable to begin a distributed transaction (When INSERT + EXEC used)
If you try to use the EXEC statement to insert data into a table, as shown below, you might encounter the following error unless the MSDTC option is turned off.
INSERT INTO MyTable EXEC('select * from tbl') AT MyLinkedServer"Protocol error in TDS stream" The operation could not be performed because OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11" for linked server "ls_Json2" was unable to begin a distributed transaction. --OR-- The operation could not be performed because OLE DB provider "MSOLEDBSQL" for linked server "ls_Json" was unable to begin a distributed transaction.
Solution:
Method-1: Go to linked server properties | Server Options | Enable Promotion of Distributed Transaction | Change to false (Default is true)
Now your try your INSERT with EXEC AT and it should work
Method-2: Run the below command if you dont want to use UI
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'My_Linked_Server', @optname=N'remote proc transaction promotion', @optvalue=N'false'Error: Cannot use OPENQUERY with JOIN / UNION
When you perform a JOIN or UNION ALL on the same Linked Server, it may fail to process sometimes because the Data Gateway doesn't support parallel query requests on the same connection. A workaround for that would be to create multiple linked servers for the same data source. Refer to the section above for the same workaround.
Error: Truncation errors due to data length mismatch
Many times, you may encounter truncation errors if a table column's length is less than the actual column size from the query column. To solve this issue, use the new version of Data Gateway and check the 'Use nvarchar(max) for string options' option found on the General Tab.
Performance Tips
Now, let's look at a few performance tips in this section.
Use INSERT INTO rather than SELECT INTO to avoid extra META request
We discussed some Pros and Cons of OPENQUERY vs EXEC (…) AT in previous section. One obvious advantage of EXEC (….) AT is it reduces number of requests to driver (It sends pass through query). With EXEC you cannot load data dynamically like SELECT INTO tmp FROM OPENQUERY. Table must exist before hand if you use EXEC.
INSERT INTO tmp_API_Report_Load(col1,col2)
EXEC('select col1,col2 from some_api_table') AT [API-LINKED-SERVER]
--OR--
INSERT INTO tmp_API_Report_Load(col1,col2)
select col1,col2 from OPENQUERY([API-LINKED-SERVER], 'select col1,col2 from some_api_table')The advantage of this method is that your query speed will increase because the system only calls the API once when you use EXEC AT. In contrast, with OPENROWSET, the query needs to be called twice: once to obtain metadata and once to retrieve the data.
Use Cached Metadata if possible
By default, most SQL queries sent to the Data Gateway need to invoke two phases: first, to get metadata, and second, to fetch data. However, you can bypass the metadata API call by supplying static metadata. Use the META property in the WITH clause, as explained in this article , to speed up your SQL queries.Query Examples
This guide provides examples for using the ZappySys Salesforce ODBC Driver to perform bulk API operations and DML (Data Manipulation Language) actions on Salesforce. You’ll learn how to leverage the Bulk API to insert, update, upsert, and delete large datasets from external sources such as MSSQL, CSV, Oracle, and other ODBC-compatible systems. By using external IDs and lookup fields, you can easily map data from your source systems to Salesforce. These examples will help you execute high-performance operations efficiently using EnableBulkMode, EXTERNAL options, and more.
Bulk Mode - Insert Large Volume of Data from External Source (e.g., MSSQL) into Salesforce
This example demonstrates how to use the EnableBulkMode option to insert a large volume of records into Salesforce using the Bulk API (Job-based mode). By default, the standard mode writes data in batches of 200 rows. However, when Bulk API mode is enabled, it can send up to 10,000 rows per batch, offering better performance for large datasets. Note that using Bulk API mode may not provide performance benefits for small datasets (e.g., a few hundred rows).
In this example, the driver type is set to MSSQL. For other data sources such as CSV, REST API, or Oracle, update the driver type to ODBC and modify the connection string and query accordingly.
