How to integrate OData using PowerShell

Learn how to quickly and efficiently connect OData with PowerShell for smooth data access.
Read and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required. You can do it all using the high-performance OData ODBC Driver for PowerShell (often referred to as the OData Connector). We'll walk you through the entire setup.
Ready to dive in? Download the product to jump right in, or follow the step-by-step guide below to see how it works.
Create data source using OData ODBC Driver
Step-by-step instructions
To get data from OData using PowerShell, we first need to create an ODBC data source. We will later read this data in PowerShell. Perform these steps:
-
Download and install ODBC PowerPack (if you haven't already).
-
Search for
odbcand open the ODBC Data Sources (64-bit):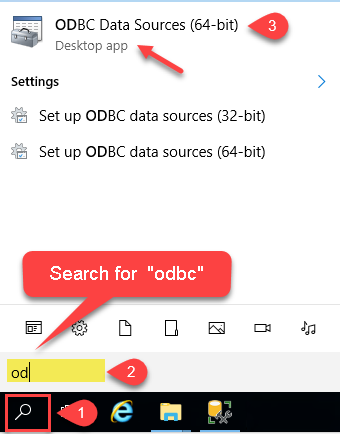
-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on the ZappySys API Driver driver:
ZappySys API Driver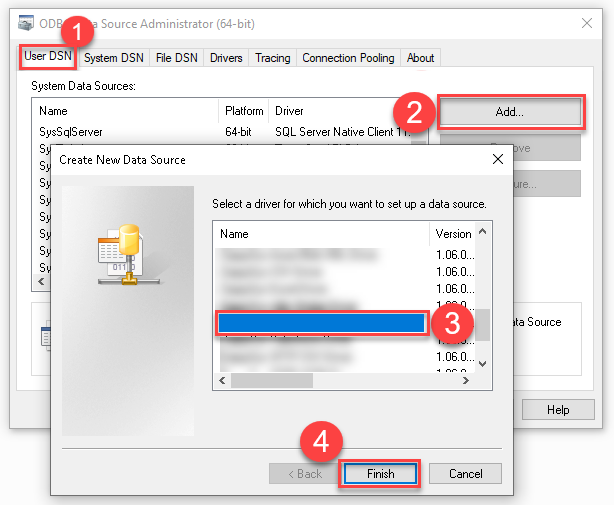
- Create and use a User DSN if the client application runs under a User Account. This is the ideal option at design time (e.g., when developing in Visual Studio). Use it for both types of applications (64-bit and 32-bit).
- Create and use a System DSN if the client application runs under a System Account (e.g., as a Windows Service). This is usually the required option in a production environment. If your Windows Service is a 32-bit application, you must use the 32-bit ODBC Data Source Administrator to configure this
-
When the Configuration window appears give your data source a name if you haven't done that already, then select "OData" from the list of Popular Connectors. If "OData" is not present in the list, then click "Search Online" and download it. Then set the path to the location where you downloaded it. Finally, click Continue >> to proceed with configuring the DSN:
OdataDSNOData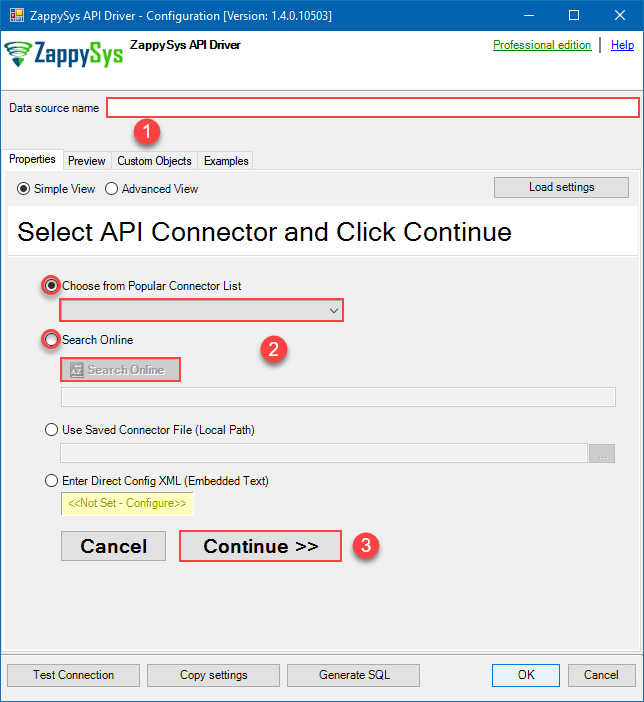
-
Now it's time to configure the Connection Manager. Select Authentication Type, e.g. Token Authentication. Then select API Base URL (in most cases, the default one is the right one). More info is available in the Authentication section.
OData authentication
No instructions available.
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
No Authentication [Http] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
OdataDSNODataNo Authentication [Http]https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svcOptional Parameters RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True IgnoreSSLCertificateErrors SslVersion 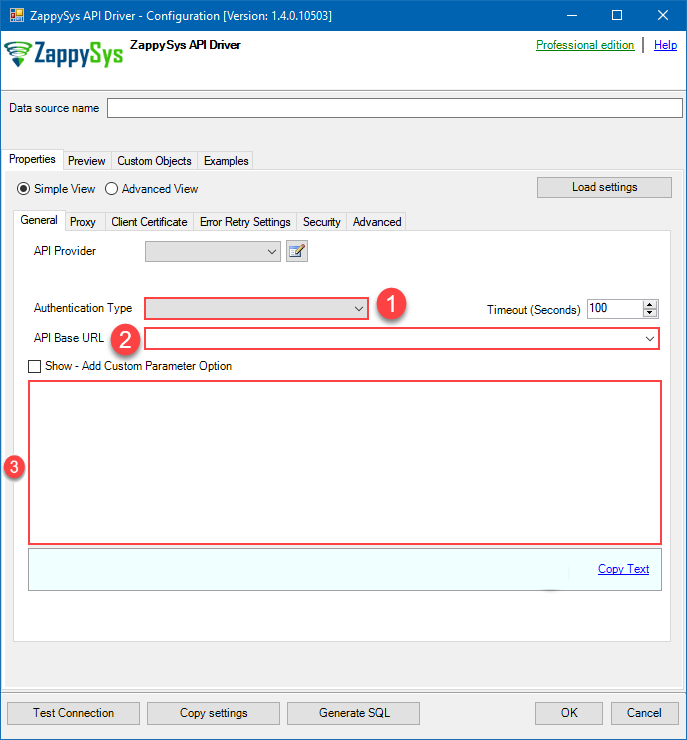
OData authentication
No instructions available.
