ElasticSearch Connector for Azure Data Factory (Pipeline) How to Get documents from Index or Alias
Introduction
In this article we will delve deeper into ElasticSearch and Azure Data Factory (Pipeline) integration, and will learn how to get documents from index or alias. We are continuing from where we left off. By this time, you must have installed ODBC PowerPack, created ODBC Data Source, and configured authentication settings in your ElasticSearch account .
So, let's not waste time and begin.
Use Query Builder to generate SQL query
-
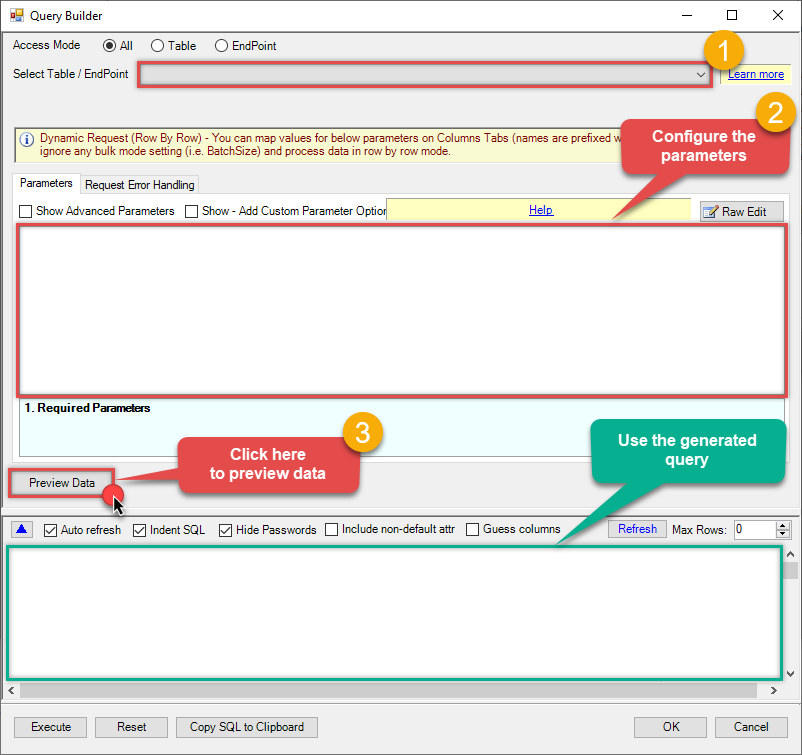
The first thing you have to do is open Query Builder:
ZappySys API Driver - ElasticSearchRead / write ElasticSearch data inside your app; perform many ElasticSearch operations without coding, just use easy to use high performance API Connector for ElasticSearchElasticsearchDSN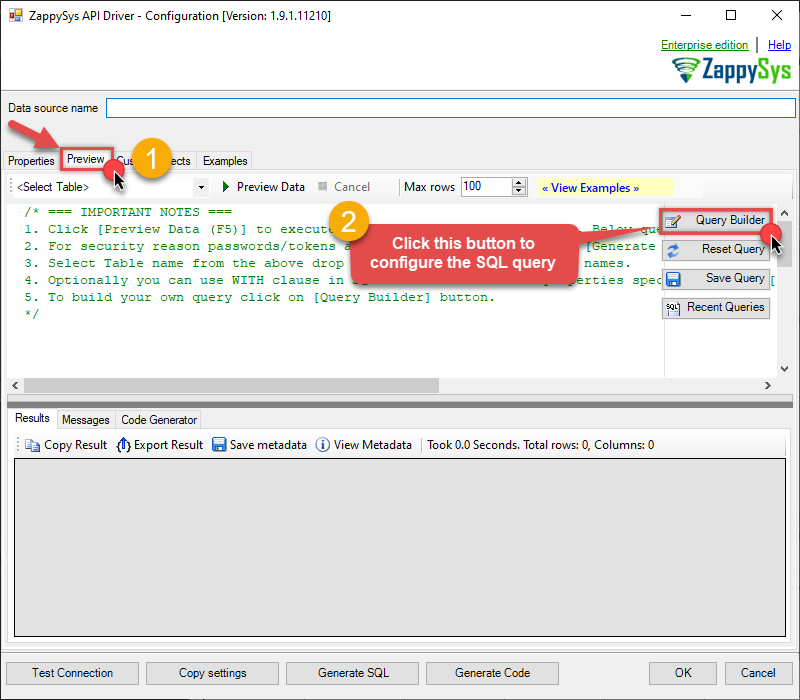
-
Then simply select the Get documents from Index or Alias endpoint (action).
