Google BigQuery Connector for MS Access
Read / write Google BigQuery data inside your app without coding using easy to use high performance API Connector
In this article you will learn how to quickly and efficiently integrate Google BigQuery data in MS Access without coding. We will use high-performance Google BigQuery Connector to easily connect to Google BigQuery and then access the data inside MS Access.
Let's follow the steps below to see how we can accomplish that!
Google BigQuery Connector for MS Access is based on ZappySys API Driver which is part of ODBC PowerPack. It is a collection of high-performance ODBC drivers that enable you to integrate data in SQL Server, SSIS, a programming language, or any other ODBC-compatible application. ODBC PowerPack supports various file formats, sources and destinations, including REST/SOAP API, SFTP/FTP, storage services, and plain files, to mention a few.
Create ODBC Data Source (DSN) based on ZappySys API Driver
Step-by-step instructions
To get data from Google BigQuery using MS Access we first need to create a DSN (Data Source) which will access data from Google BigQuery. We will later be able to read data using MS Access. Perform these steps:
-
Download and install ODBC PowerPack.
-
Open ODBC Data Sources (x64):
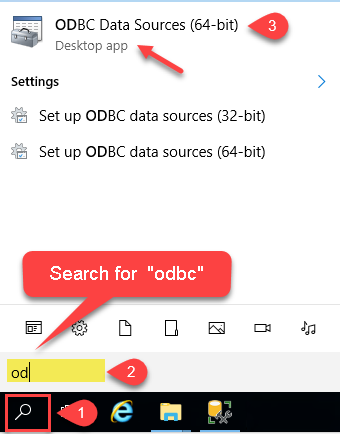
-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on ZappySys API Driver:
ZappySys API Driver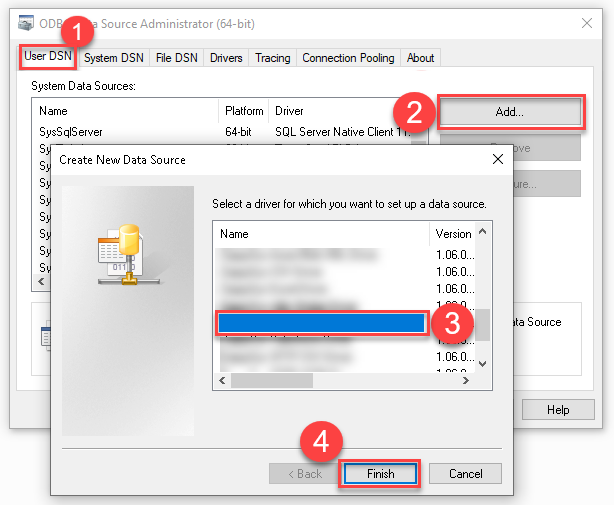
-
Create and use User DSN
if the client application is run under a User Account.
This is an ideal option
in design-time , when developing a solution, e.g. in Visual Studio 2019. Use it for both type of applications - 64-bit and 32-bit. -
Create and use System DSN
if the client application is launched under a System Account, e.g. as a Windows Service.
Usually, this is an ideal option to use
in a production environment . Use ODBC Data Source Administrator (32-bit), instead of 64-bit version, if Windows Service is a 32-bit application.
-
Create and use User DSN
if the client application is run under a User Account.
This is an ideal option
-
When the Configuration window appears give your data source a name if you haven't done that already, then select "Google BigQuery" from the list of Popular Connectors. If "Google BigQuery" is not present in the list, then click "Search Online" and download it. Then set the path to the location where you downloaded it. Finally, click Continue >> to proceed with configuring the DSN:
GoogleBigqueryDSNGoogle BigQuery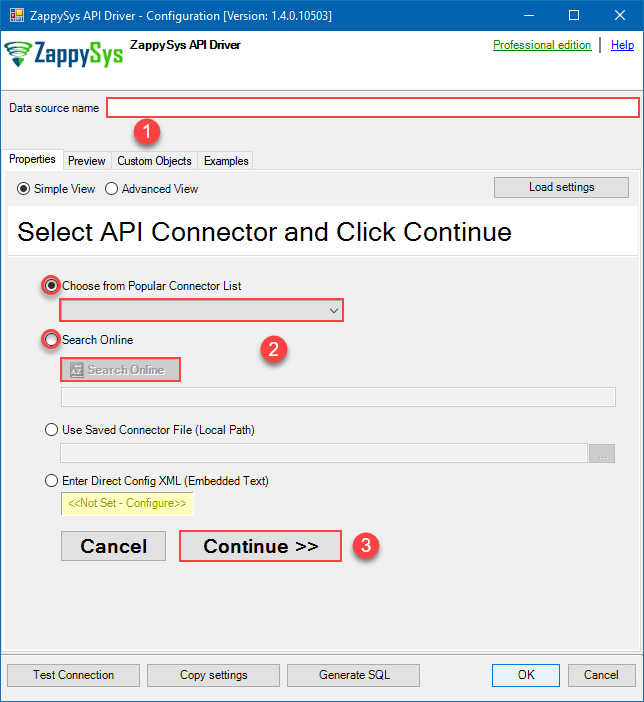
-
Now it's time to configure the Connection Manager. Select Authentication Type, e.g. Token Authentication. Then select API Base URL (in most cases, the default one is the right one). More info is available in the Authentication section.
Google BigQuery authentication
User accounts represent a developer, administrator, or any other person who interacts with Google APIs and services. User accounts are managed as Google Accounts, either with Google Workspace or Cloud Identity. They can also be user accounts that are managed by a third-party identity provider and federated with Workforce Identity Federation. [API reference]
Follow these steps on how to create Client Credentials (User Account principle) to authenticate and access BigQuery API in SSIS package or ODBC data source:
WARNING: If you are planning to automate processes, we recommend that you use a Service Account authentication method. In case, you still need to use User Account, then make sure you use a system/generic account (e.g.automation@my-company.com). When you use a personal account which is tied to a specific employee profile and that employee leaves the company, the token may become invalid and any automated processes using that token will start to fail.Step-1: Create project
This step is optional, if you already have a project in Google Cloud and can use it. However, if you don't, proceed with these simple steps to create one:
-
First of all, go to Google API Console.
-
Then click Select a project button and then click NEW PROJECT button:
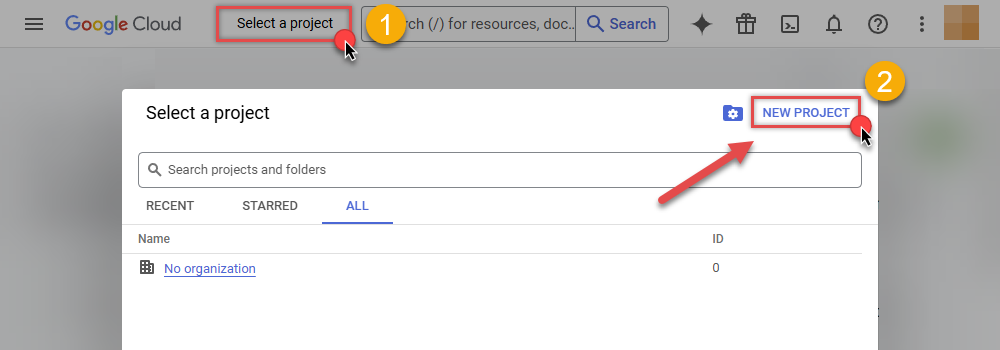
-
Name your project and click CREATE button:
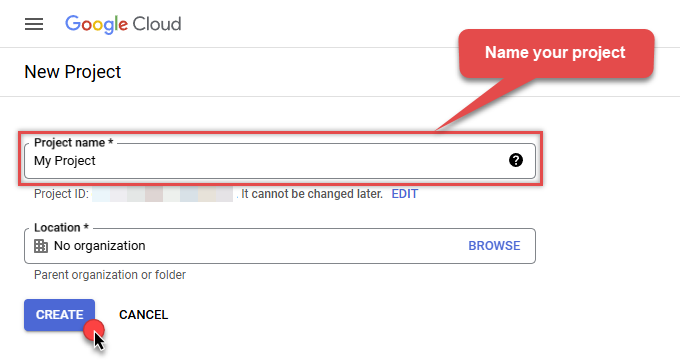
-
Wait until the project is created:
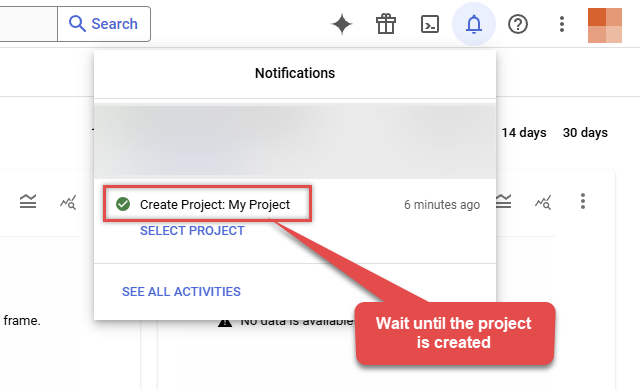
- Done! Let's proceed to the next step.
Step-2: Enable Google Cloud APIs
In this step we will enable BigQuery API and Cloud Resource Manager API:
-
Select your project on the top bar:
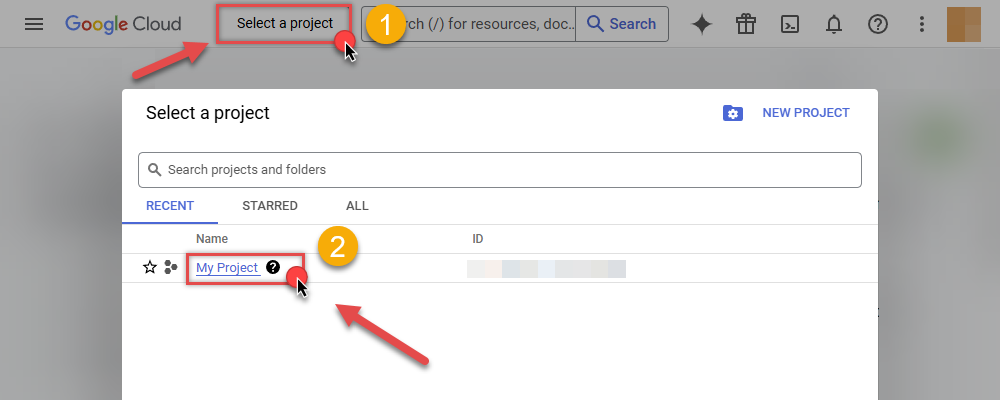
-
Then click the "hamburger" icon on the top left and access APIs & Services:
-
Now let's enable several APIs by clicking ENABLE APIS AND SERVICES button:
-
In the search bar search for
bigquery apiand then locate and select BigQuery API:
-
If BigQuery API is not enabled, enable it:
-
Then repeat the step and enable Cloud Resource Manager API as well:
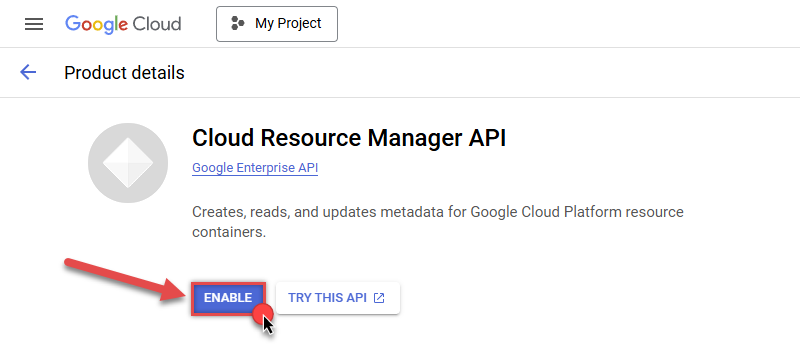
- Done! Let's proceed to the next step.