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
Windows Authentication [Http] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
OdataDSNODataWindows Authentication [Http]https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svcThere are no parameters to configure. 
OData authentication
No instructions available.
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
Basic Authentication [Http] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
OdataDSNODataBasic Authentication [Http]https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svcRequired Parameters UserName Fill-in the parameter... Password Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True IgnoreSSLCertificateErrors SslVersion 
OData authentication
No instructions available.
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
NTLM Authentication [Http] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
OdataDSNODataNTLM Authentication [Http]https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svcRequired Parameters UserName (i.e. Domain\UserName) Fill-in the parameter... Password Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True IgnoreSSLCertificateErrors SslVersion 
OData authentication
No instructions available.
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
Token Authentication [Http] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
OdataDSNODataToken Authentication [Http]https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svcRequired Parameters Token Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters AuthScheme Bearer AuthHeader Authorization RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True IgnoreSSLCertificateErrors SslVersion 
OData authentication
No instructions available.
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
OAuth Connection for OData API [OAuth] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Press Generate Token button to generate the tokens.
- Finally, hit OK button:
OdataDSNODataOAuth Connection for OData API [OAuth]https://services.odata.org/V3/Northwind/Northwind.svcOptional Parameters GrantType Default OAuthVersion Default ClientId ClientSecret UserName Password Scope AuthUrl https://some-domain.com/api/auth TokenUrl https://some-domain.com/api/token ReturnUrl https://zappysys.com/oauth ExtraAttributesForTokenRequest ExtraAttributesForAuthRequest DoNotIncludeCredentialsInHeader DoNotIncludeCredentialsInBody RenewBeforeSec ExtraHeaders (e.g. x-hdr1:AAA||x-hdr2:BBB) ContentType EnableCodeVerifier RemoveAuthHeader CustomAuthHeader CustomTokenPrefix RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True IgnoreSSLCertificateErrors SslVersion 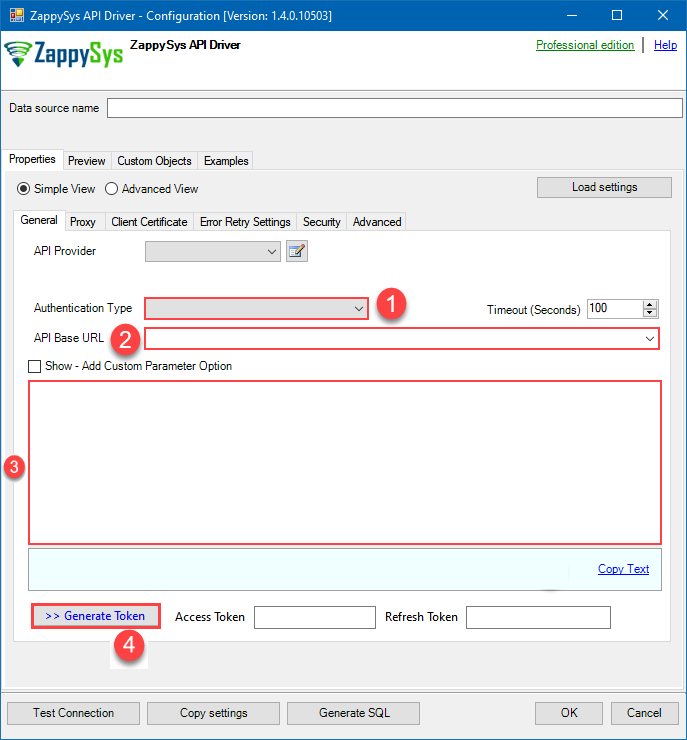
-
Set Authentication Type to
-
Once the data source connection has been configured, it's time to configure the SQL query. Select the Preview tab and then click Query Builder button to configure the SQL query:
 ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN
ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN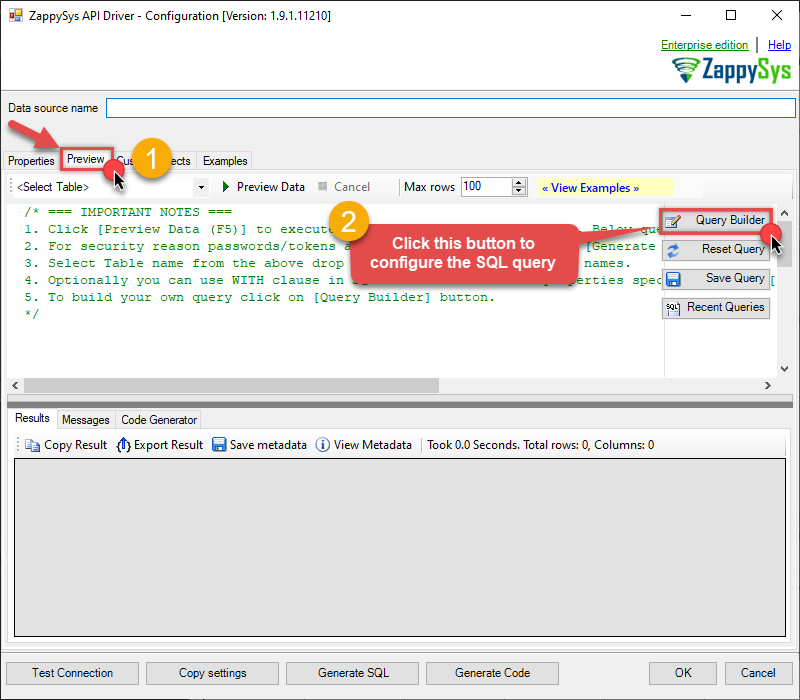
-
Start by selecting the Table or Endpoint you are interested in and then configure the parameters. This will generate a query that we will use in PowerShell to retrieve data from OData. Hit OK button to use this query in the next step.