-
Continue by configuring the Required parameters. You can also set optional parameters too.
-
Move on by hitting Preview Data button to preview the results.
-
If you see the results you need, simply copy the generated query:
-
That's it! You can use this query in Azure Data Factory (Pipeline).
Let's not stop here and explore SQL query examples, including how to use them in Stored Procedures and Views (virtual tables) in the next steps.
SQL query examples
Use these SQL queries in your Azure Data Factory (Pipeline) data source:
How to Read ElasticSearch documents from Index (all or with filter)
Gets documents by index name (i.e. Table name) or alias name (i.e. View name). Using WHERE clause invokes client side engine so try to avoid WHERE clause and use WITH clause QUERY attribute. Use search endpoint instead to invoke query.
SELECT * FROM MyIndexOrAliasName --WITH(Query='{"match": { "PartNumber" : "P50" } }')How to Read ElasticSearch documents from Alias (all or with filter)
Gets documents by index name (i.e. Table name) or alias name (i.e. View name). Using WHERE clause invokes client side engine so try to avoid WHERE clause and use WITH clause QUERY attribute. Use search endpoint instead to invoke query.
SELECT * FROM MyIndexOrAliasName --WITH(Query='{"match": { "PartNumber" : "P50" } }')How to Search documents from Index using ElasticSearch Query language
Below example shows how to search on a comment field for TV word anywhere in the text for Index named MyIndexOrAliasName (it can be index name or alias name). For more information on ElasticSearch Query expression check this link https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-match-query.html
SELECT * FROM MyIndexOrAliasName WITH(Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')
--or use below - slight faster (avoids table / alias list validation)
--SELECT * FROM search WITH(Index='MyIndexName', Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')
--SELECT * FROM search WITH(Index='MyIndexName', Alias='MyAliasName', Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')How to Search documents from Alias using ElasticSearch Query language
Below example shows how to search on Alias rather than Index name. Alias is build on index (consider like a view in RDBMS). This example filtes data from Alias with some condition in the Query Text. For more information on ElasticSearch Query expression check this link https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-match-query.html
SELECT * FROM MyAliasName WITH(Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')
--or use search endpoint then you must supply both Index name and Alias name
--calling /search endpoint in FROM clause is slight faster (avoids table / alias list validation)
--SELECT * FROM search WITH(Index='MyIndexName',Index='MyAliasName', Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')How to Read ElasticSearch documents from Index (all or with filter)
Gets documents by index name (i.e. Table name) or alias name (i.e. View name). Using WHERE clause invokes client side engine so try to avoid WHERE clause and use WITH clause QUERY attribute. Use search endpoint instead to invoke query.
SELECT * FROM MyIndexOrAliasName --WITH(Query='{"match": { "PartNumber" : "P50" } }')How to Read ElasticSearch documents from Alias (all or with filter)
Gets documents by index name (i.e. Table name) or alias name (i.e. View name). Using WHERE clause invokes client side engine so try to avoid WHERE clause and use WITH clause QUERY attribute. Use search endpoint instead to invoke query.