Step-3: Create OAuth application
-
First of all, click the "hamburger" icon on the top left and then hit VIEW ALL PRODUCTS:
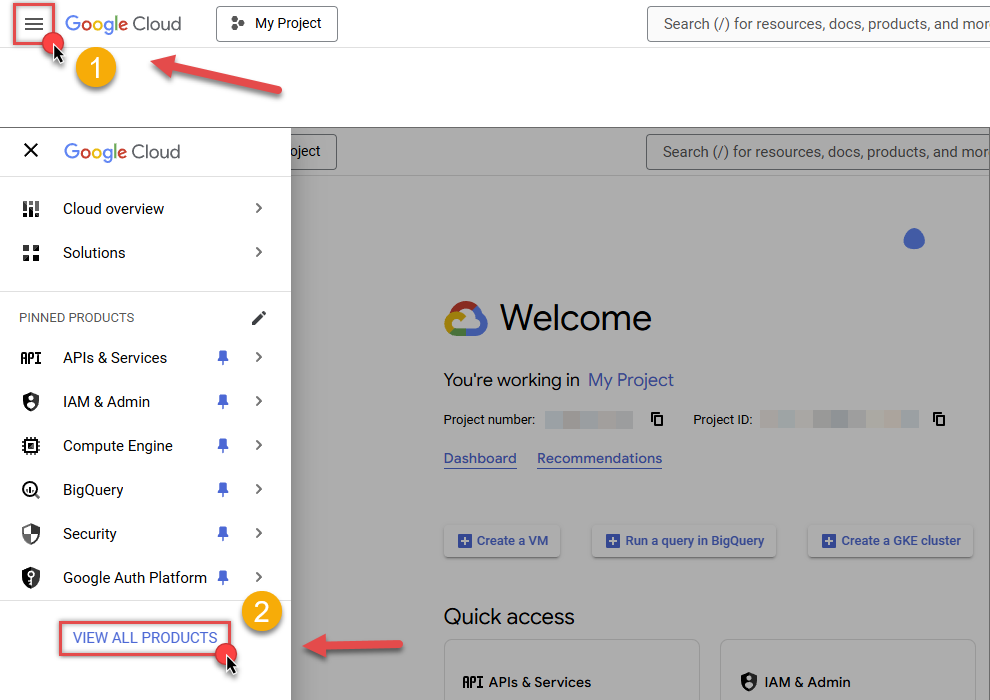
-
Then access Google Auth Platform to start creating an OAuth application:
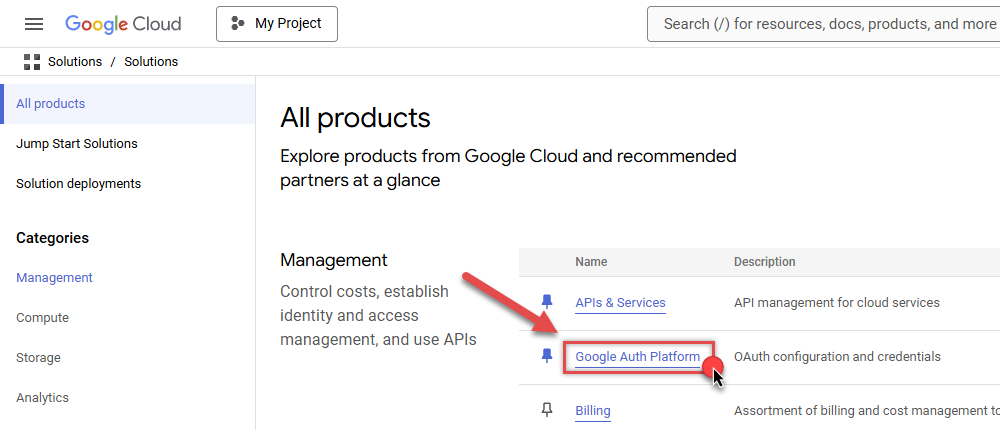
-
Start by pressing GET STARTED button:
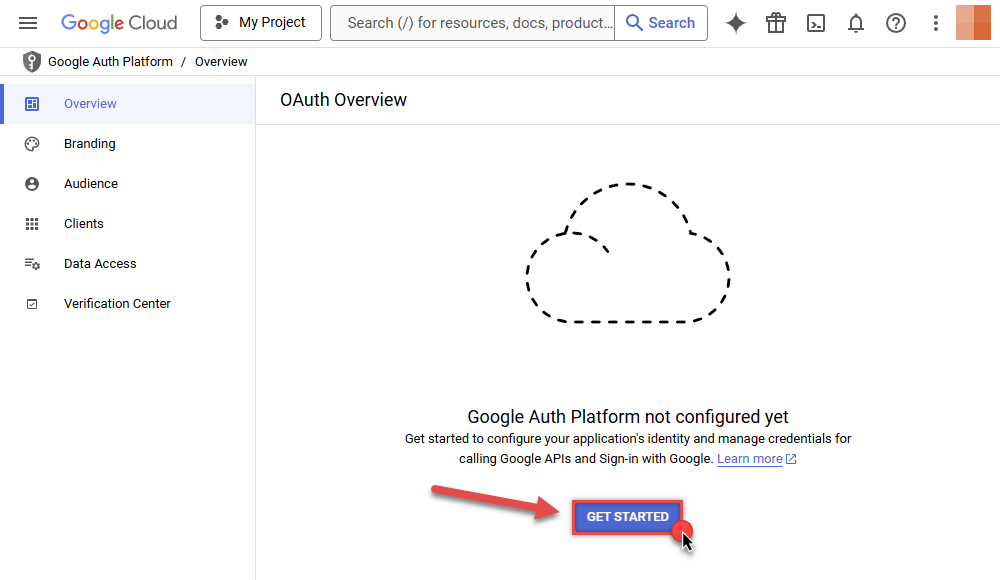
-
Next, continue by filling in App name and User support email fields:
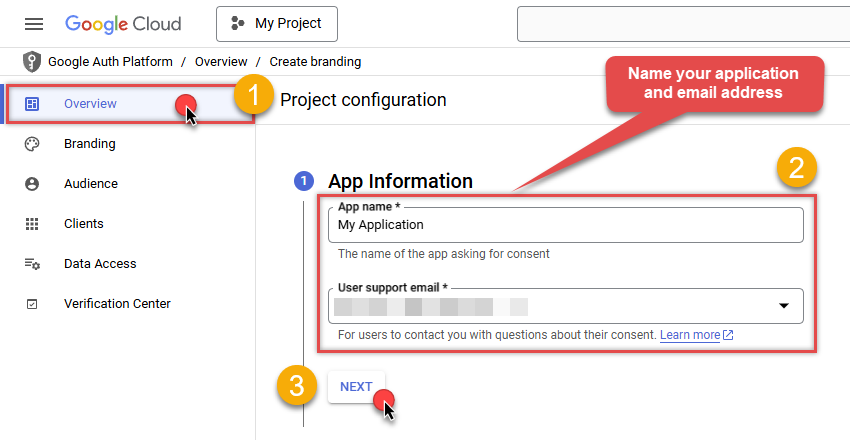
-
Choose Internal option, if it's enabled, otherwise select External:
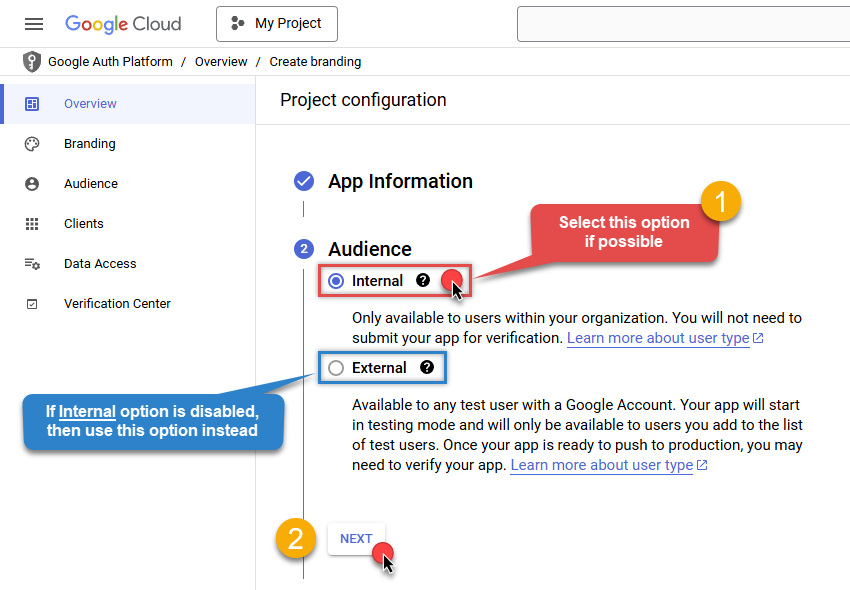
-
Optional step if you used
Internaloption in the previous step. Nevertheless, if you had to useExternaloption, then click ADD USERS to add a user: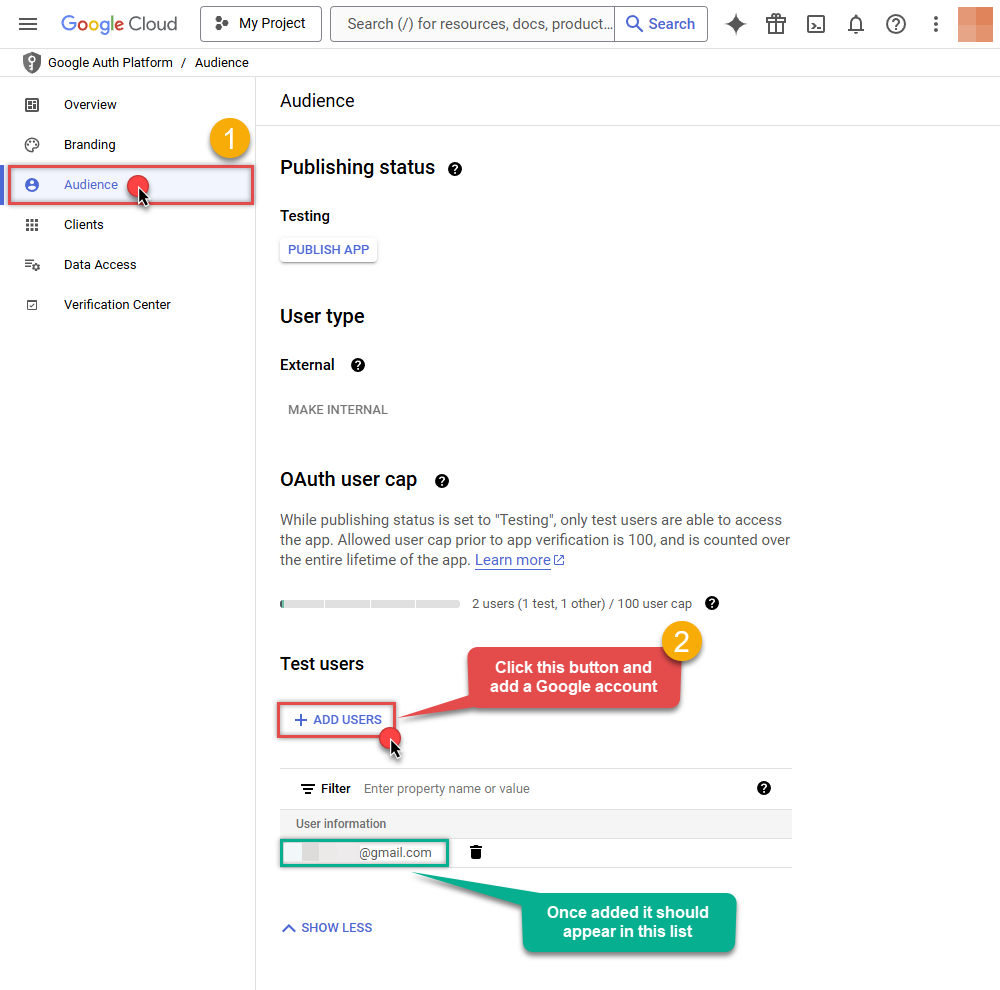
-