SELECT * FROM Customers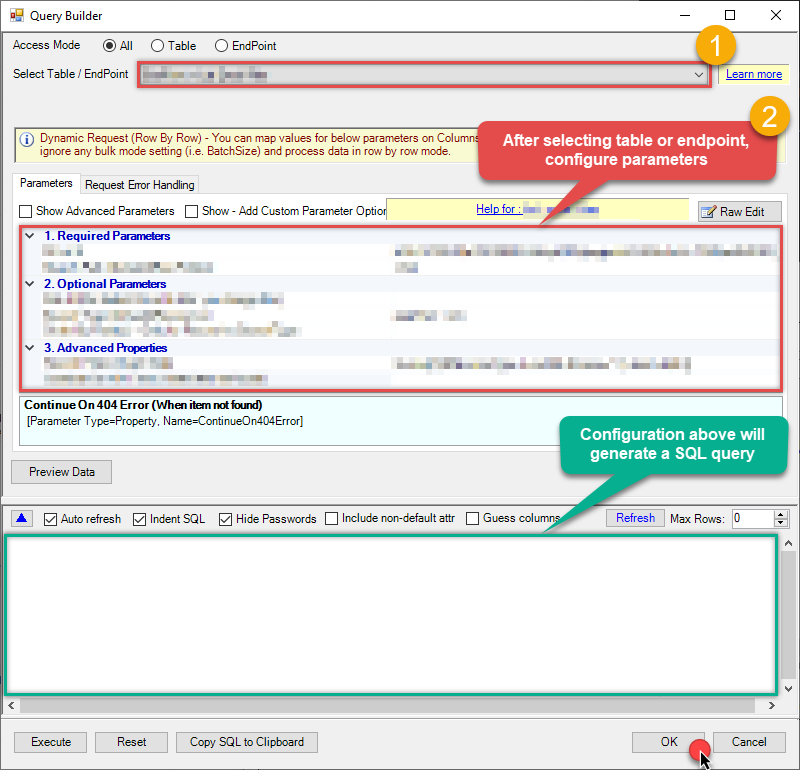 Some parameters configured in this window will be passed to the OData API, e.g. filtering parameters. It means that filtering will be done on the server side (instead of the client side), enabling you to get only the meaningful data
Some parameters configured in this window will be passed to the OData API, e.g. filtering parameters. It means that filtering will be done on the server side (instead of the client side), enabling you to get only the meaningful datamuch faster . -
Now hit Preview Data button to preview the data using the generated SQL query. If you are satisfied with the result, use this query in PowerShell:
 ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN
ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSNSELECT * FROM Customers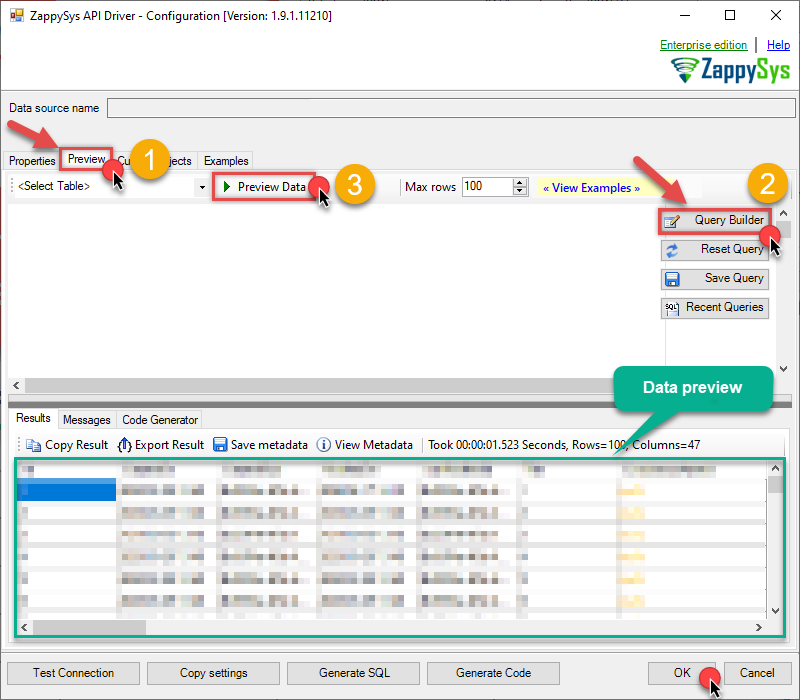 You can also access data quickly from the tables dropdown by selecting <Select table>.A
You can also access data quickly from the tables dropdown by selecting <Select table>.AWHEREclause,LIMITkeyword will be performed on the client side, meaning that thewhole result set will be retrieved from the OData API first, and only then the filtering will be applied to the data. If possible, it is recommended to use parameters in Query Builder to filter the data on the server side (in OData servers). -
Click OK to finish creating the data source.
Video Tutorial
Read OData data in PowerShell
Sometimes, you need to quickly access and work with your OData data in PowerShell. Whether you need a quick data overview or the complete dataset, this article will guide you through the process. Here are some common scenarios:
Viewing data in a terminal- Quickly peek at OData data
- Monitor data constantly in your console
- Export data to a CSV file so that it can be sliced and diced in Excel
- Export data to a JSON file so that it can ingested by other processes
- Export data to an HTML file for user-friendly view and easy sharing
- Create a schedule to make it an automatic process
- Store data internally for analysis or for further ETL processes
- Create a schedule to make it an automatic process
- Integrate data with other systems via external APIs
In this article, we will delve deeper into how to quickly view the data in PowerShell terminal and how to save it to a file. But let's stop talking and get started!
Reading individual fields
-
Open your favorite PowerShell IDE (we are using Visual Studio Code).