SELECT * FROM MyIndexOrAliasName --WITH(Query='{"match": { "PartNumber" : "P50" } }')How to Search documents from Index using ElasticSearch Query language
Below example shows how to search on a comment field for TV word anywhere in the text for Index named MyIndexOrAliasName (it can be index name or alias name). For more information on ElasticSearch Query expression check this link https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-match-query.html
SELECT * FROM MyIndexOrAliasName WITH(Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')
--or use below - slight faster (avoids table / alias list validation)
--SELECT * FROM search WITH(Index='MyIndexName', Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')
--SELECT * FROM search WITH(Index='MyIndexName', Alias='MyAliasName', Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')How to Search documents from Alias using ElasticSearch Query language
Below example shows how to search on Alias rather than Index name. Alias is build on index (consider like a view in RDBMS). This example filtes data from Alias with some condition in the Query Text. For more information on ElasticSearch Query expression check this link https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-match-query.html
SELECT * FROM MyAliasName WITH(Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')
--or use search endpoint then you must supply both Index name and Alias name
--calling /search endpoint in FROM clause is slight faster (avoids table / alias list validation)
--SELECT * FROM search WITH(Index='MyIndexName',Index='MyAliasName', Query='{"match": { "comment" : "TV" } }')
get_documents endpoint belongs to
[Dynamic Table]
, [Dynamic Table]
table(s), and can therefore be used via those table(s).
Stored Procedures and Views
Create Custom Stored Procedure
You can create procedures to encapsulate custom logic and then only pass handful parameters rather than long SQL to execute your API call.
Steps to create Custom Stored Procedure in ZappySys Driver. You can insert Placeholders anywhere inside Procedure Body. Read more about placeholders here
-
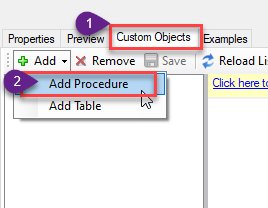