Ensure that your source query returns column names that match the target Salesforce object fields. The EXTERNAL option is used to map Salesforce target fields based on the output of the source query.
Important: If you’re using Windows authentication, the service account running the ZappySys Data Gateway must have the appropriate permissions on the source system.
SELECT *
FROM OPENQUERY([MY_LINKED_SERVER],
'
INSERT INTO Account
SOURCE (
''MSSQL'',
''Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=tempdb;Integrated Security=true'',
''SELECT TOP 1000000
C_NAME AS Name,
C_CITY AS BillingCity,
C_LOC AS NumberofLocations__c
FROM very_large_staging_table''
)
WITH (
Output = 1,
EnableBulkMode = 1
)
')
-- Notes:
-- ''MSSQL'': External driver type (MSSQL, ODBC, OLEDB)
-- Output: Enables capturing __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage
-- EnableBulkMode: Improves performance with bulk batches (uses 10000 rows per batch rather than 200)
Bulk Mode - Insert Records with Lookup Field (Read from External Source)
This example demonstrates how to use the EnableBulkMode option to insert a large number of records into Salesforce using the Bulk API (Job-based mode). Additionally, it shows how to set a lookup field—specifically the Owner field—by referencing an external ID from the User object instead of using the internal Salesforce ID.
If you are performing an Update operation, you must include the Id field in the source data. If your source field has a different name, alias it to Id in the SQL query. For Upsert operations, you can specify a custom external ID field using the Key='ExternalId_Field_Name' option. However, for standard Update operations, the Id field is mandatory.
By default, data is written in batches of 200 rows. When Bulk API mode is enabled, up to 10,000 rows can be sent per batch. This improves performance for large datasets, but offers little advantage for smaller volumes.
In this example, the driver type is set to MSSQL. For other sources such as CSV, REST API, or Oracle, change the driver type to ODBC and adjust the connection string and query accordingly.
Make sure the query outputs column names that match the target fields in the Salesforce object. The EXTERNAL option is used to map input columns to Salesforce fields dynamically.
Important: If you’re using Windows authentication, ensure that the service account running the ZappySys Data Gateway has the appropriate access permissions on the source system.
SELECT *
FROM OPENQUERY([MY_LINKED_SERVER],
'
INSERT INTO Account
SOURCE (
''MSSQL'',
''Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=tempdb;Integrated Security=true'',
''SELECT TOP 1000000
Account_Name as Name,
AccountOwnerId as [Owner.ExternalId]
FROM very_large_staging_table''
)
WITH (
Output = 1,
EnableBulkMode = 1
)
')
-- Notes:
-- ''MSSQL'': External driver type (MSSQL, ODBC, OLEDB)
-- Output: Enables capturing __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage
-- EnableBulkMode: Improves performance with bulk batches (uses 10000 rows per batch rather than 200)
Bulk Mode - Delete Large Volume of Data (Read IDs from External Source)
This example demonstrates how to use the EnableBulkMode option to delete a large number of records from Salesforce using the Bulk API (Job-based mode). To perform a delete operation, the source query must return the Id column. If your source column has a different name, make sure to alias it as Id in the SQL query.
By default, data is processed in batches of 200 rows. When Bulk API mode is enabled, batches can include up to 10,000 rows, which significantly improves performance when working with large datasets. However, for small volumes (a few hundred records), Bulk API mode may not offer a noticeable performance benefit.
In this example, the driver type is set to MSSQL. For other data sources such as CSV, REST API, or Oracle, set the driver type to ODBC and update the connection string and query as needed.
Ensure that the query output includes column names that match the target Salesforce object fields. The EXTERNAL option allows dynamic mapping of input columns to Salesforce fields based on the source query.
Important: If you’re using Windows authentication, make sure the service account running the ZappySys Data Gateway has the necessary permissions to access the data source.