-
Use this code snippet to read the data using
OdataDSNdata source:"DSN=OdataDSN"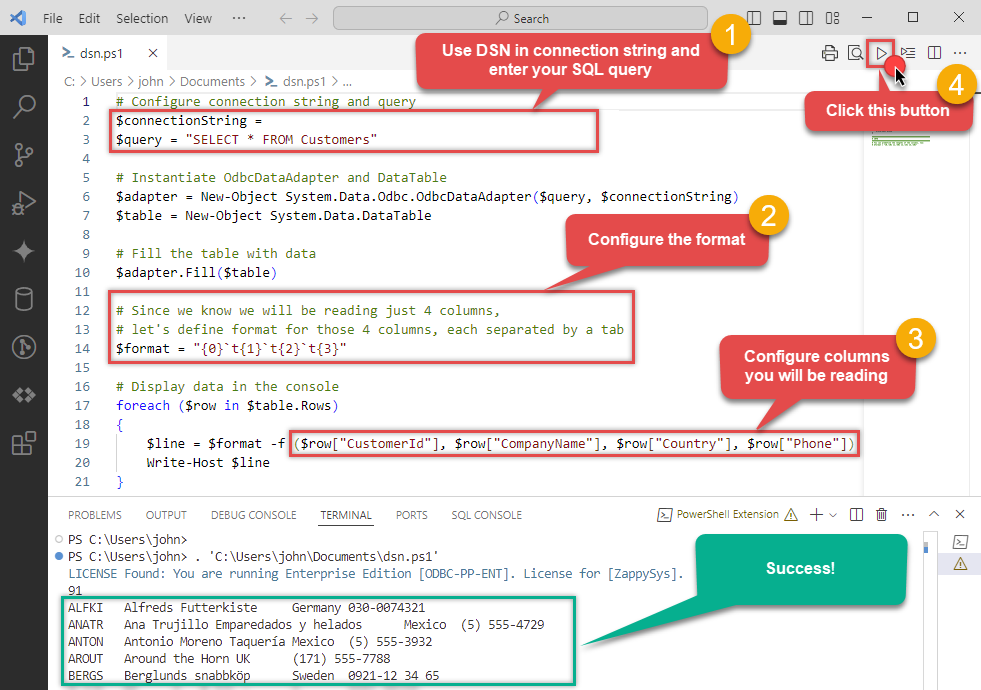
For your convenience, here is the whole PowerShell script:
# Configure connection string and query $connectionString = "DSN=OdataDSN" $query = "SELECT * FROM Customers" # Instantiate OdbcDataAdapter and DataTable $adapter = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcDataAdapter($query, $connectionString) $table = New-Object System.Data.DataTable # Fill the table with data $adapter.Fill($table) # Since we know we will be reading just 4 columns, let's define format for those 4 columns, each separated by a tab $format = "{0}`t{1}`t{2}`t{3}" # Display data in the console foreach ($row in $table.Rows) { # Construct line based on the format and individual OData fields $line = $format -f ($row["CustomerId"], $row["CompanyName"], $row["Country"], $row["Phone"]) Write-Host $line }Access specific OData table field using this code snippet:
You will find more info on how to manipulate$field = $row["ColumnName"]DataTable.Rowsproperty in Microsoft .NET reference.For demonstration purposes we are using sample tables which may not be available in OData. -
To read values in a console, save the script to a file and then execute this command inside PowerShell terminal:
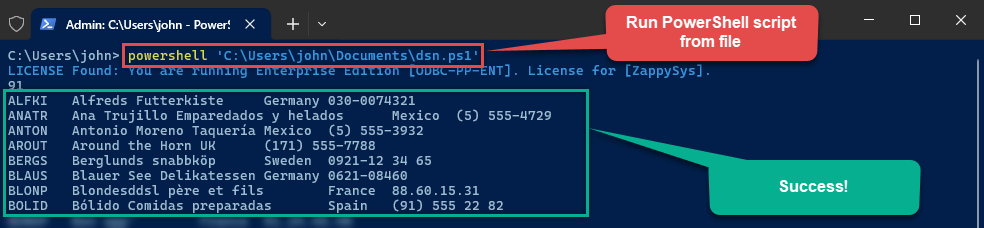 You can also use even a simpler command inside the terminal, e.g.:
You can also use even a simpler command inside the terminal, e.g.:. 'C:\Users\john\Documents\dsn.ps1'
Retrieving all fields
However, there might be case, when you want to retrieve all columns of a query. Here is how you do it:
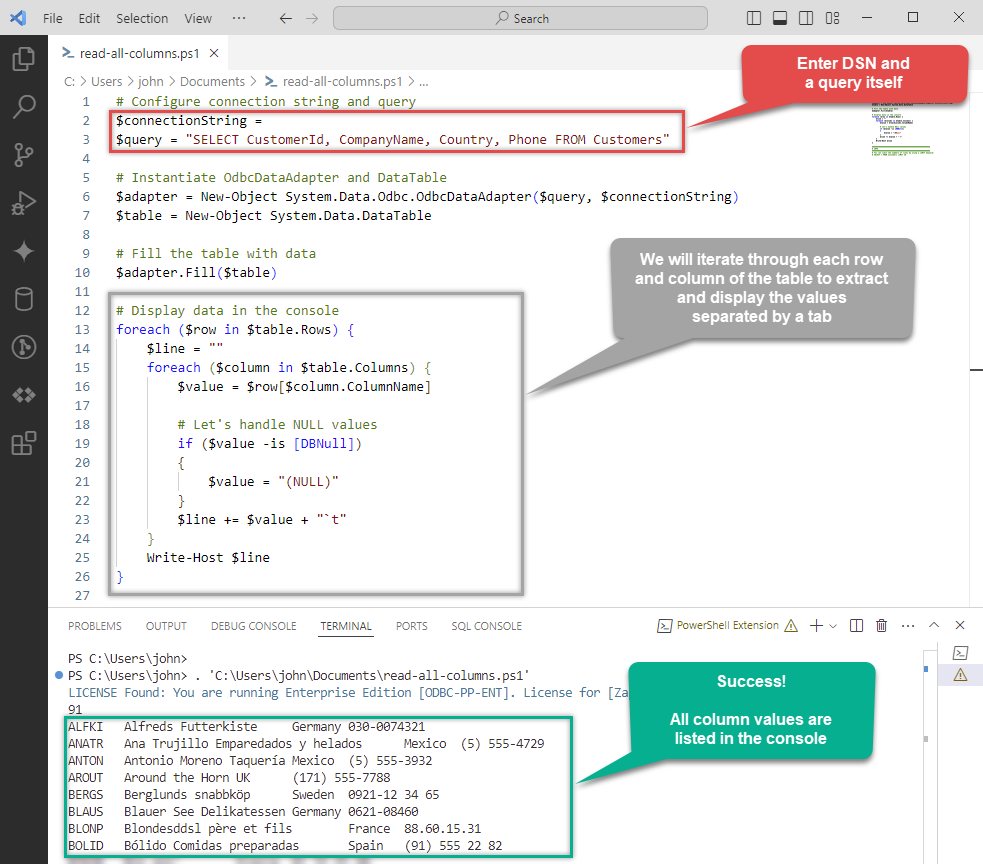
Again, for your convenience, here is the whole PowerShell script:
# Configure connection string and query
$connectionString = "DSN=OdataDSN"
$query = "SELECT CustomerId, CompanyName, Country, Phone FROM Customers"
# Instantiate OdbcDataAdapter and DataTable
$adapter = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcDataAdapter($query, $connectionString)
$table = New-Object System.Data.DataTable
# Fill the table with data
$adapter.Fill($table)
# Display data in the console
foreach ($row in $table.Rows) {
$line = ""
foreach ($column in $table.Columns) {
$value = $row[$column.ColumnName]
# Let's handle NULL values
if ($value -is [DBNull])
