CSV Connector for Python
CSV Connector can be used to extract and output CSV data from Web URL/REST API web service calls (Web URL) or direct CSV String (variables or DB columns) or local CSV files data.
In this article you will learn how to quickly and efficiently integrate CSV data in Python. We will use high-performance CSV Connector to easily connect to CSV and then access the data inside Python.
Let's follow the steps below to see how we can accomplish that!
CSV Connector for Python is based on ZappySys CSV Driver which is part of ODBC PowerPack. It is a collection of high-performance ODBC drivers that enable you to integrate data in SQL Server, SSIS, a programming language, or any other ODBC-compatible application. ODBC PowerPack supports various file formats, sources and destinations, including REST/SOAP API, SFTP/FTP, storage services, and plain files, to mention a few.
Create ODBC Data Source (DSN) based on ZappySys CSV Driver
Step-by-step instructions
To get data from CSV using Python we first need to create a DSN (Data Source) which will access data from CSV. We will later be able to read data using Python. Perform these steps:
-
Download and install ODBC PowerPack.
-
Open ODBC Data Sources (x64):
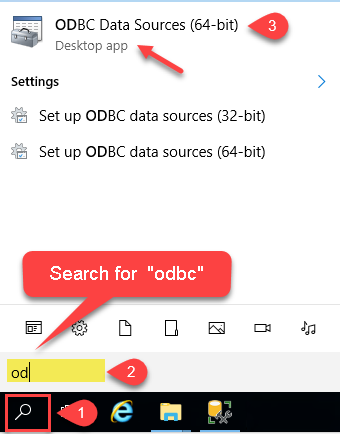
-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on ZappySys CSV Driver:
ZappySys CSV Driver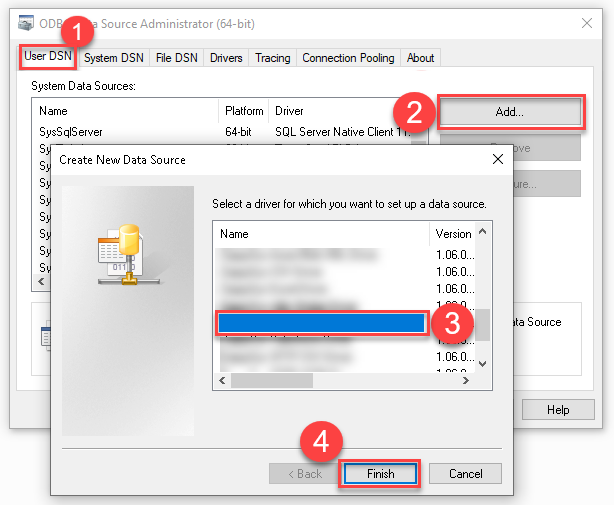
-
Create and use User DSN
if the client application is run under a User Account.
This is an ideal option
in design-time , when developing a solution, e.g. in Visual Studio 2019. Use it for both type of applications - 64-bit and 32-bit. -
Create and use System DSN
if the client application is launched under a System Account, e.g. as a Windows Service.
Usually, this is an ideal option to use
in a production environment . Use ODBC Data Source Administrator (32-bit), instead of 64-bit version, if Windows Service is a 32-bit application.
-
Create and use User DSN
if the client application is run under a User Account.
This is an ideal option
-
Select Url or File.
Read CSV API in Python
-
Paste the following Url. In this example, We are using Zip format CSV File URL, but you need to refer your CSV File/URL.