SELECT *
FROM OPENQUERY([MY_LINKED_SERVER],
'
DELETE FROM Account
SOURCE (
''MSSQL'',
''Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=tempdb;Integrated Security=true'',
''SELECT TOP 1000000
Account_ID as Id
FROM very_large_staging_table''
)
WITH (
Output = 1,
EnableBulkMode = 1
)
')
-- Notes:
-- ''MSSQL'': External driver type (MSSQL, ODBC, OLEDB)
-- Output: Enables capturing __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage
-- EnableBulkMode: Improves performance with bulk batches (uses 10000 rows per batch rather than 200)
Bulk Mode - Update Large Volume of Data (Read from External Source)
This example illustrates how to use the EnableBulkMode option to update a large number of records in Salesforce via the Bulk API (Job-based mode). When performing an Update operation, the source query must include the Id column. If the source column is named differently, be sure to alias it as Id in your SQL query.
By default, records are processed in batches of 200 rows. When Bulk API mode is enabled, batches can handle up to 10,000 rows, which greatly improves performance for large datasets. However, for smaller datasets (e.g., a few hundred records), Bulk API may not offer a significant performance boost.
In this example, the driver type is set to MSSQL. For other sources such as CSV, REST API, or Oracle, change the driver type to ODBC and modify the connection string and query accordingly.
Ensure that your query returns column names matching the fields in the Salesforce target object. The EXTERNAL option is used to dynamically map input columns to Salesforce fields based on the query output.
Important: When using Windows authentication, the service account running the ZappySys Data Gateway must have the necessary permissions on the source system.
SELECT *
FROM OPENQUERY([MY_LINKED_SERVER],
'
UPDATE Account
SOURCE (
''MSSQL'',
''Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=tempdb;Integrated Security=true'',
''SELECT TOP 1000000
Account_ID as Id,
Account_Name as Name,
City as BillingCity
FROM very_large_staging_table''
)
WITH (
Output = 1,
EnableBulkMode = 1
)
')
-- Notes:
-- ''MSSQL'': External driver type (MSSQL, ODBC, OLEDB)
-- Output: Enables capturing __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage
-- EnableBulkMode: Improves performance with bulk batches (uses 10000 rows per batch rather than 200)
Bulk Mode - Update Lookup Field (Read from External Source)
This example shows how to use the EnableBulkMode option to update a large number of Salesforce records using the Bulk API (Job-based mode). In this scenario, we update a lookup field—specifically the Owner field—by referencing the external ID from the User object instead of using the internal Salesforce ID.
When performing an Update, the Id field must be included in the source data. If your source column has a different name, alias it as Id in the SQL query. For Upsert operations, you can specify a custom external ID using the Key='ExternalId_Field_Name' option. However, for standard Update operations, the Id field is required.
By default, the system processes 200 rows per batch. When EnableBulkMode is enabled, it can process up to 10,000 rows per batch, offering improved performance for large datasets. This mode is less effective for smaller data volumes.
In this example, the driver type is set to MSSQL. For other data sources (e.g., CSV, REST API, Oracle), change the driver type to ODBC and update the connection string and query as needed.
Ensure the query returns column names that match the fields in the target Salesforce object. The EXTERNAL option dynamically maps input columns to Salesforce fields based on the query output.
Important: If using Windows authentication, ensure the service account running the ZappySys Data Gateway has appropriate permissions on the source system.
SELECT *
FROM OPENQUERY([MY_LINKED_SERVER],
'
UPDATE Account
SOURCE (
''MSSQL'',
''Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=tempdb;Integrated Security=true'',
''SELECT TOP 1000000
Account_ID as Id,
Account_Name as Name,
AccountOwnerId as [Owner.ExternalId]
FROM very_large_staging_table''
)
WITH (
Output = 1,
EnableBulkMode = 1
)
')
-- Notes:
-- ''MSSQL'': External driver type (MSSQL, ODBC, OLEDB)
-- Output: Enables capturing __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage
-- EnableBulkMode: Improves performance with bulk batches (uses 10000 rows per batch rather than 200)
External Input from ODBC - Insert Multiple Rows from ODBC Source (e.g., CSV) into Salesforce
This example demonstrates how to perform an INSERT operation in Salesforce using multiple input rows from an external data source such as MSSQL, ODBC, or OLEDB. The operation reads records via an external query and inserts them directly into Salesforce.