{
$value = "(NULL)"
}
$line += $value + "`t"
}
Write-Host $line
}
LIMIT keyword in the query, e.g.:
SELECT * FROM Customers LIMIT 10Using a full ODBC connection string
In the previous steps we used a very short format of ODBC connection string - a DSN. Yet sometimes you don't want a dependency on an ODBC data source (and an extra step). In those times, you can define a full connection string and skip creating an ODBC data source entirely. Let's see below how to accomplish that in the below steps:
-
Open ODBC data source configuration and click Copy settings:
 ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN
ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN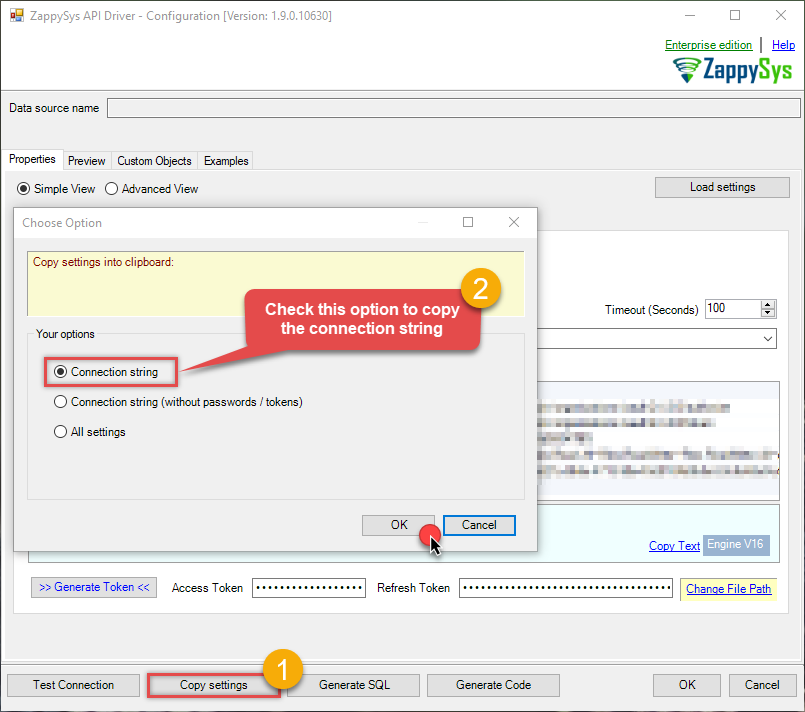
-
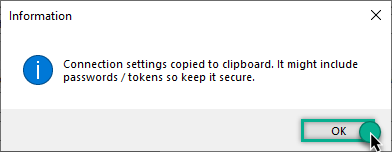
The window opens, telling us the connection string was successfully copied to the clipboard:
-
Then just paste the connection string into your script:
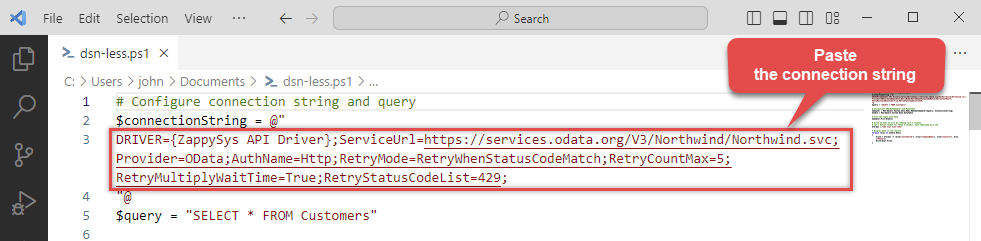
- You are good to go! The script will execute the same way as using a DSN.
Have in mind that a full connection string has length limitations.
Proceed to the next step to find out the details.
Handling limitations of using a full connection string
Despite using a full ODBC connection string may be very convenient it comes with a limitation: it's length is limited to 1024 symbols (or sometimes more). It usually happens when API provider generates a very long Refresh Token when OAuth is at play. If you are using such a long ODBC connection string, you may get this error:
"Connection string exceeds maximum allowed length of 1024"But there is a solution to this by storing the full connection string in a file. Follow the steps below to achieve this:
- Open your ODBC data source.
- Click Copy settings button to copy a full connection string (see the previous section on how to accomplish that).
- Then create a new file, let's say, in C:\temp\odbc-connection-string.txt.
- Continue by pasting the copied connection string into a newly created file and save it.
-
Finally, the last step! Just construct a shorter ODBC connection string using this format:
DRIVER={ZappySys API Driver};SettingsFile=C:\temp\odbc-connection-string.txt - Our troubles are over! Now you should be able to use this connection string in PowerShell with no problems.