Go to Custom Objects Tab and Click on Add button and Select Add Procedure:
-
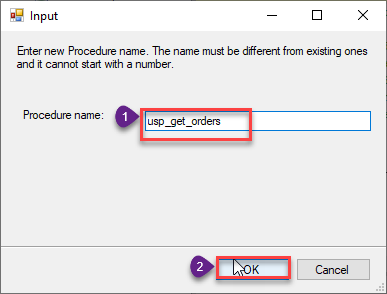
Enter the desired Procedure name and click on OK:
-
Select the created Stored Procedure and write the your desired stored procedure and Save it and it will create the custom stored procedure in the ZappySys Driver:
Here is an example stored procedure for ZappySys Driver. You can insert Placeholders anywhere inside Procedure Body. Read more about placeholders here
CREATE PROCEDURE [usp_get_orders] @fromdate = '<<yyyy-MM-dd,FUN_TODAY>>' AS SELECT * FROM Orders where OrderDate >= '<@fromdate>';
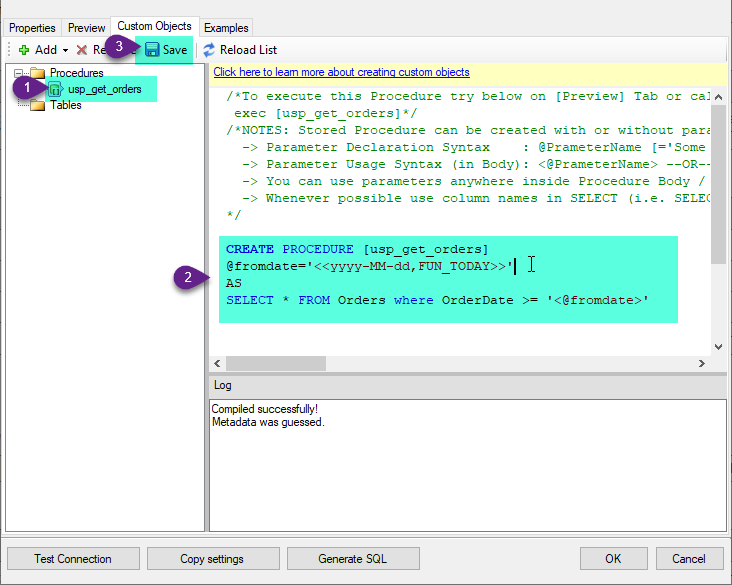
-
That's it now go to Preview Tab and Execute your Stored Procedure using Exec Command. In this example it will extract the orders from the date 1996-01-01:
Exec usp_get_orders '1996-01-01';
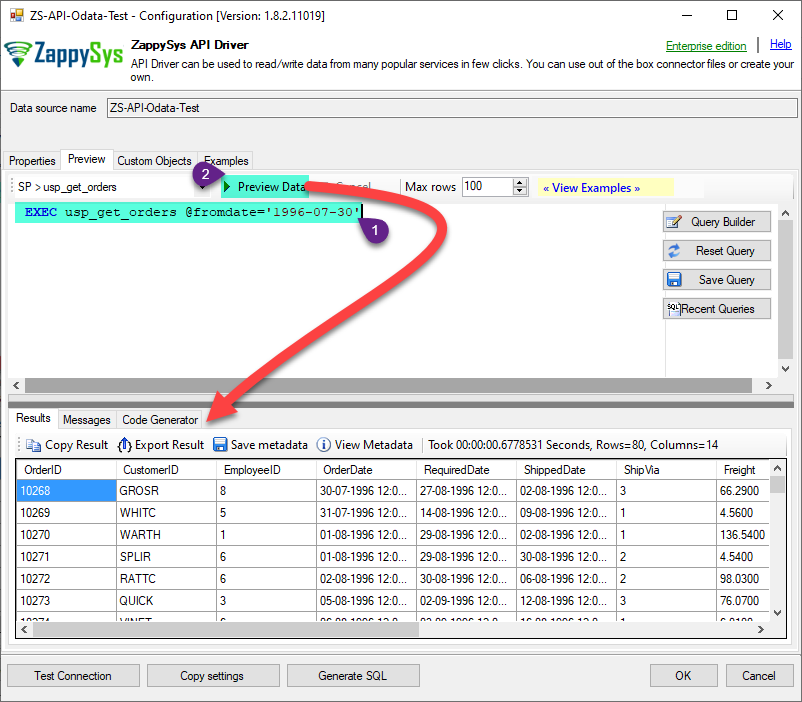
Create Custom Virtual Table
ZappySys API Drivers support flexible Query language so you can override Default Properties you configured on Data Source such as URL, Body. This way you don't have to create multiple Data Sources if you like to read data from multiple EndPoints. However not every application support supplying custom SQL to driver so you can only select Table from list returned from driver.
If you're dealing with Microsoft Access and need to import data from an SQL query, it's important to note that Access doesn't allow direct import of SQL queries. Instead, you can create custom objects (Virtual Tables) to handle the import process.
Many applications like MS Access, Informatica Designer wont give you option to specify custom SQL when you import Objects. In such case Virtual Table is very useful. You can create many Virtual Tables on the same Data Source (e.g. If you have 50 URLs with slight variations you can create virtual tables with just URL as Parameter setting.
-
Go to Custom Objects Tab and Click on Add button and Select Add Table:
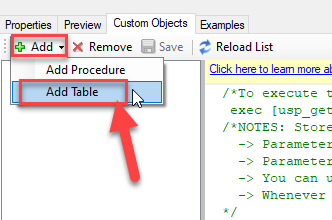
-
Enter the desired Table name and click on OK:
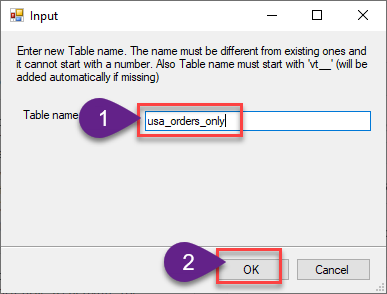
-
And it will open the New Query Window Click on Cancel to close that window and go to Custom Objects Tab.