Then add your contact Email address:
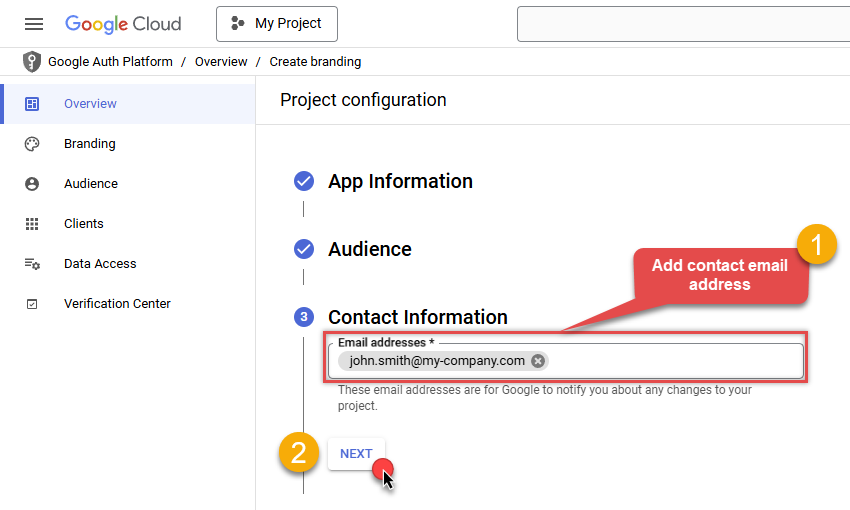
-
Finally, check the checkbox and click CREATE button:
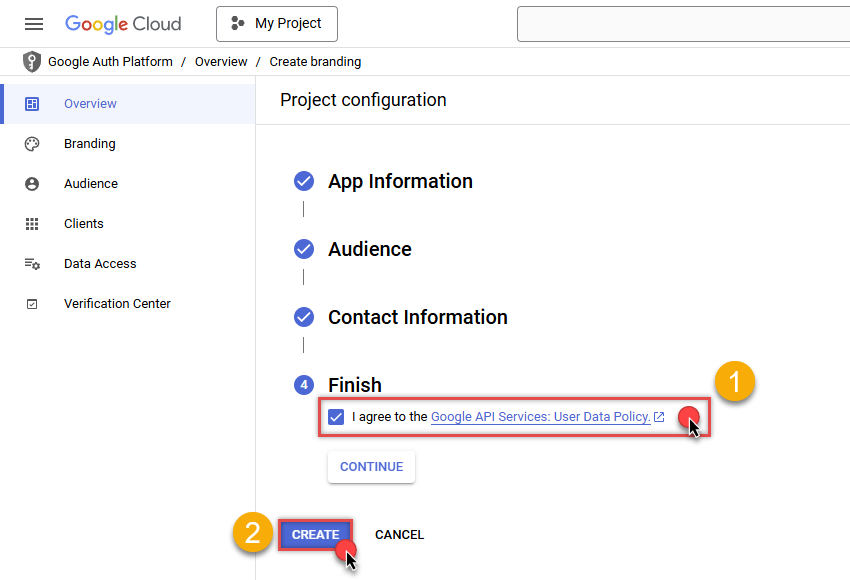
- Done! Let's create Client Credentials in the next step.
Step-4: Create Client Credentials
-
In Google Auth Platform, select Clients menu item and click CREATE CLIENT button:
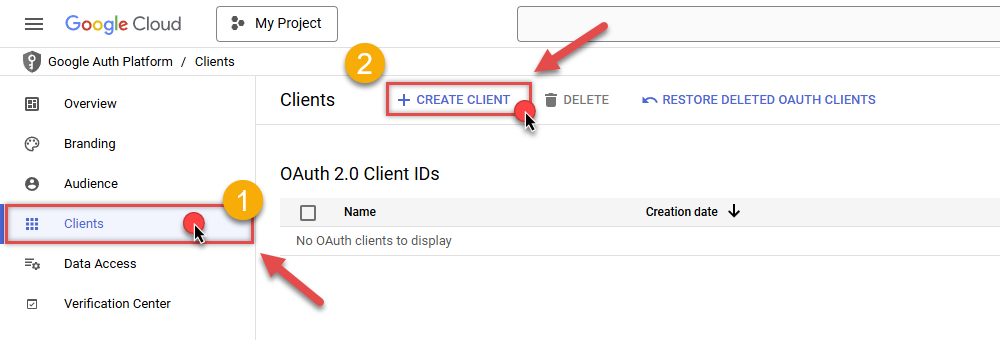
-
Choose
Desktop appas Application type and name your credentials: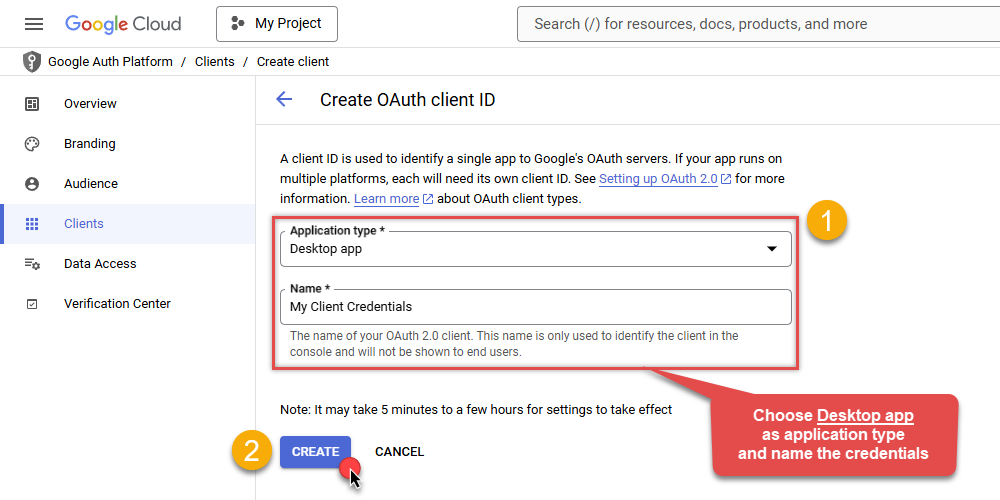
-
Continue by opening the created credentials:
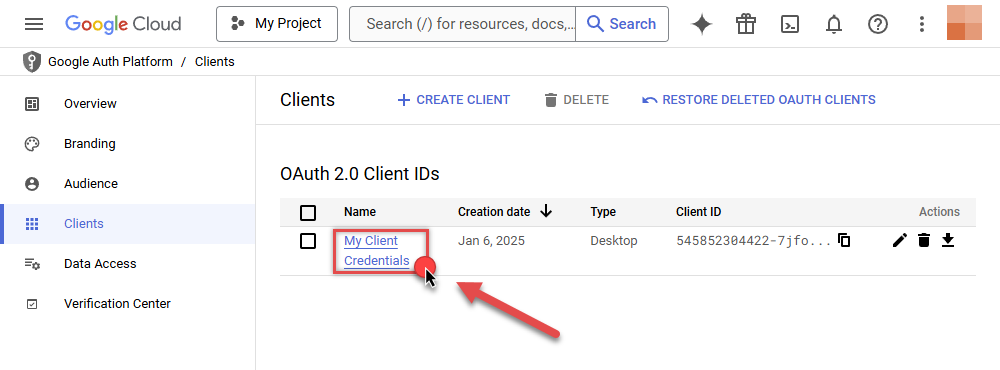
-
Finally, copy Client ID and Client secret for the later step:
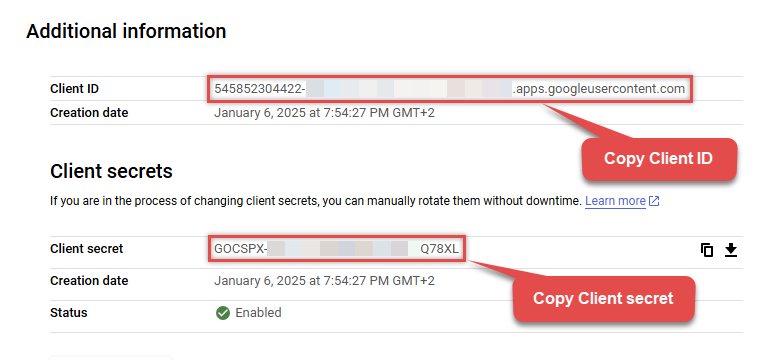
-
Done! We have all the data needed for authentication, let's proceed to the last step!