Write OData data to a file in PowerShell
Save data to a CSV file
Export data to a CSV file so that it can be sliced and diced in Excel:
# Configure connection string and query
$connectionString = "DSN=OdataDSN"
$query = "SELECT * FROM Customers"
# Instantiate OdbcDataAdapter and DataTable
$adapter = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcDataAdapter($query, $connectionString)
$table = New-Object System.Data.DataTable
# Fill the table with data
$adapter.Fill($table)
# Export table data to a file
$table | ConvertTo-Csv -NoTypeInformation -Delimiter "`t" | Out-File "C:\Users\john\saved-data.csv" -ForceSave data to a JSON file
Export data to a JSON file so that it can ingested by other processes (use the above script, but change this part):
# Export table data to a file
$table | ConvertTo-Json | Out-File "C:\Users\john\saved-data.json" -ForceSave data to an HTML file
Export data to an HTML file for user-friendly view and easy sharing (use the above script, but change this part):
# Export table data to a file
$table | ConvertTo-Html | Out-File "C:\Users\john\saved-data.html" -ForceConvertTo-Csv, ConvertTo-Json, and ConvertTo-Html for other data manipulation scenarios.
Optional: Centralized data access via ZappySys Data Gateway
In some situations, you may need to provide OData data access to multiple users or services. Configuring the data source on a Data Gateway creates a single, centralized connection point for this purpose.
This configuration provides two primary advantages:
-
Centralized data access
The data source is configured once on the gateway, eliminating the need to set it up individually on each user's machine or application. This significantly simplifies the management process.
-
Centralized access control
Since all connections route through the gateway, access can be governed or revoked from a single location for all users.
| Data Gateway |
Local ODBC
data source
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Simple configuration | ||
| Installation | Single machine | Per machine |
| Connectivity | Local and remote | Local only |
| Connections limit | Limited by License | Unlimited |
| Central data access | ||
| Central access control | ||
| More flexible cost |
To achieve this, you must first create a data source in the Data Gateway (server-side) and then create an ODBC data source in PowerShell (client-side) to connect to it.
Let's not wait and get going!
Create OData data source in the gateway
In this section we will create a data source for OData in the Data Gateway. Let's follow these steps to accomplish that:
-
Search for
gatewayin the Windows Start Menu and open ZappySys Data Gateway Configuration:
-
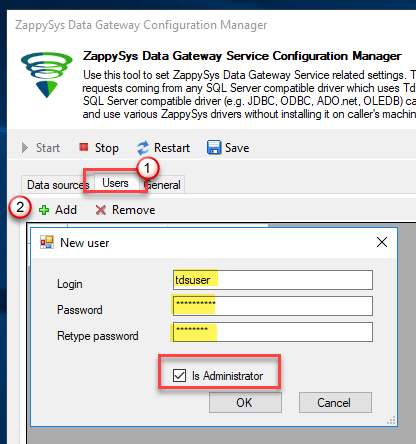
Go to the Users tab and follow these steps to add a Data Gateway user:
- Click the Add button
-
In the Login field enter a username, e.g.,
john - Then enter a Password
- Check the Is Administrator checkbox
- Click OK to save
-
Now we are ready to add a data source:
- Click the Add button
- Give the Data source a name (have it handy for later)
- Then select Native - ZappySys API Driver
- Finally, click OK
OdataDSNZappySys API Driver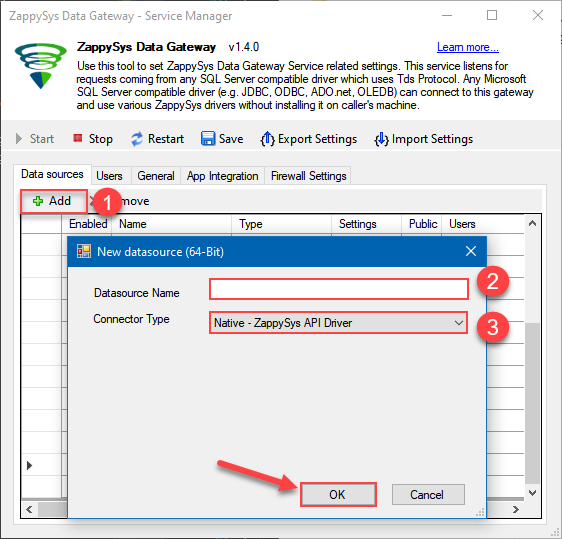
-
When the ZappySys API Driver configuration window opens, go back to ODBC Data Source Administrator where you already have the OData ODBC data source created and configured, and follow these steps on how to Import data source configuration into the Gateway:
-
Open ODBC data source configuration and click Copy settings:
 ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN
ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN
-
The window opens, telling us the connection string was successfully copied to the clipboard:

-
Then go to Data Gateway configuration and in data source configuration window click Load settings:
OdataDSN ZappySys API Driver - Configuration [Version: 2.0.1.10418]ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN
ZappySys API Driver - Configuration [Version: 2.0.1.10418]ZappySys API Driver - ODataRead and write OData API data effortlessly. Query, integrate, and manage entities and feeds — almost no coding required.OdataDSN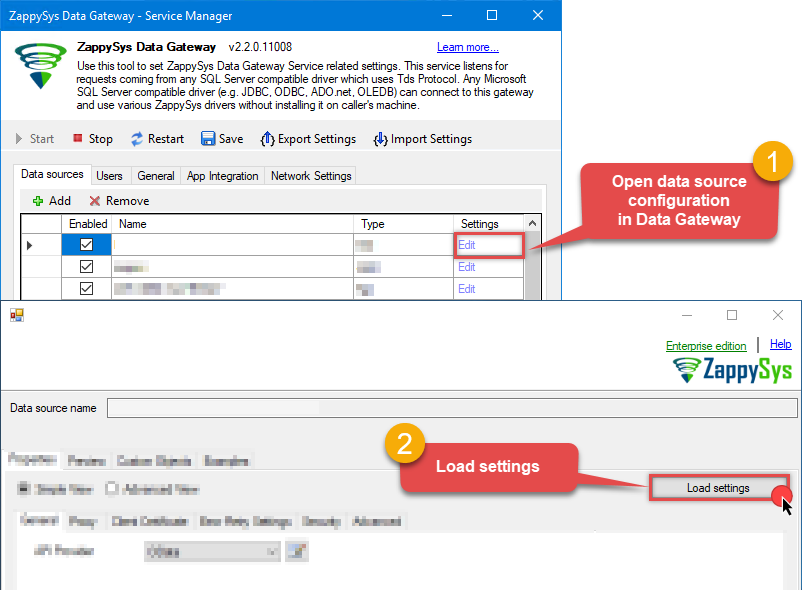
-
Once a window opens, just paste the settings by pressing
CTRL+Vor by clicking right mouse button and then Paste option.