In this example, the driver type is set to MSSQL. For other systems like CSV, REST API, or Oracle, set the driver type to ODBC and update the connection string and query accordingly.
Ensure that the query returns column names that match the fields in the Salesforce target object. The EXTERNAL option is used to map these input columns to the corresponding Salesforce fields based on the source query output.
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([MY_LINKED_SERVER]
, 'INSERT INTO Account
SOURCE (
''ODBC'', -- External driver type: MSSQL, ODBC, or OLEDB
''Driver={ZappySys CSV Driver};DataPath=c:\somefile.csv'', -- ODBC connection string
''
SELECT
Acct_Name AS Name,
Billing_City AS BillingCity,
Locations AS NumberofLocations__c
FROM $
WITH (
-- Either use SRC to point to a file or use inline DATA. Comment out one as needed.
-- Examples:
-- SRC = ''''c:\file_1.csv''''
-- SRC = ''''c:\some*.csv''''
-- SRC = ''''https://abc.com/api/somedata-in-csv''''
DATA = ''''Acct_Name,Billing_City,Locations
Account001,City001,1
Account002,City002,2
Account003,City003,3''''
)''
)
-- Notes:
-- Column aliases in SELECT must match Salesforce target fields.
-- Preview the Account object to verify available fields.
WITH (
Output = 1, -- Capture __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage for each record
-- EnableBulkMode = 1, -- Use Bulk API (recommended for 5,000+ rows)
EnableParallelThreads = 1, -- Use multiple threads for real-time inserts
MaxParallelThreads = 6 -- Set maximum number of threads
)
')
DML - Upsert Lookup Field Value Using External ID Instead of Salesforce ID
This example demonstrates how to set a lookup field value in Salesforce using an external ID rather than the internal Salesforce ID during DML operations such as INSERT, UPDATE, or UPSERT.
Typically, updating a lookup field requires the Salesforce ID of the related record. However, Salesforce also allows referencing a related record using an external ID field. To do this, use the following field name syntax:
[relationship_name.external_id_field_name(child_object_name)]
relationship_name: The API name of the relationship (e.g.,OwnerorYourObject__r).external_id_field_name: A custom field on the related object, marked as External ID.child_object_name(optional): The API name of the related object. If omitted, Salesforce derives it from the relationship name (without the__rsuffix).
Example:
To assign a record owner using a custom external ID on the User object:
Owner.SomeExternalId__c(User)
Owner: The relationship name for the user record.SomeExternalId__c: A custom external ID field in the User object.User: The related (child) object name.
If you’re using the SOURCE(...) clause to read input data and enabling BulkApiMode=1 in the WITH(...) clause, you can omit the child object name. In that case, use the format:
relationship_name.external_id_field_name
Setting a Field to NULL:
To set a lookup or standard field to null, use:
FieldName = null
For example:
AccountId = null
Avoid using:
relation_name.external_id_name(target_table) = null
More Information:
For full details and examples, visit the official guide: ZappySys Docs - External ID in Lookup Fields
-- Upsert record into Salesforce Account object
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([MY_LINKED_SERVER]
, '
UPSERT INTO Account (
Name,
BillingCity,
[Owner.SomeExternalId__c(User)] -- Use external ID field on related Owner (User) object
)
VALUES (
''mycompany name'',
''New York'',
''K100'' -- External ID value of the User (Owner)
)
WITH (
KEY = ''SupplierId__c'', -- External ID field used for UPSERT on Account object
Output = 1 -- Return __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage for result diagnostics
)
')Supported WITH Properties in BULK Mode
When using the ZappySys Salesforce ODBC Driver with BULK mode, you can pass additional options using the WITH clause to customize behavior.