Step-5: Configure connection
-
Now go to SSIS package or ODBC data source and use previously copied values in User Account authentication configuration:
- In the ClientId field paste the Client ID value.
- In the ClientSecret field paste the Client secret value.
-
Press Generate Token button to generate Access and Refresh Tokens.
-
Then choose ProjectId from the drop down menu.
-
Continue by choosing DatasetId from the drop down menu.
-
Finally, click Test Connection to confirm the connection is working.
-
Done! Now you are ready to use Google BigQuery Connector!
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
User Account [OAuth] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Press Generate Token button to generate the tokens.
- Finally, hit OK button:
GoogleBigqueryDSNGoogle BigQueryUser Account [OAuth]https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2Required Parameters UseCustomApp Fill-in the parameter... ProjectId (Choose after [Generate Token] clicked) Fill-in the parameter... DatasetId (Choose after [Generate Token] clicked and ProjectId selected) Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters ClientId ClientSecret Scope https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bigquery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bigquery.insertdata https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform.read-only https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.full_control https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429|503 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True Job Location Redirect URL (Only for Web App) 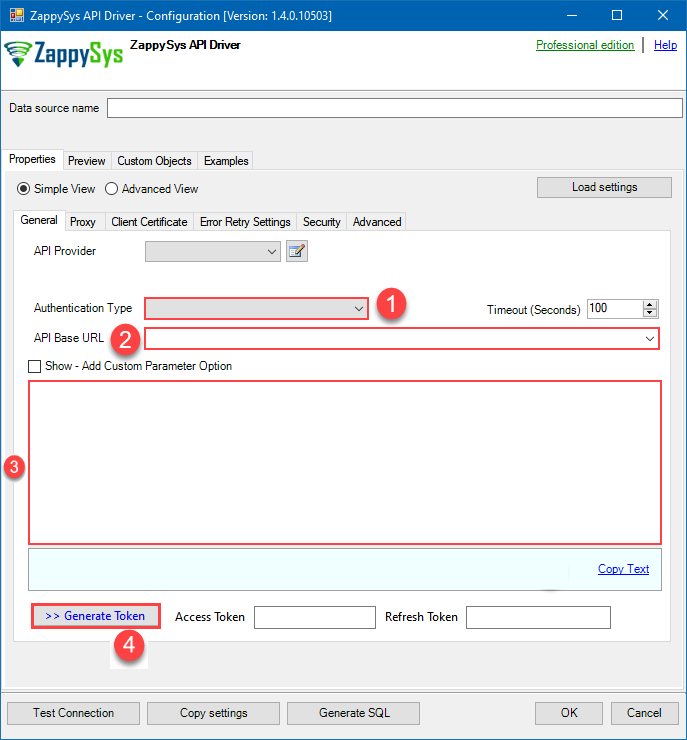
Google BigQuery authentication
Service accounts are accounts that do not represent a human user. They provide a way to manage authentication and authorization when a human is not directly involved, such as when an application needs to access Google Cloud resources. Service accounts are managed by IAM. [API reference]
Follow these steps on how to create Service Account to authenticate and access BigQuery API in SSIS package or ODBC data source:
Step-1: Create project
This step is optional, if you already have a project in Google Cloud and can use it. However, if you don't, proceed with these simple steps to create one:
-
First of all, go to Google API Console.
-
Then click Select a project button and then click NEW PROJECT button:

-
Name your project and click CREATE button:

-
Wait until the project is created:

- Done! Let's proceed to the next step.
Step-2: Enable Google Cloud APIs
In this step we will enable BigQuery API and Cloud Resource Manager API:
-
Select your project on the top bar:

-
Then click the "hamburger" icon on the top left and access APIs & Services:

-
Now let's enable several APIs by clicking ENABLE APIS AND SERVICES button:

-
In the search bar search for
bigquery apiand then locate and select BigQuery API:
-
If BigQuery API is not enabled, enable it:

-
Then repeat the step and enable Cloud Resource Manager API as well:

- Done! Let's proceed to the next step and create a service account.
Step-3: Create Service Account
Use the steps below to create a Service Account in Google Cloud:
-
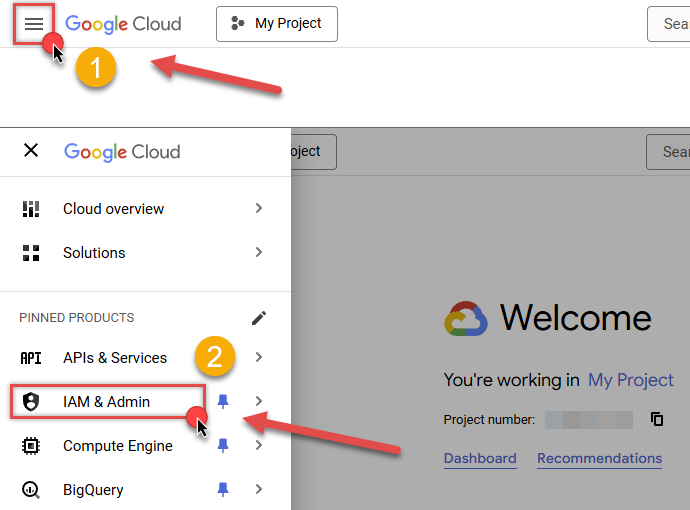
First of all, go to IAM & Admin in Google Cloud console:
-
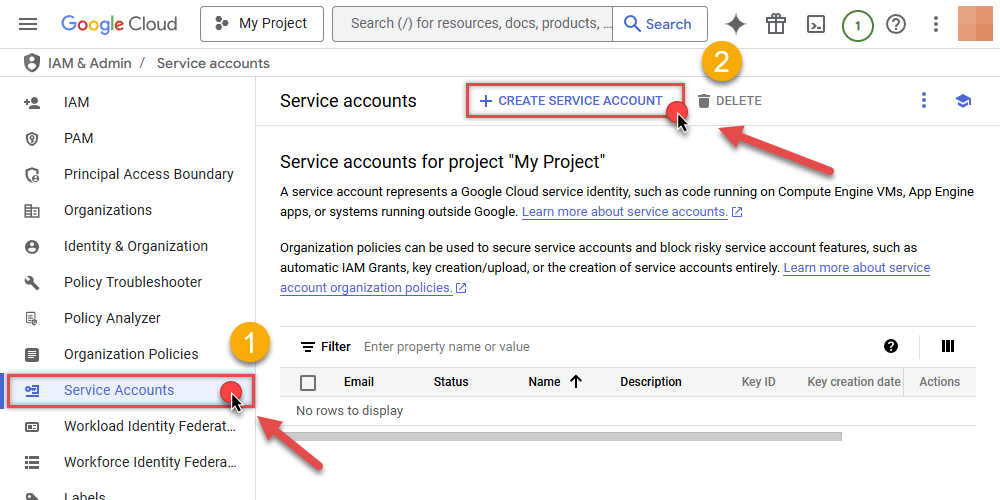
Once you do that, click Service Accounts on the left side and click CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT button:
-
Then name your service account and click CREATE AND CONTINUE button:
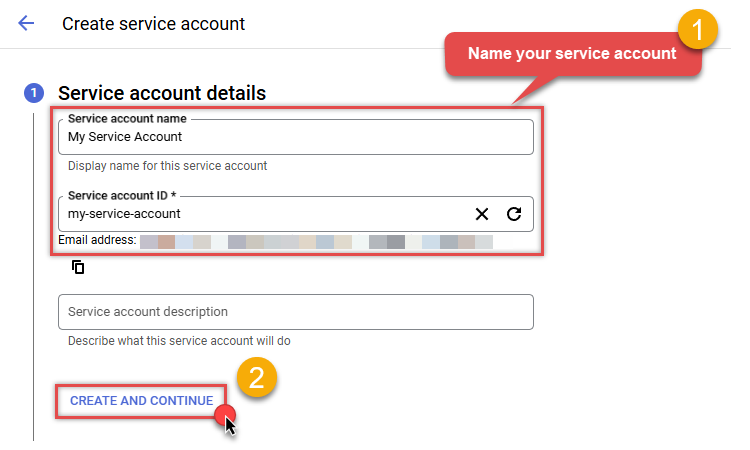
-
Continue by clicking Select a role dropdown and start granting service account BigQuery Admin and Project Viewer roles:
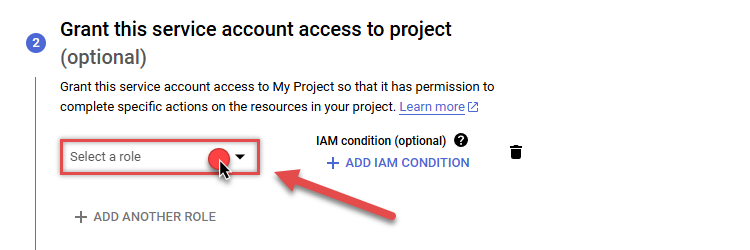
-
Find BigQuery group on the left and then click on BigQuery Admin role on the right:
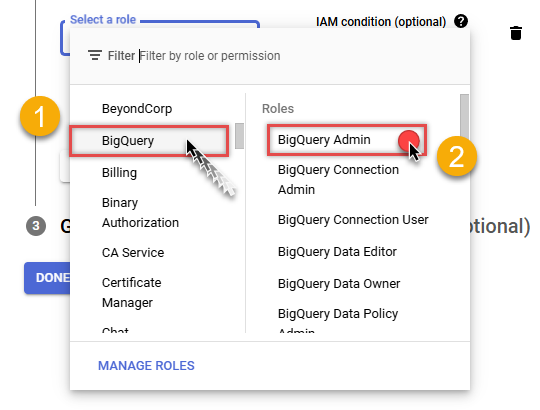
-
Then click ADD ANOTHER ROLE button, find Project group and select Viewer role:
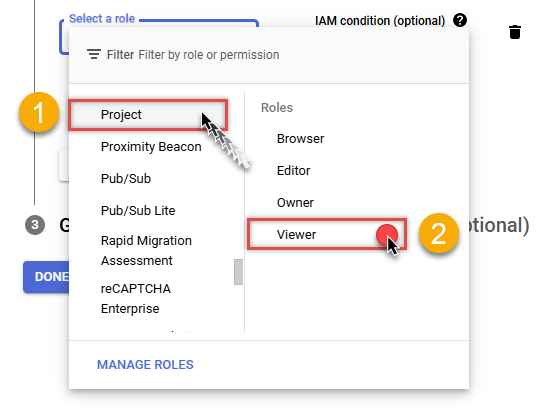
-
Finish adding roles by clicking CONTINUE button:
 You can always add or modify permissions later in IAM & Admin.
You can always add or modify permissions later in IAM & Admin. -
Finally, in the last step, just click button DONE:
-
Done! We are ready to add a Key to this service account in the next step.