-
Open ODBC data source configuration and click Copy settings:
-
Once done, go to the Network Settings tab and Add a firewall rule for inbound traffic:
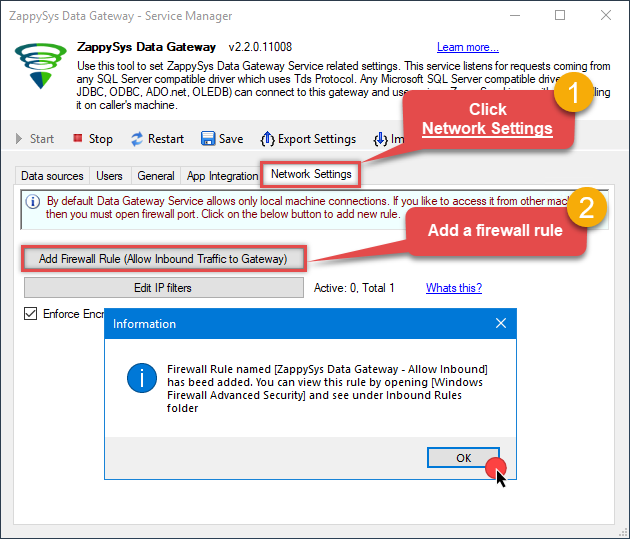
- This will initially allow all inbound traffic.
- Click Edit IP filters to restrict access to specific IP addresses or ranges.
-
Crucial Step: After creating or modifying the data source, you must:
- Click the Save button to persist your changes.
- Hit Yes when prompted to restart the Data Gateway service.
This ensures all changes are properly applied:
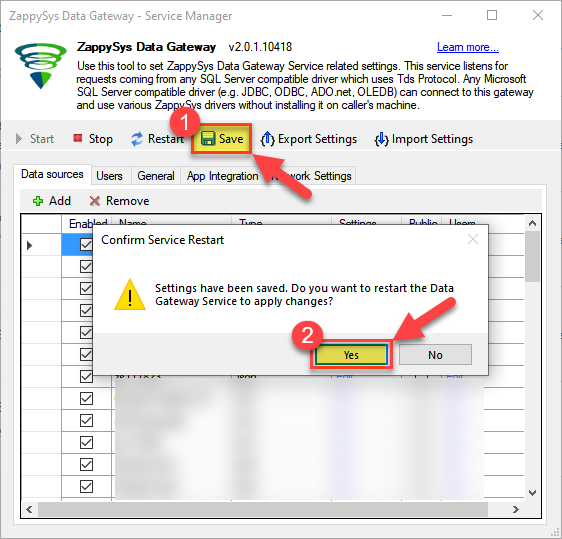 Skipping this step may cause the new settings to fail, preventing you from connecting to the data source.
Skipping this step may cause the new settings to fail, preventing you from connecting to the data source.
Create ODBC data source to connect to the gateway
In this part we will create an ODBC data source to connect to the ZappySys Data Gateway from PowerShell. To achieve that, let's perform these steps:
-
Search for
odbcand open the ODBC Data Sources (64-bit):
-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on the ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver:
ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server If you don't see the ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version.
If you don't see the ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version. -
Then set a Name for the data source (e.g.
Gateway) and the address of the Data Gateway:ZappySysGatewayDSNlocalhost,5000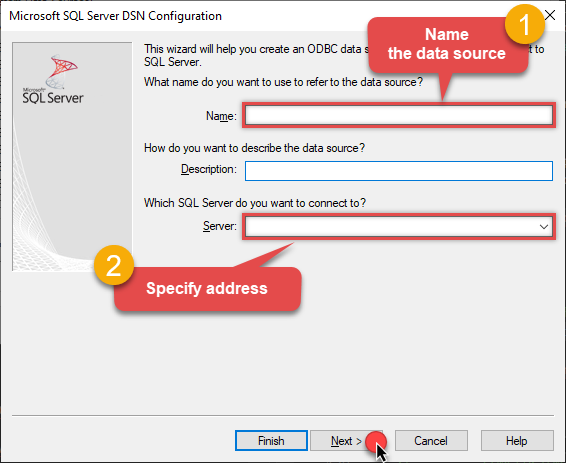 Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.
Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.localhost,5000. -
Proceed with the authentication part:
- Select SQL Server authentication
-
In the Login ID field enter the user name you created in the Data Gateway, e.g.,
john - Set Password to the one you configured in the Data Gateway
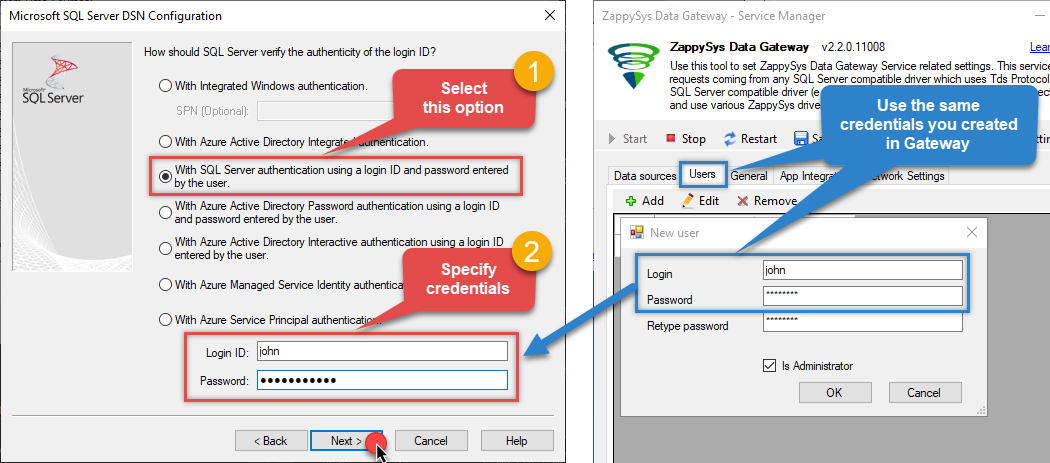
-
Then set the default database property to
OdataDSN(the one we used in the Data Gateway):OdataDSNOdataDSN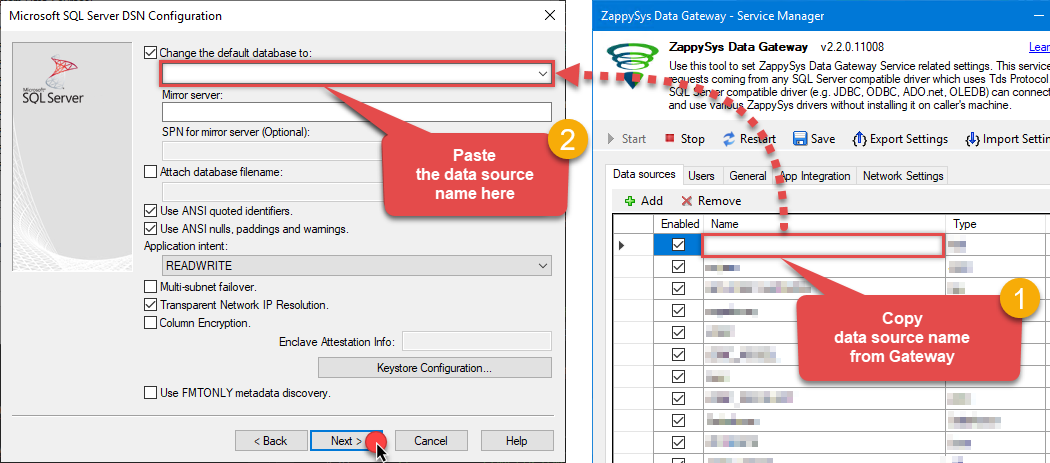 Make sure to type the data source name manually or copy/paste it directly into the field. Using the dropdown might fail because the Trust server certificate option is not enabled yet (next step).