-
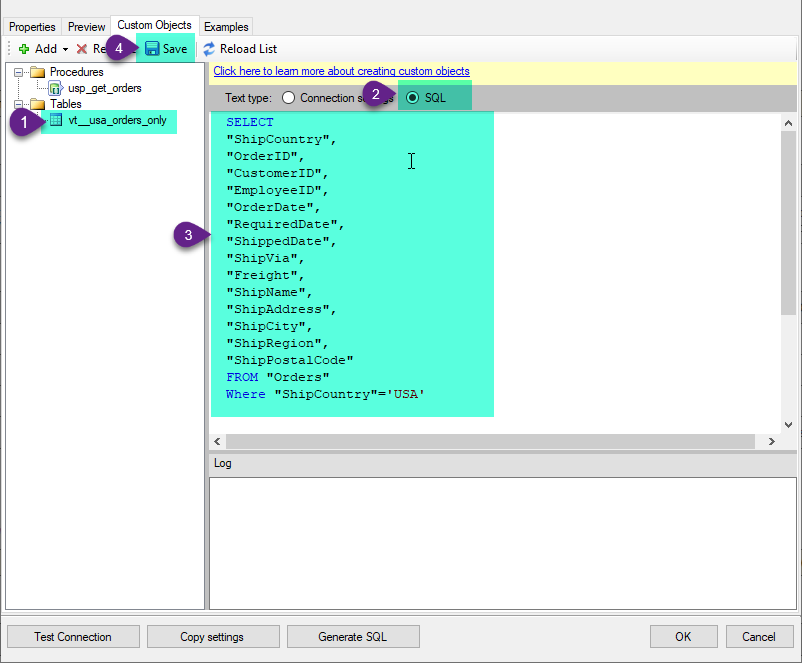
Select the created table, Select Text Type AS SQL and write the your desired SQL Query and Save it and it will create the custom table in the ZappySys Driver:
Here is an example SQL query for ZappySys Driver. You can insert Placeholders also. Read more about placeholders here
SELECT "ShipCountry", "OrderID", "CustomerID", "EmployeeID", "OrderDate", "RequiredDate", "ShippedDate", "ShipVia", "Freight", "ShipName", "ShipAddress", "ShipCity", "ShipRegion", "ShipPostalCode" FROM "Orders" Where "ShipCountry"='USA'
-
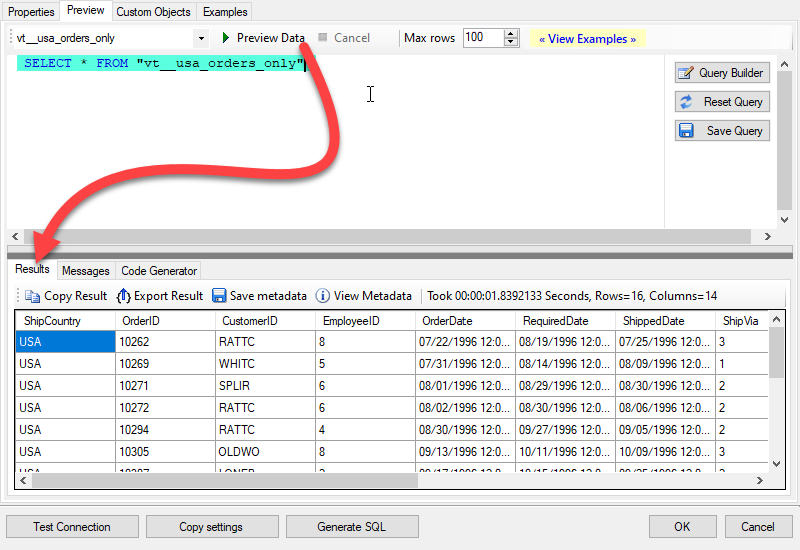
That's it now go to Preview Tab and Execute your custom virtual table query. In this example it will extract the orders for the USA Shipping Country only:
SELECT * FROM "vt__usa_orders_only"
Get documents from Index or Alias in Azure Data Factory (Pipeline)
-
Sign in to Azure Portal
-
Open your browser and go to: https://portal.azure.com
-
Enter your Azure credentials and complete MFA if required.
-
After login, go to Data factories.
-
-
Under Azure Data Factory Resource - Create or select the Data Factory you want to work with.
-
Inside the Data Factory resource page, click Launch studio.