Step-4: Add Key to Service Account
We are ready to add a Key (JSON or P12 key file) to the created Service Account:
-
In Service Accounts open newly created service account:
-
Next, copy email address of your service account for the later step:
-
Continue by selecting KEYS tab, then press ADD KEY dropdown, and click Create new key menu item:
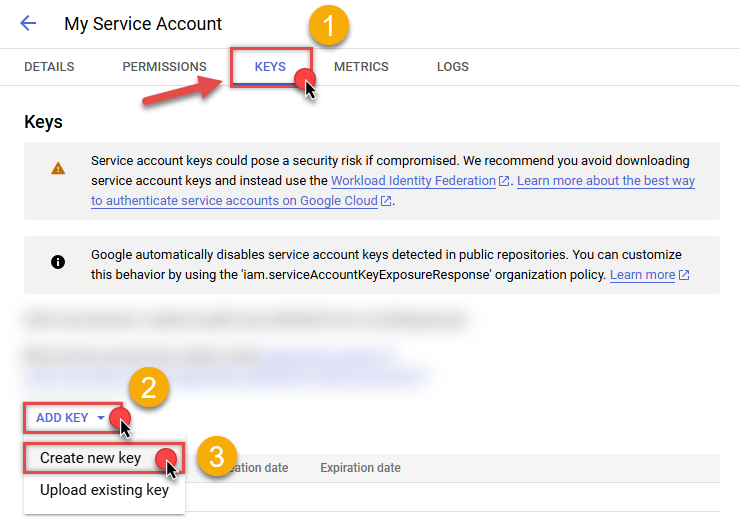
-
Finally, select JSON (Engine v19+) or P12 option and hit CREATE button:
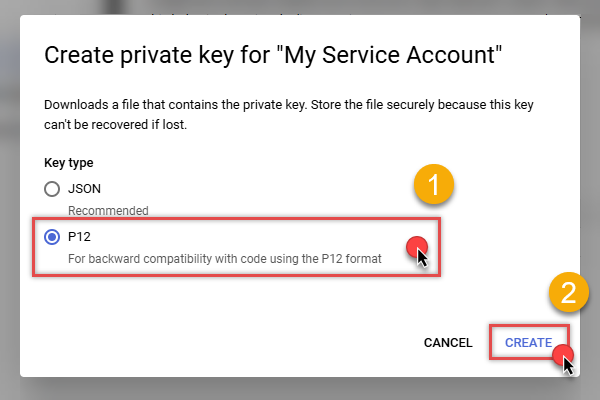
- Key file downloads into your machine. We have all the data needed for authentication, let's proceed to the last step!
Step-5: Configure connection
-
Now go to SSIS package or ODBC data source and configure these fields in Service Account authentication configuration:
- In the Service Account Email field paste the service account Email address value you copied in the previous step.
- In the Service Account Private Key Path (i.e. *.json OR *.p12) field use downloaded certificate's file path.
- Done! Now you are ready to use Google BigQuery Connector!
API Connection Manager configuration
Just perform these simple steps to finish authentication configuration:
-
Set Authentication Type to
Service Account (Using *.json OR *.p12 key file) [OAuth] - Optional step. Modify API Base URL if needed (in most cases default will work).
- Fill in all the required parameters and set optional parameters if needed.
- Finally, hit OK button:
GoogleBigqueryDSNGoogle BigQueryService Account (Using *.json OR *.p12 key file) [OAuth]https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2Required Parameters Service Account Email Fill-in the parameter... Service Account Private Key Path (i.e. *.json OR *.p12) Fill-in the parameter... ProjectId Fill-in the parameter... DatasetId (Choose after ProjectId) Fill-in the parameter... Optional Parameters Scope https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bigquery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bigquery.insertdata https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform.read-only https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.full_control https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write RetryMode RetryWhenStatusCodeMatch RetryStatusCodeList 429 RetryCountMax 5 RetryMultiplyWaitTime True Job Location Impersonate As (Enter Email Id) 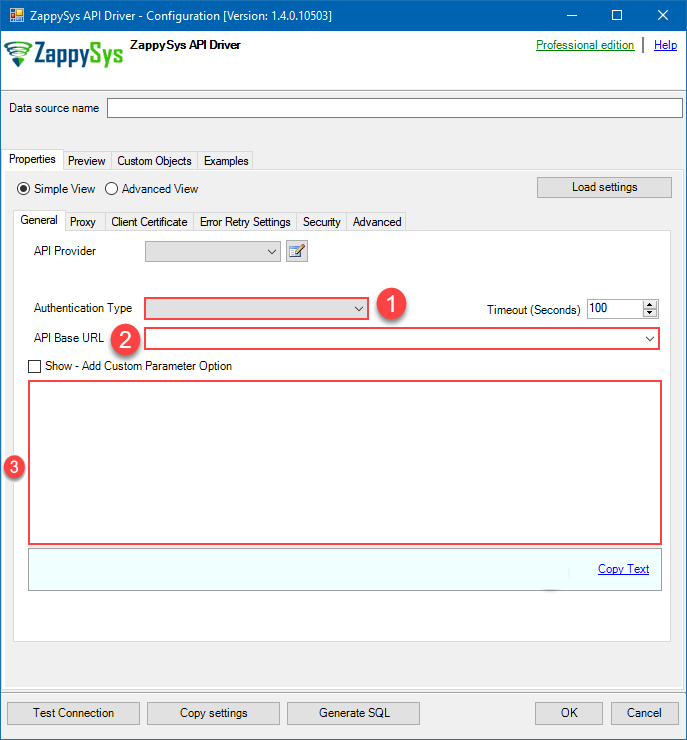
-
-
Once the data source connection has been configured, it's time to configure the SQL query. Select the Preview tab and then click Query Builder button to configure the SQL query:
 ZappySys API Driver - Google BigQueryRead / write Google BigQuery data inside your app without coding using easy to use high performance API ConnectorGoogleBigqueryDSN
ZappySys API Driver - Google BigQueryRead / write Google BigQuery data inside your app without coding using easy to use high performance API ConnectorGoogleBigqueryDSN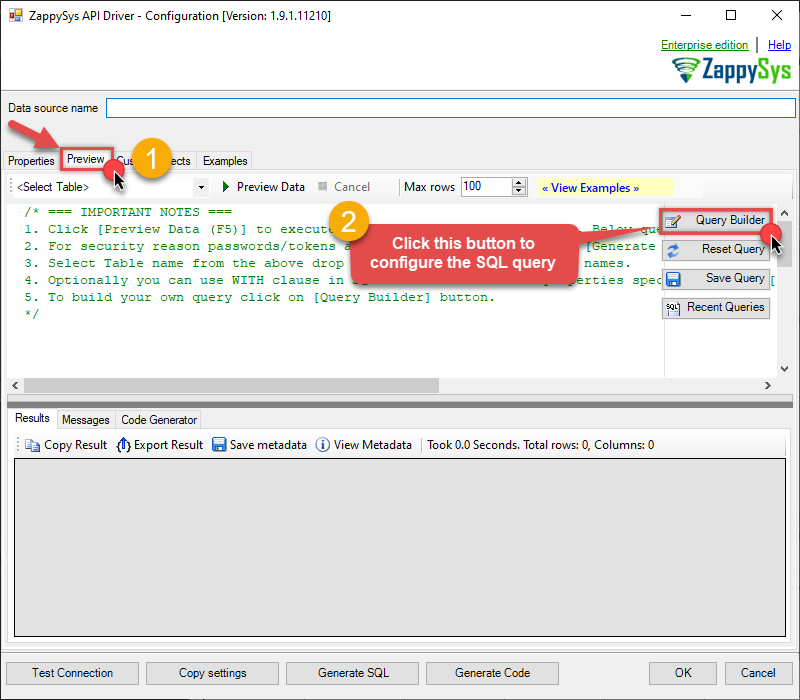
-
Start by selecting the Table or Endpoint you are interested in and then configure the parameters. This will generate a query that we will use in MS Access to retrieve data from Google BigQuery. Hit OK button to use this query in the next step.
#DirectSQL SELECT * FROM bigquery-public-data.samples.wikipedia LIMIT 1000 /* try your own dataset or Some FREE dataset like nyc-tlc.yellow.trips -- 3 parts ([Project.]Dataset.Table) */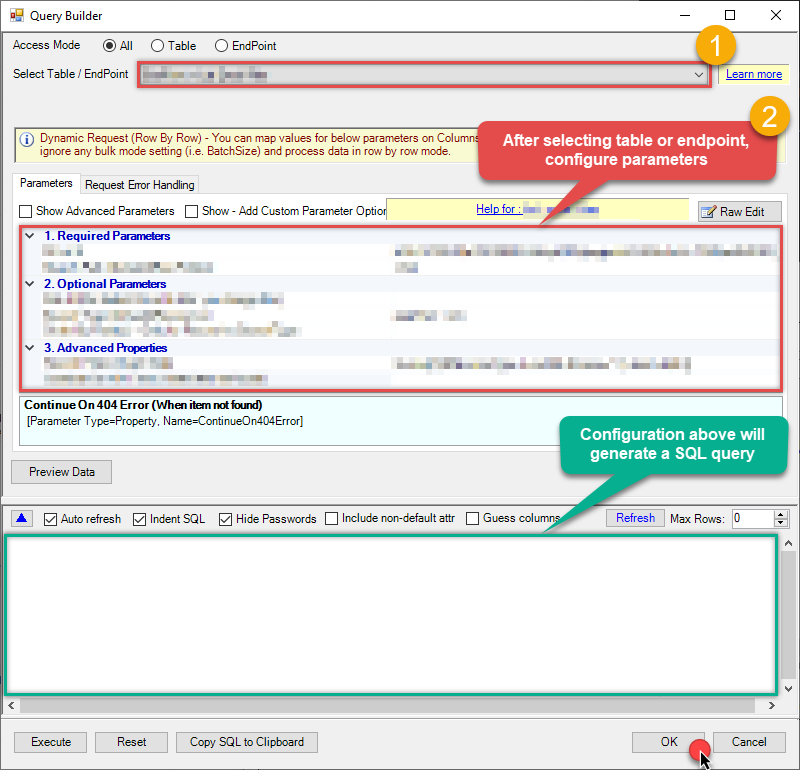 Some parameters configured in this window will be passed to the Google BigQuery API, e.g. filtering parameters. It means that filtering will be done on the server side (instead of the client side), enabling you to get only the meaningful data
Some parameters configured in this window will be passed to the Google BigQuery API, e.g. filtering parameters. It means that filtering will be done on the server side (instead of the client side), enabling you to get only the meaningful datamuch faster . -
Now hit Preview Data button to preview the data using the generated SQL query. If you are satisfied with the result, use this query in MS Access:
 ZappySys API Driver - Google BigQueryRead / write Google BigQuery data inside your app without coding using easy to use high performance API ConnectorGoogleBigqueryDSN
ZappySys API Driver - Google BigQueryRead / write Google BigQuery data inside your app without coding using easy to use high performance API ConnectorGoogleBigqueryDSN#DirectSQL SELECT * FROM bigquery-public-data.samples.wikipedia LIMIT 1000 /* try your own dataset or Some FREE dataset like nyc-tlc.yellow.trips -- 3 parts ([Project.]Dataset.Table) */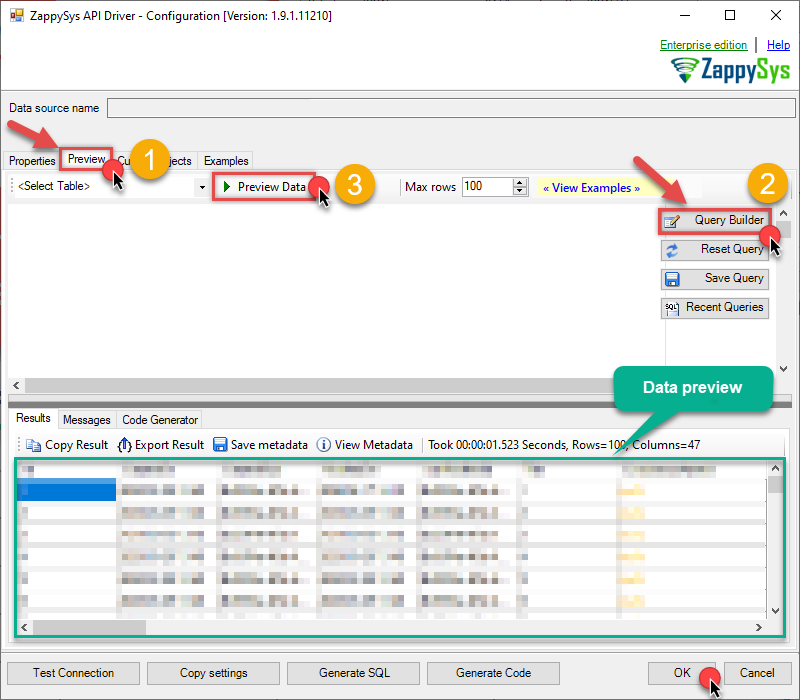 You can also access data quickly from the tables dropdown by selecting <Select table>.A
You can also access data quickly from the tables dropdown by selecting <Select table>.AWHEREclause,LIMITkeyword will be performed on the client side, meaning that thewhole result set will be retrieved from the Google BigQuery API first, and only then the filtering will be applied to the data. If possible, it is recommended to use parameters in Query Builder to filter the data on the server side (in Google BigQuery servers). -
Click OK to finish creating the data source.