Here are other supported properties commonly used BULK mode:
INSERT INTO Account/UPDATE Account/DELETE FROM Account
SOURCE(...)
WITH(
Output=1 /*Other values can be Output='*' , Output=1 , Output=0 , Output='Col1,Col2...ColN'. When Output option is supplied then error is not thrown but you can capture status and message in __RowStatus and __ErrorMessage output columns*/
,EnableBulkMode=1 --use Job Style Bulk API (uses 10000 rows per batch rather than 200)
--,MaxRowsPerJob=500000 --useful to control memory footprint in driver
--,ConcurrencyMode='Default' /* or 'Parallel' or 'Serial' - Must set BulkApiVersion=2 to use this, Bulk API V1 doesnt support this yet. If you get locking errors then change to Serial*/
--,BulkApiVersion=2 --default is V1
--,IgnoreFieldsIfInputNull=1 --Set this option to True if you wish to ignore fields if input value is NULL. By default target field is set to NULL if input value is NULL.
--,FieldsToSetNullIfInputNull='SomeColum1,SomeColumn5,SomeColumn7' --Comma separated CRM entity field names which you like to set as NULL when input value is NULL. This option is ignored if IgnoreFieldsIfInputNull is not set to True.
--,AssignmentRuleId='xxxxx' --rule id to invoke on value assignment
--,UseDefaultAssignmentRule=1 --sets whether you like to use default rule
--,AllOrNone=1 --If true, any failed records in a call cause all changes for the call to be rolled back. Record changes aren't committed unless all records are processed successfully. The default is false. Some records can be processed successfully while others are marked as failed in the call results.
--,OwnerChangeOptions='option1,option2...optionN' -- use one or more options from below. Use '-n' suffix to disable option execution e.g. TransferOpenActivities-n
-->>> Available owner change options: EnforceNewOwnerHasReadAccess,TransferOpenActivities,TransferNotesAndAttachments,TransferOthersOpenOpportunities,TransferOwnedOpenOpportunities,TransferOwnedClosedOpportunities,TransferOwnedOpenCases,TransferAllOwnedCases,TransferContracts,TransferOrders,TransferContacts,TransferArticleOwnedPublishedVersion,TransferArticleOwnedArchivedVersions,TransferArticleAllVersions,KeepAccountTeam,KeepSalesTeam,KeepSalesTeamGrantCurrentOwnerReadWriteAccess,SendEmail
-->>> For more information visit https://zappysys.com/link/?id=10141
--,AllowFieldTruncation=1 --If true, truncate field values that are too long, which is the behavior in API versions 14.0 and earlier.
--,AllowSaveOnDuplicates=1 --Set to true to save the duplicate record. Set to false to prevent the duplicate record from being saved.
--,EnableParallelThreads=1 --Enables sending Data in multiple threads to speedup. This option is ignored when bulk mode enabled (i.e. EnableBulkMode=1)
--,MaxParallelThreads=6 --Maximum threads to spin off to speedup write operation. This option is ignored when bulk mode enabled (i.e. EnableBulkMode=1)
--,TempStorageMode='Disk' --or 'Memory'. Use this option to overcome OutOfMemory Error if you processing many rows. This option enables how Temp Storage is used for query processing. Available options 'Disk' or 'Memory' (Default is Memory)
)
More Examples and Documentation
For additional examples and detailed guidance on using the ZappySys Salesforce ODBC Driver, visit the official documentation:
Conclusion
In this article we showed you how to connect to Salesforce in SQL Server and integrate data without any coding, saving you time and effort.
We encourage you to download Salesforce Connector for SQL Server and see how easy it is to use it for yourself or your team.
If you have any questions, feel free to contact ZappySys support team. You can also open a live chat immediately by clicking on the chat icon below.
Download Salesforce Connector for SQL Server Documentation