https://zappysys.com/downloads/files/test/cust-1.csv.zipClick on Test Connection button to view whether the Test Connection is SUCCESSFUL or Not.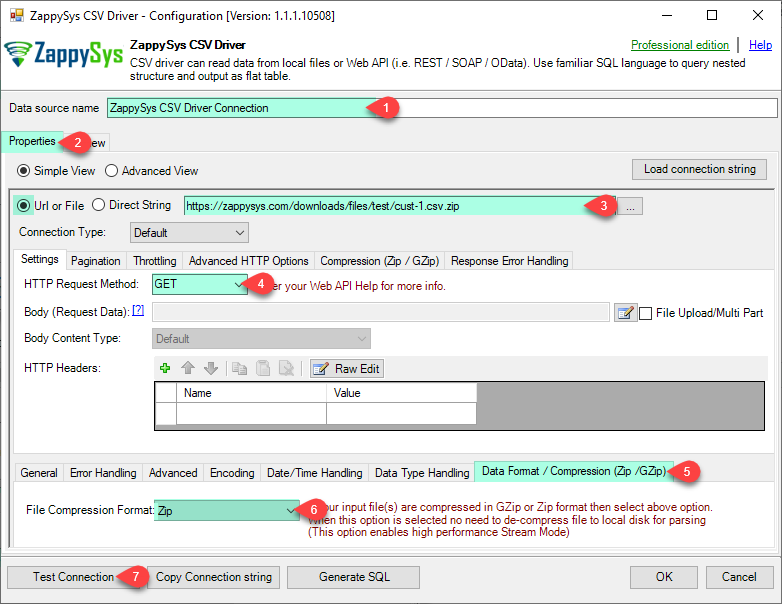
Read CSV File in Python
-
You can use pass single file or multiple file path using wildcard pattern in path and you can use select single file by clicking [...] path button or multiple file using wildcard pattern in path.
Note: If you want to operation with multiple files then use wild card pattern as below (when you use wild card pattern in source path then system will treat target path as folder regardless you end with slash) C:\SSIS\Test\reponse.csv (will read only single reponse.csv file) C:\SSIS\Test\j*.csv (all files starting with file name j) C:\SSIS\Test\*.csv (all files with .csv Extension and located under folder subfolder)
Click on Test Connection button to view whether the Test Connection is SUCCESSFUL or Not.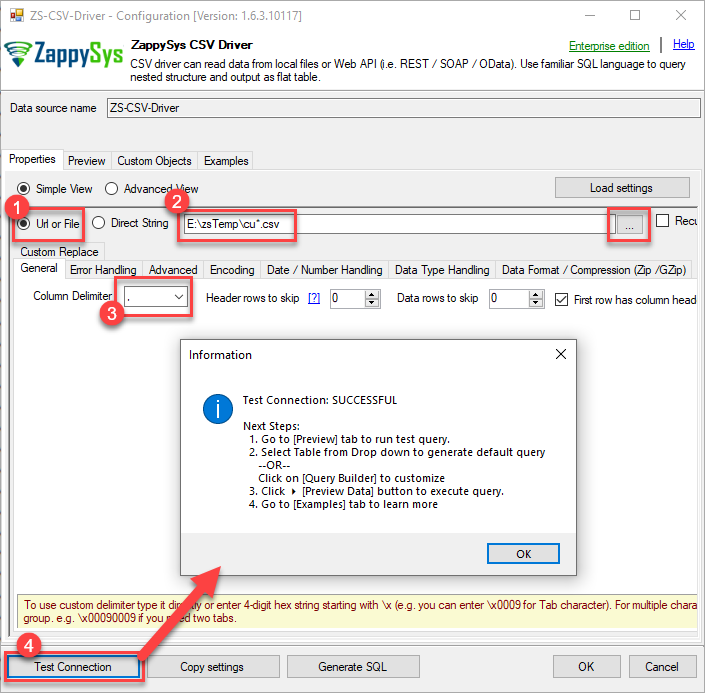
-
-
Once you configured a data source, you can preview data. Hit Preview tab, and use similar settings to preview data:
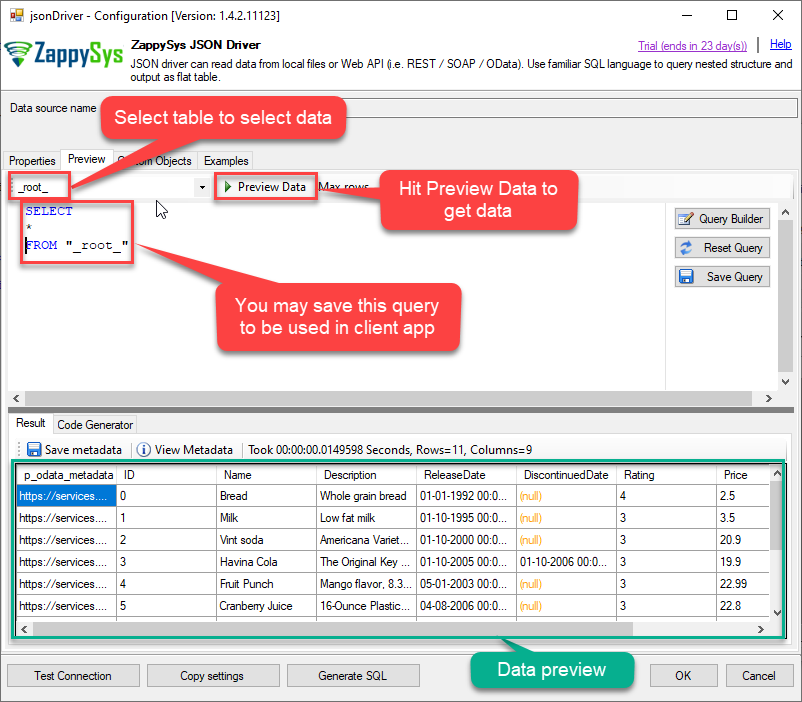
-
Click OK to finish creating the data source
-
That's it; we are done. In a few clicks we configured the read the CSV data using ZappySys CSV Connector.