Video Tutorial
Read data in Microsoft Access from the ODBC data source
-
First of all, open MS Access and create a new MS Access database.
-
In the next step, start loading ODBC data source we created:
-
Then click next until data source selection window appears. Select the data source we created in one of the previous steps and hit OK:
GoogleBigqueryDSN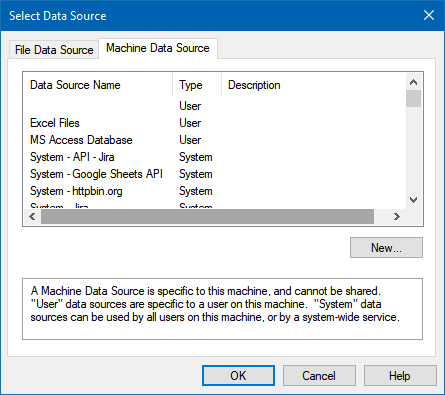
-
Continue with tables and views selection. You can extract multiple tables or views:
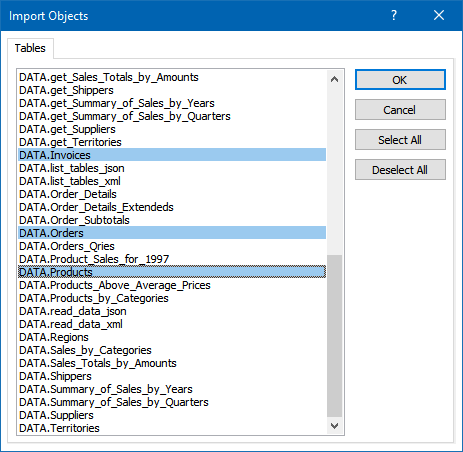
-
Finally, wait while data is being loaded and once done you should see a similar view:
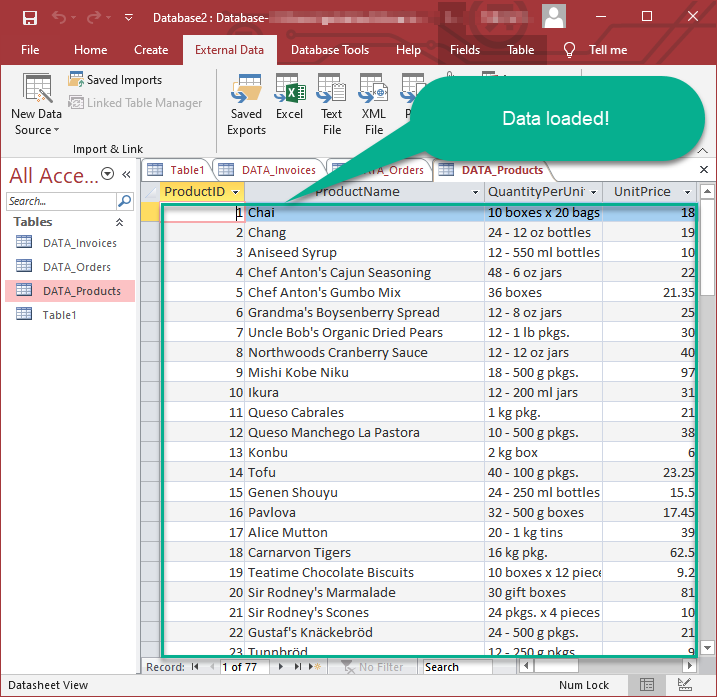
Using Linked Table for Live Data (Slow)
Linked tables in Microsoft Access are crucial for online databases because they enable real-time access to centralized data, support scalability, facilitate collaboration, enhance data security, ease maintenance tasks, and allow integration with external systems. They provide a flexible and efficient way to work with data stored in online databases, promoting cross-platform compatibility and reducing the need for data duplication.
-
Real-Time Data Access:
Access can interact directly with live data in online databases, ensuring that users always work with the most up-to-date information. -
Centralized Data Management:
Online databases serve as a centralized repository, enabling efficient management of data from various locations. -
Ease of Maintenance:
Updates or modifications to the online database structure are automatically reflected in Access, streamlining maintenance tasks. -
Adaptability to Changing Requirements:
Linked tables provide flexibility, allowing easy adaptation to changing data storage needs or migration to different online database systems.
Let's create the linked table.
-
Launch Microsoft Access and open the database where you want to create the linked table.
-
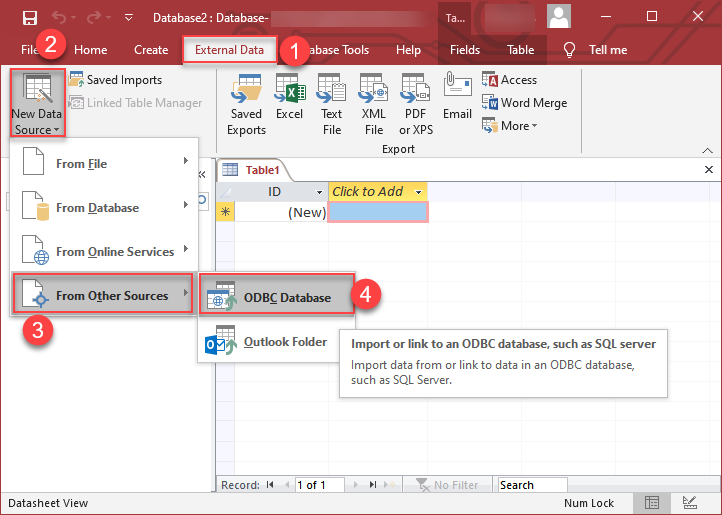
Go to the "External Data" tab on the Ribbon. >> "New Data Source" >> "From Other Sources" >> "ODBC Database"

-
Select the option "Link to Data Source by creating a linked table:
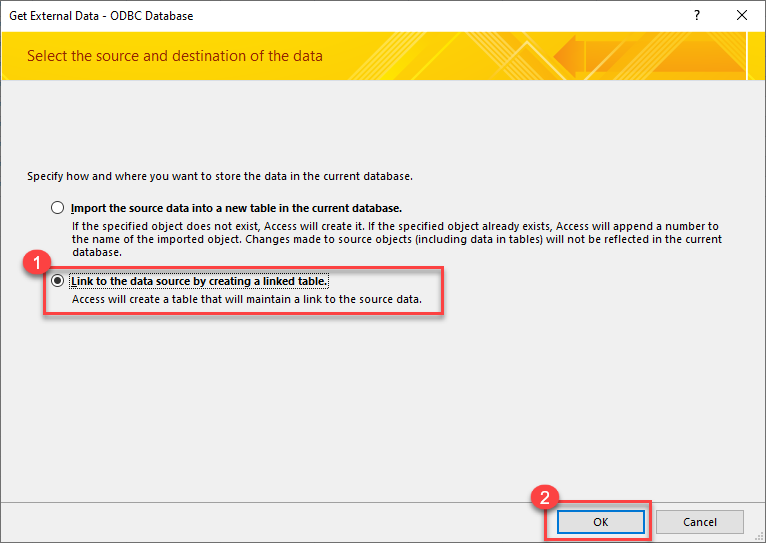
-
Continue by clicking 'Next' until the Data Source Selection window appears. Navigate to the Machine Data Source tab and select the desired data source established in one of the earlier steps. Click 'OK' to confirm your selection.