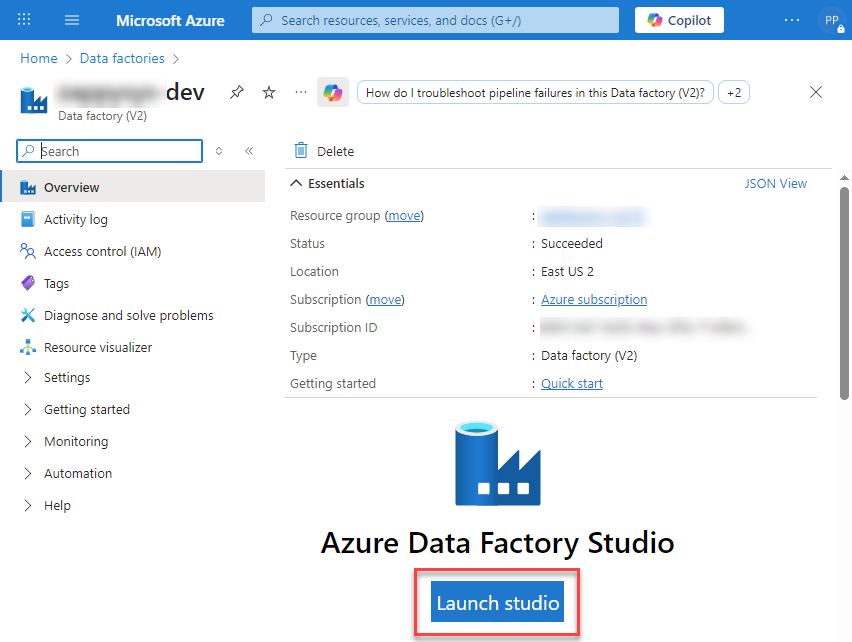
-
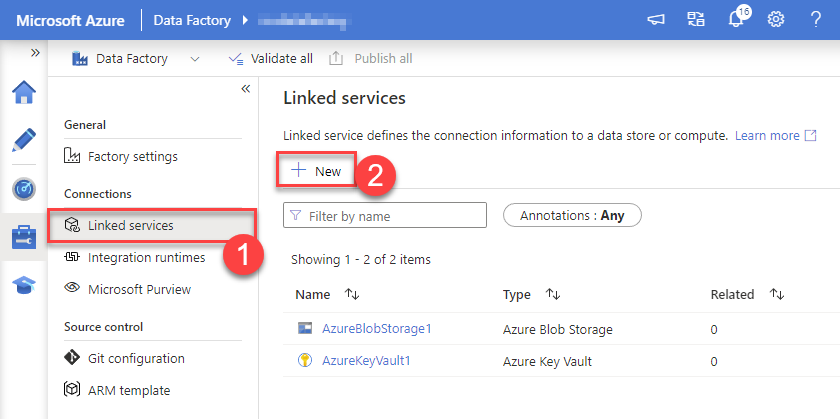
Create a New Linked service:
In the Manage section (left menu).
Under Connections, select Linked services.
Click + New to create a new Linked service based on ODBC.
-
Select ODBC service:
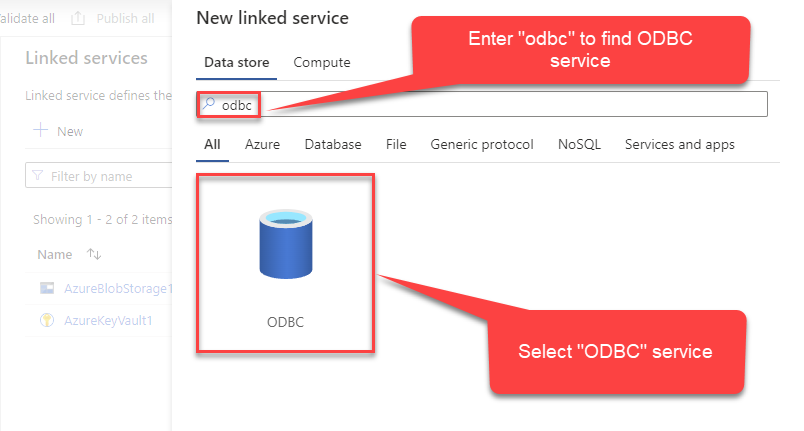
-
Configure new ODBC service. Use the same DSN name we used in the previous step and copy it to Connection string box:
ElasticsearchDSNDSN=ElasticsearchDSN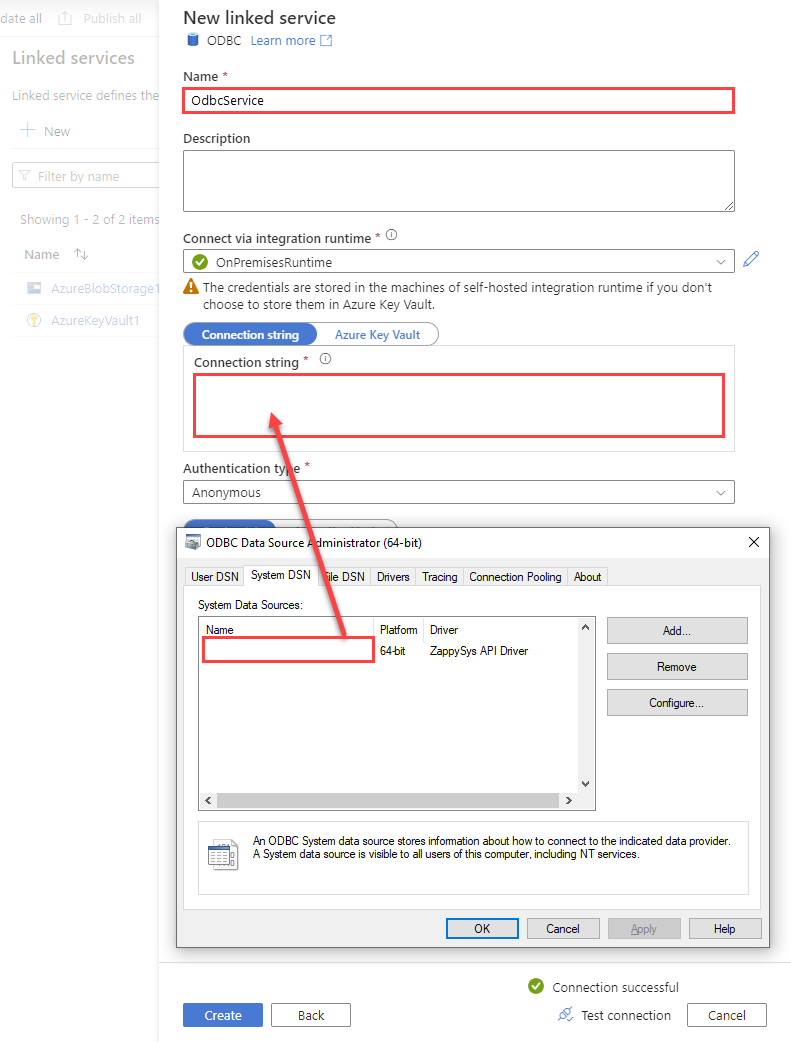
-