Make sure to type the data source name manually or copy/paste it directly into the field. Using the dropdown might fail because the Trust server certificate option is not enabled yet (next step). -
Continue by checking the Trust server certificate option:
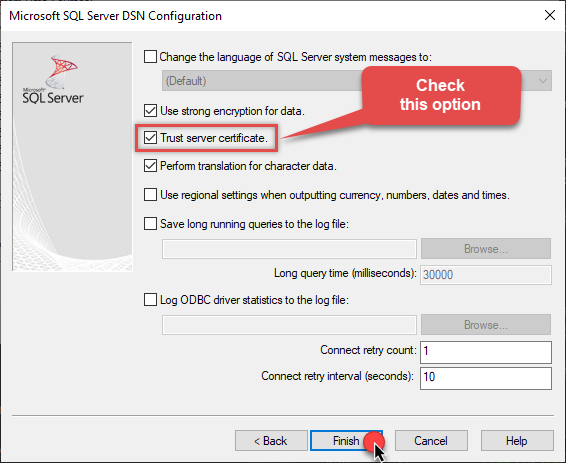
-
Once you do that, test the connection:
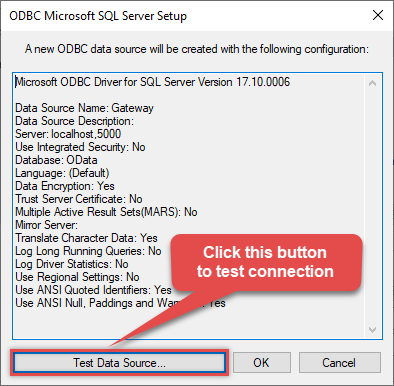
-
If the connection is successful, everything is good:
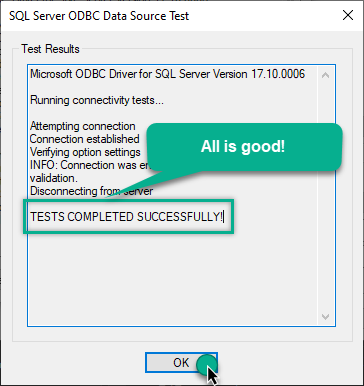
-
Done!
We are ready to move to the final step. Let's do it!
Access data in PowerShell via the gateway
Finally, we are ready to read data from OData in PowerShell via the Data Gateway. Follow these final steps:
-
Go back to PowerShell.
-
Use this code snippet to read the data using
ZappySysGatewayDSNdata source:"DSN=ZappySysGatewayDSN"
For your convenience, here is the whole PowerShell script:
# Configure connection string and query $connectionString = "DSN=ZappySysGatewayDSN" $query = "SELECT * FROM Customers" # Instantiate OdbcDataAdapter and DataTable $adapter = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcDataAdapter($query, $connectionString) $table = New-Object System.Data.DataTable # Fill the table with data $adapter.Fill($table) # Since we know we will be reading just 4 columns, let's define format for those 4 columns, each separated by a tab $format = "{0}`t{1}`t{2}`t{3}" # Display data in the console foreach ($row in $table.Rows) { # Construct line based on the format and individual OData fields $line = $format -f ($row["CustomerId"], $row["CompanyName"], $row["Country"], $row["Phone"]) Write-Host $line }Access specific OData table field using this code snippet:
You will find more info on how to manipulate$field = $row["ColumnName"]DataTable.Rowsproperty in Microsoft .NET reference.For demonstration purposes we are using sample tables which may not be available in OData. -
Read the data the same way we discussed at the beginning of this article.
-
That's it!
Now you can connect to OData data in PowerShell via the Data Gateway.
john and your password.
Supported OData Connector actions
Got a specific use case in mind? We've mapped out exactly how to perform a variety of essential OData operations directly in PowerShell, so you don't have to figure out the setup from scratch. Check out the step-by-step guides below:
- Generic Read Data (JSON API)
- Generic Read Data (XML API)
- List Columns
- List Tables
- List Tables (JSON API)
- List Tables (XML API)
- Read [Dynamic Endpoint]
- Make Generic REST API Request
- Make Generic REST API Request (Bulk Write)
Conclusion
In this article we showed you how to connect to OData in PowerShell and integrate data without writing complex code — all of this was powered by OData ODBC Driver.
Download ODBC PowerPack now or ping us via chat if you have any questions or are looking for a specific feature (you can also reach out to us by submitting a ticket):