GoogleBigqueryDSN
-
Proceed to the selection of Tables and Views. You have the option to extract multiple tables or views:

-
When prompted to select Unique Key column DO NOT select any column(s) and just click OK:
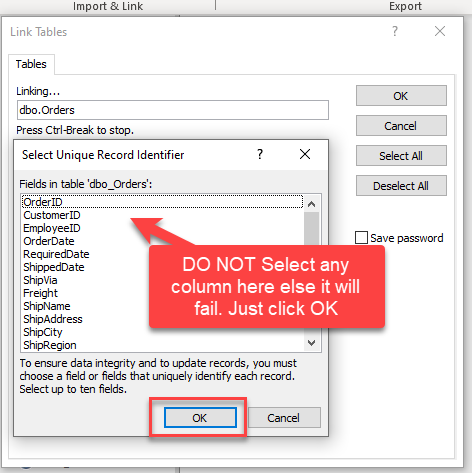
-
Finally, Simply double-click the newly created Linked Table to load the data:
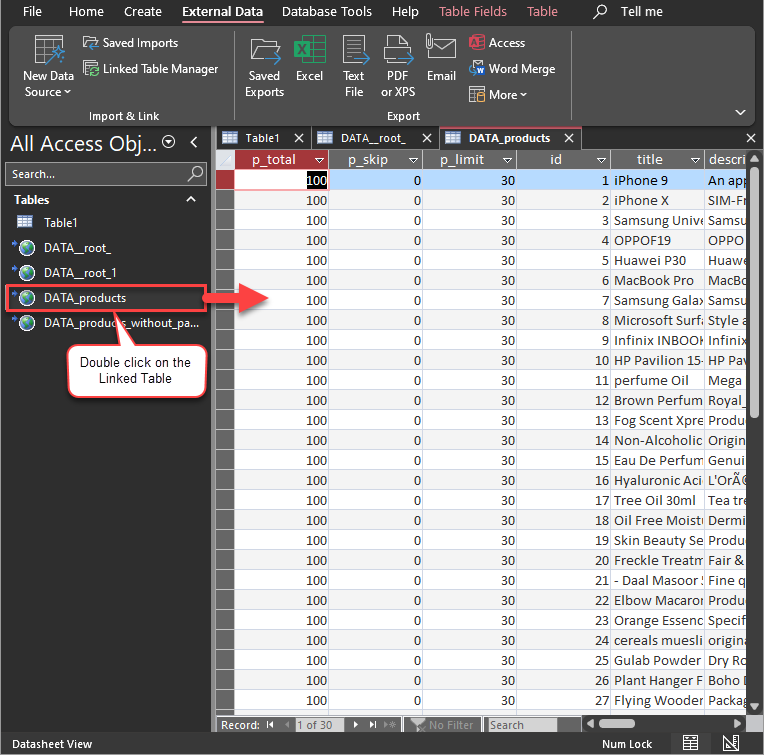
Guide to Effectively Addressing Known Issues
Discover effective strategies to address known issues efficiently in this guide. Get solutions and practical tips to streamline troubleshooting and enhance system performance, ensuring a smoother user experience.
Fewer Rows Imported
The reason for this is that MS Access has a default query timeout of 60 seconds, which means it stops fetching data if the query takes longer than that. As a result, only a limited number of rows are fetched within this time frame.
To address this, we can adjust the Query Timeout by following the steps below.
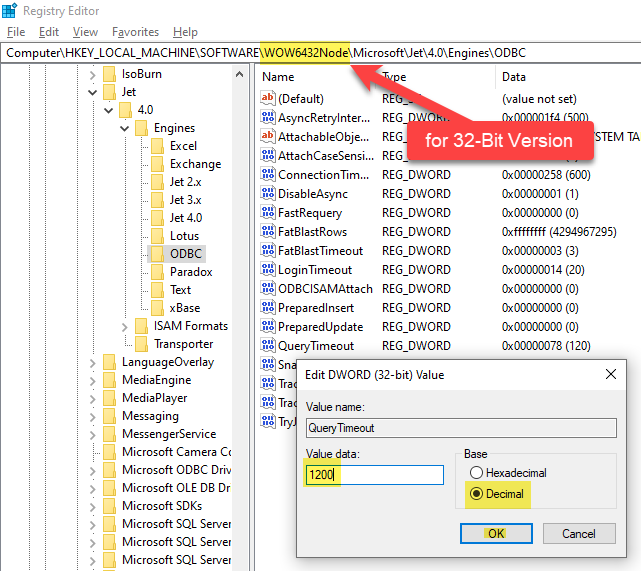
The path may vary depending on the MS Access bitness, such as 32-bit versus 64-bit.
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Jet\4.0\Engines\ODBC
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Jet\4.0\Engines\ODBC
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\ClickToRun\REGISTRY\MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Office\16.0\Access Connectivity Engine\Engines\ODBC
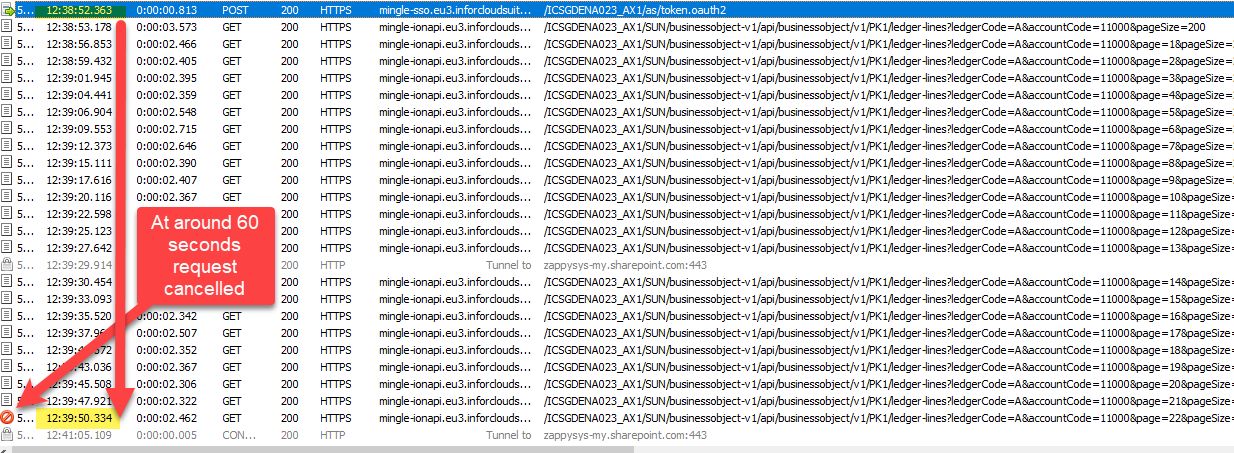
We can identify this issue by examining the Fiddler Log, as MS Access doesn't display any error regarding partial import, which is quite unusual
Please refer to this link : How to use Fiddler to analyze HTTP web requests
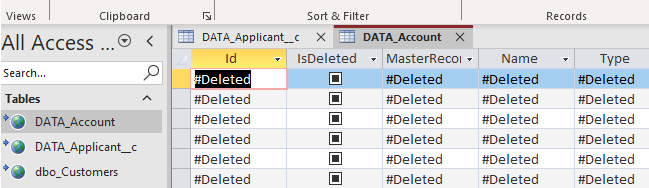
#Deleted word appears for column value in MS Access for Linked Table mode
If you used Linked Table mode to get external data and it shows #deleted word rather than actual value for column after you open then most likely its following issue.
Make sure to re-create Linked Table and DO NOT select any key column when prompted (Just click OK)
How to Fix
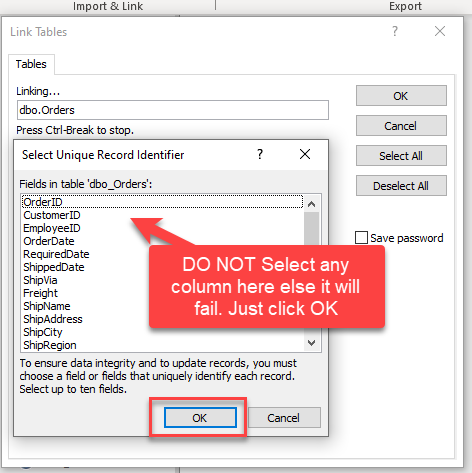
Table Selection UI Opening Delays
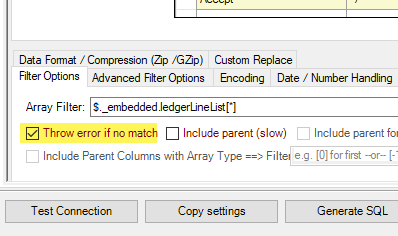
The Table selection UI takes a significant amount of time to open after clicking the 'New Data Source' -> 'Other Data Sources' -> 'ODBC'
The reason for this issue is that MS Access sends a dummy query, leading to several unnecessary pagination cycles before an error is thrown. To mitigate this, we can prevent wasted cycles by configuring the 'Throw error if no match' setting on the Filter Options Tab.
Enhancing Performance through Metadata Addition (Reduces Query Time)
We can optimize query performance by creating Virtual Tables (i.e. views with custom SQL) on Datasource and incorporating META=static columns. Learn how to capture static metadata in this guide.
Performance Options - Generate Metadata Manually
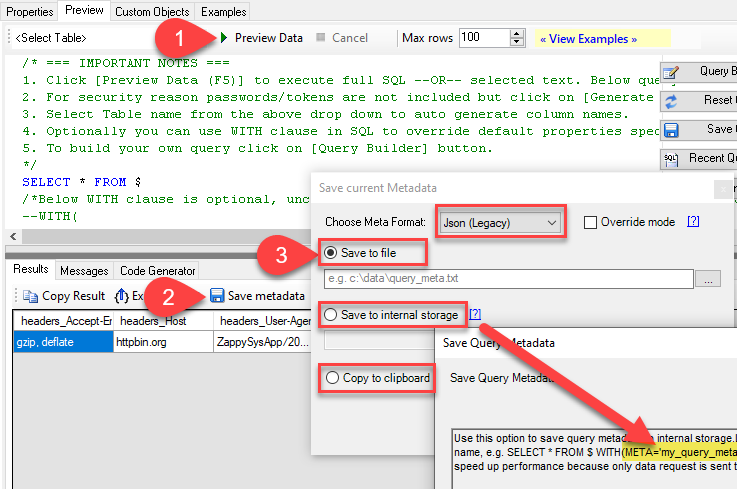
Execute the query initially, save the metadata by selecting 'Save to Meta' (choose Compact Format), and then click 'Save to Clipboard.' Utilize the resulting list by pasting it into the META attribute as follows: 'META=paste here.'
SELECT * FROM products
WITH(
META='id:String(20); title:String(100); description:String(500);'
)
Optimize Workflow with Automated Import
Employ Automated Import when Linked Tables are not feasible, and we need to depend on Imported Tables with static data.
While using Linked Tables sometime it encounter errors, and we are left with no alternative but to utilize Imported Tables, Automatic Refresh becomes crucial in such scenarios.
Here's a guide on automating refreshes. We can set up automatic refresh on different events, such as when the database opens, a form is opened, or a button is clicked.
To initiate the import process, follow these steps:
- Perform the data import using the standard manual steps.
- In the final step, we'll encounter a checkbox labeled 'Save Import Steps.' Ensure to check this option.
- After saving the steps, we can locate their name in the Save Imports UI. Identify the name associated with the saved steps.
- "Now, we can execute the code as shown below:"
Private Sub cmdYes_Click()
Label0.Visible = True
DoCmd.RunSavedImportExport "Import-DATA.products"
Label0.Visible = False
End Sub
Centralized data access via Data Gateway
In some situations, you may need to provide Google BigQuery data access to multiple users or services. Configuring the data source on a Data Gateway creates a single, centralized connection point for this purpose.