For created ODBC service create ODBC-based dataset:
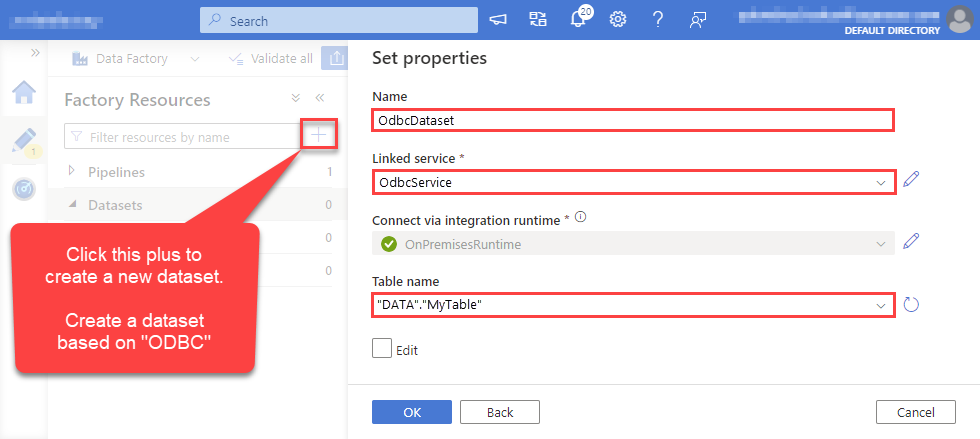
-
Go to your pipeline and add Copy data connector into the flow. In Source section use OdbcDataset we created as a source dataset:
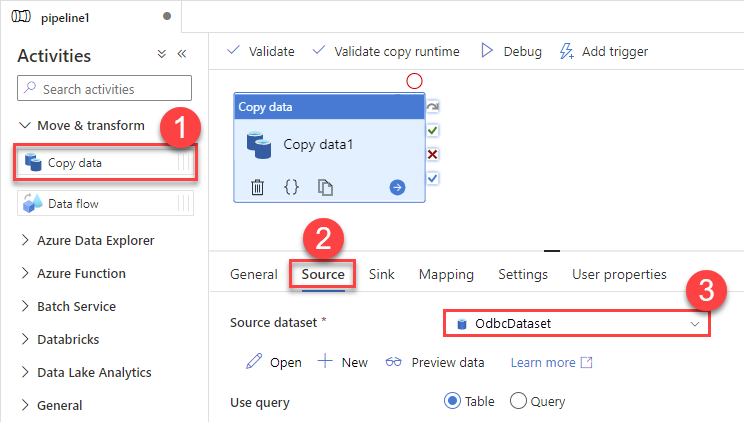
-
Then go to Sink section and select a destination/sink dataset. In this example we use precreated AzureBlobStorageDataset which saves data into an Azure Blob:
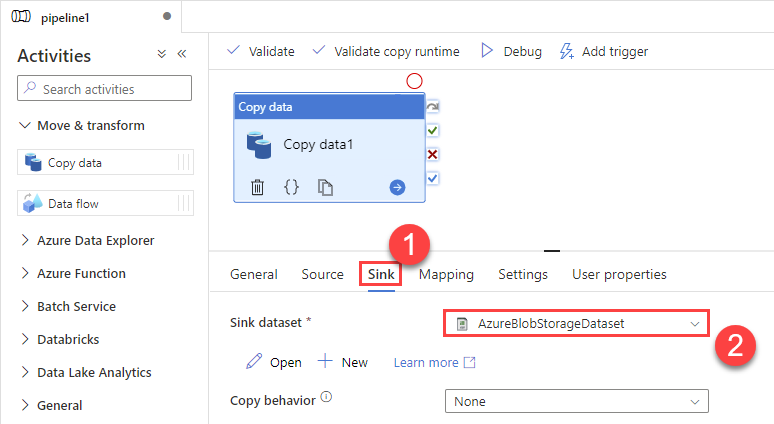
-
Finally, run the pipeline and see data being transferred from OdbcDataset to your destination dataset:
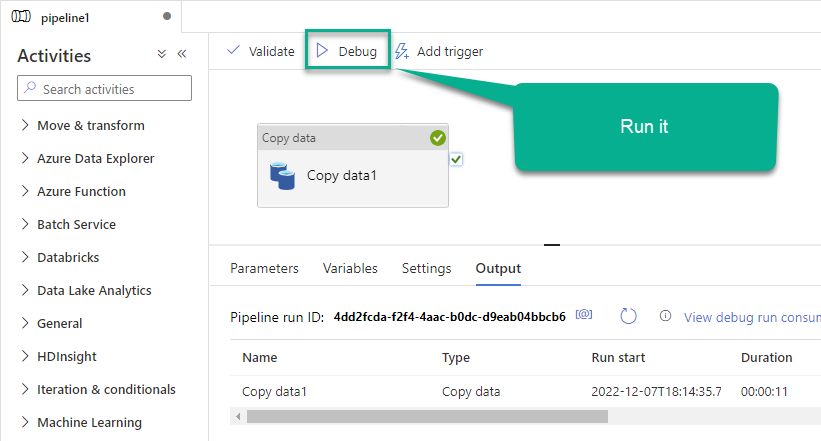
More actions supported by ElasticSearch Connector
Learn how to perform other actions directly in Azure Data Factory (Pipeline) with these how-to guides:
- Count documents
- Create Index
- Delete documents
- Delete Index
- Get document by ID from Index or Alias
- Get Index or Alias metadata
- Insert documents
- List aliases
- List indexes
- Search / Query documents
- Update documents
- Upsert documents
- Make Generic API Request
- Make Generic API Request (Bulk Write)