This configuration provides two primary advantages:
-
Centralized data access
The data source is configured once on the gateway, eliminating the need to set it up individually on each user's machine or application. This significantly simplifies the management process.
-
Centralized access control
Since all connections route through the gateway, access can be governed or revoked from a single location for all users.
| Data Gateway |
Local ODBC
data source
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Simple configuration | ||
| Installation | Single machine | Per machine |
| Connectivity | Local and remote | Local only |
| Connections limit | Limited by License | Unlimited |
| Central data access | ||
| Central access control | ||
| More flexible cost |
If you need any of these requirements, you will have to create a data source in Data Gateway to connect to Google BigQuery, and to create an ODBC data source to connect to Data Gateway in MS Access.
Let's not wait and get going!
Creating Google BigQuery data source in Gateway
In this section we will create a data source for Google BigQuery in Data Gateway. Let's follow these steps to accomplish that:
-
Search for
gatewayin Windows Start Menu and open ZappySys Data Gateway Configuration:
-
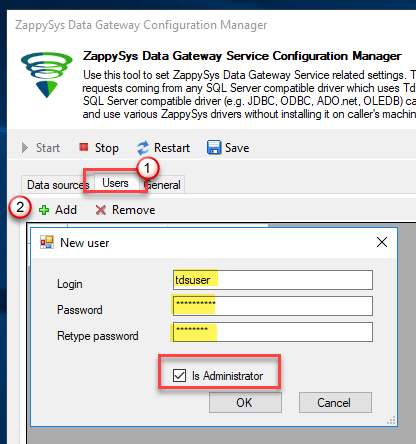
Go to Users tab and follow these steps to add a Data Gateway user:
- Click Add button
-
In Login field enter username, e.g.,
john - Then enter a Password
- Check Is Administrator checkbox
- Click OK to save
-
Now we are ready to add a data source:
- Click Add button
- Give Datasource a name (have it handy for later)
- Then select Native - ZappySys API Driver
- Finally, click OK
GoogleBigqueryDSNZappySys API Driver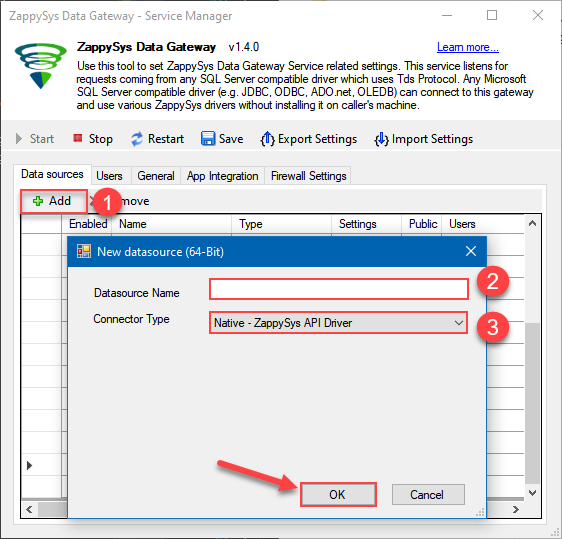
-
When the ZappySys API Driver configuration window opens, configure the Data Source the same way you configured it in ODBC Data Sources (64-bit), in the beginning of this article.
-
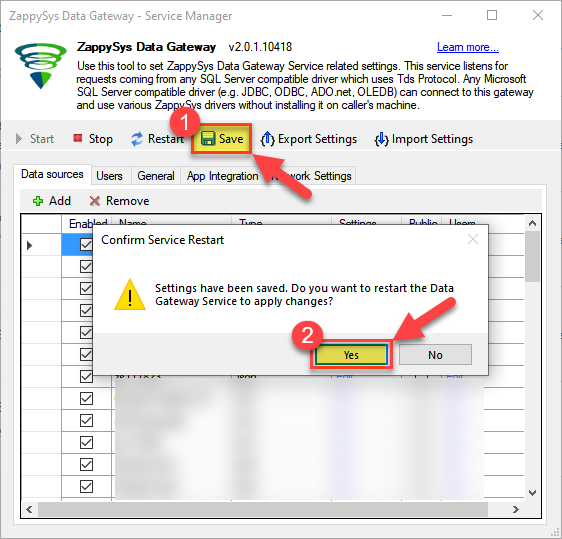
Very important step. Now, after creating or modifying the data source make sure you:
- Click the Save button to persist your changes.
- Hit Yes, once asked if you want to restart the Data Gateway service.
This will ensure all changes are properly applied:
 Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Creating ODBC data source for Data Gateway
In this part we will create ODBC data source to connect to Data Gateway from MS Access. To achieve that, let's perform these steps:
-
Open ODBC Data Sources (x64):

-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server:
ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server If you don't see ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version driver.
If you don't see ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version driver. -
Then set a Name of the data source (e.g.
Gateway) and the address of the Data Gateway:GatewayDSNlocalhost,5000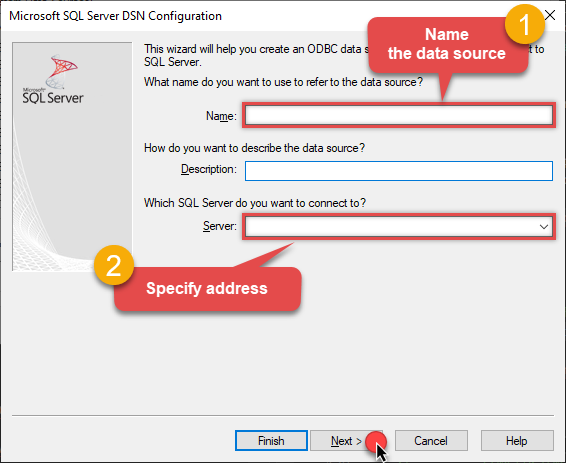 Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.
Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.localhost,5000. -
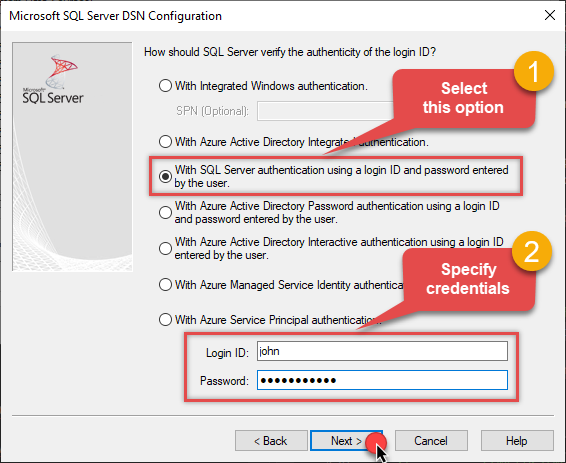
Proceed with authentication part:
- Select SQL Server authentication
-
In Login ID field enter the user name you used in Data Gateway, e.g.,
john - Set Password to the one you configured in Data Gateway
-
Then set the default database property to
GoogleBigqueryDSN(the one we used in Data Gateway):GoogleBigqueryDSN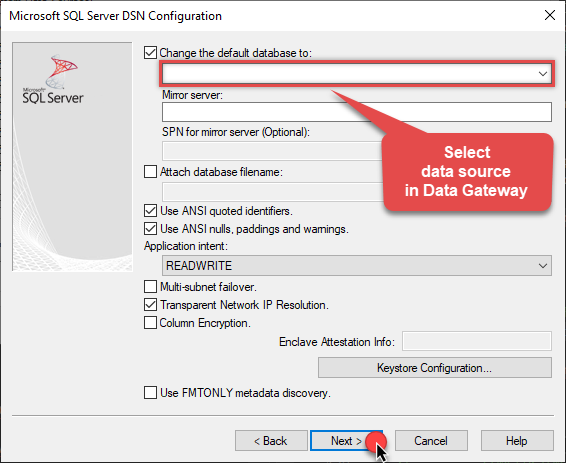
-
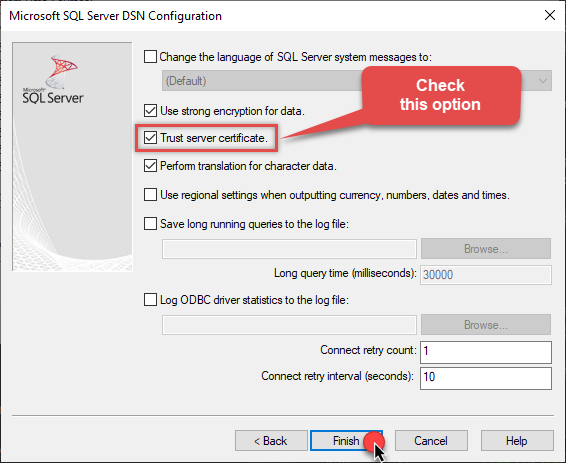
Continue by checking Trust server certificate option:
-
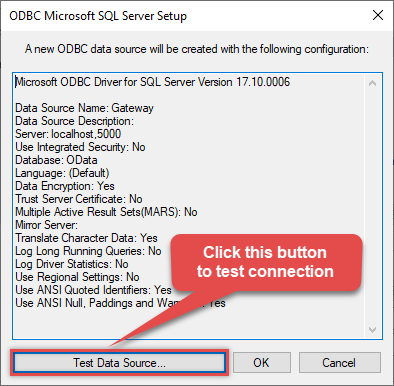
Once you do that, test the connection:
-
If connection is successful, everything is good:
-
Done!
We are ready to move to the final step. Let's do it!
Accessing data in MS Access via Data Gateway
Finally, we are ready to read data from Google BigQuery in MS Access via Data Gateway. Follow these final steps:
-
Go back to MS Access.
-
First of all, open MS Access and create a new MS Access database.
-
In the next step, start loading ODBC data source we created:

-
Then click next until data source selection window appears. Select the data source we created in one of the previous steps and hit OK:
GatewayDSN
-
Read the data the same way we discussed at the beginning of this article.
-
That's it!
Now you can connect to Google BigQuery data in MS Access via the Data Gateway.
john and your password.
Actions supported by Google BigQuery Connector
Learn how to perform common Google BigQuery actions directly in MS Access with these how-to guides:
- [Dynamic Endpoint]
- Create Dataset
- Delete Dataset
- Delete Table
- Get Query Schema (From SQL)
- Get Table Schema
- Insert Table Data
- List Datasets
- List Projects
- List Tables
- Post Dynamic Endpoint
- Read Data using SQL Query -OR- Execute Script (i.e. CREATE, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
- Read Table Rows
- Make Generic API Request
- Make Generic API Request (Bulk Write)
Conclusion
In this article we showed you how to connect to Google BigQuery in MS Access and integrate data without any coding, saving you time and effort.
We encourage you to download Google BigQuery Connector for MS Access and see how easy it is to use it for yourself or your team.
If you have any questions, feel free to contact ZappySys support team. You can also open a live chat immediately by clicking on the chat icon below.
Download Google BigQuery Connector for MS Access Documentation