Read data in Python
Using ODBC DSN
-
Use this code snippet to read the data using
CsvDSNdata source:CsvDSN')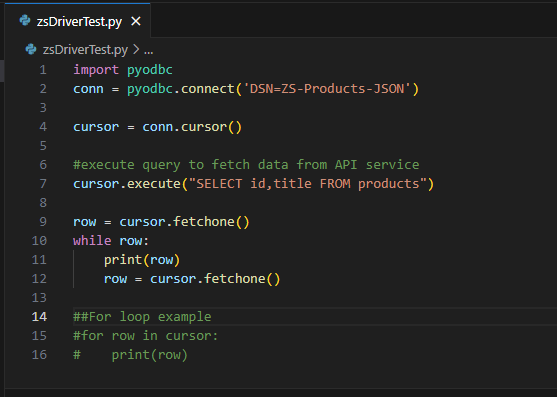
-
When you run the code it will make the API call and read the data:
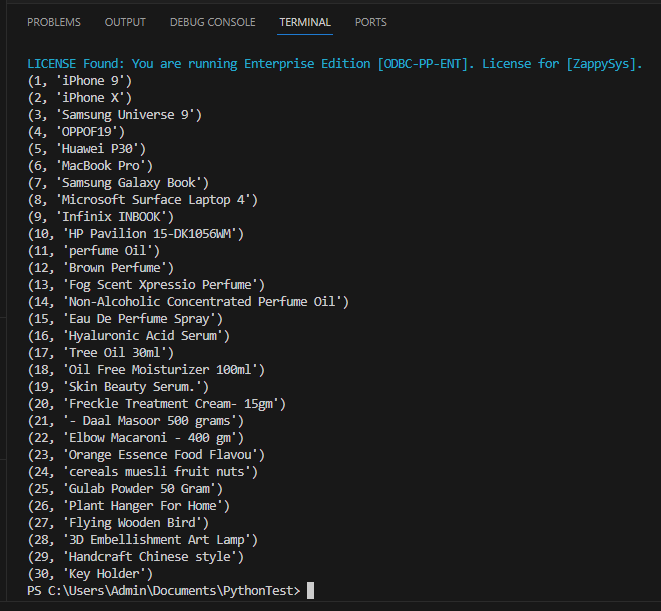
-
Here is Python program's code in text format:
import pyodbc conn = pyodbc.connect('DSN=CsvDSN') cursor = conn.cursor() #execute query to fetch data from API service cursor.execute("SELECT id,title FROM products") row = cursor.fetchone() while row: print(row) row = cursor.fetchone() ##For loop example #for row in cursor: # print(row)
Using a full ODBC connection string
If you want to avoid being dependent on a DSN and creating multiple DSNs for each platform (x86, x64), then you can use a fully qualified connection string. Simply go to your DSN and copy the Connection String:
-
Open ODBC data source configuration and click Copy settings:
 ZappySys CSV Driver - CSVCSV Connector can be used to extract and output CSV data from Web URL/REST API web service calls (Web URL) or direct CSV String (variables or DB columns) or local CSV files data.CsvDSN
ZappySys CSV Driver - CSVCSV Connector can be used to extract and output CSV data from Web URL/REST API web service calls (Web URL) or direct CSV String (variables or DB columns) or local CSV files data.CsvDSN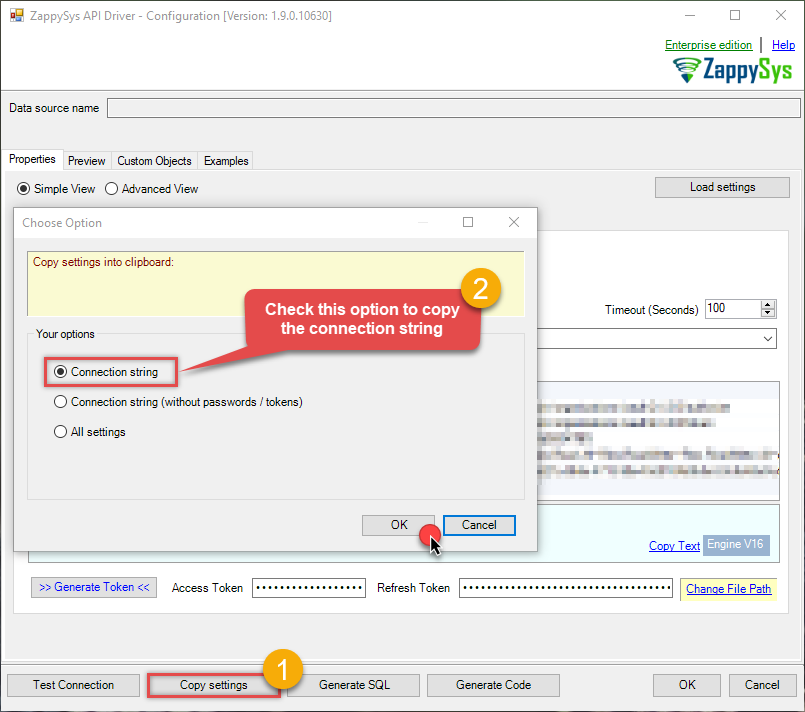
-
The window opens, telling us the connection string was successfully copied to the clipboard:
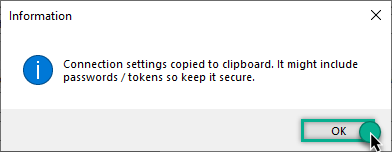
-
Then in your Python code use Connection String when initializing OdbcConnection object, for example:
conn = pyodbc.connect('DRIVER={ZappySys CSV Driver};ServiceUrl=https://yourservices.provider.com/api/xxxx....;AuthName=Http;')
How to install `pyodbc` in the Python?
You would need to install pyodbc in Python if you intend to establish connections to databases that support ODBC (Open Database Connectivity). This module facilitates communication between Python applications and various database management systems, enabling you to perform operations such as querying, retrieving data, and managing databases. Here's how you can install pyodbc in Python:
Installation Steps:
Ensure you have Python installed on your system. If not, download it from the official Python website and follow the installation instructions.
Open your terminal or command prompt.
-
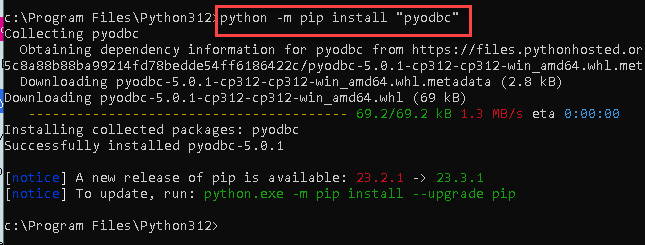
Use the following command to install
pyodbcusing pip, the Python package installer:python -m pip install "pyodbc"Make sure you have a stable internet connection and the necessary permissions to install Python packages.
Reasons to Install:
- If pyodbc is not installed, your Python script will generate the following error:
"ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pyodbc'"
. Database Connectivity:
pyodbcallows Python to connect to various databases that support ODBC, such as Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, and more.Data Operations: It facilitates the execution of SQL queries, retrieval of data, and other database operations from within Python scripts.
Cross-Platform Support:
pyodbcis designed to work across different operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and various Linux distributions.Simplicity and Efficiency: The module provides an intuitive interface for managing database transactions and connections, simplifying the process of working with databases in Python.
By installing pyodbc, you can seamlessly integrate your Python applications with a wide range of ODBC-supported databases, enabling efficient and effective data management and analysis.
Centralized data access via Data Gateway
In some situations, you may need to provide CSV data access to multiple users or services. Configuring the data source on a Data Gateway creates a single, centralized connection point for this purpose.
This configuration provides two primary advantages:
-
Centralized data access
The data source is configured once on the gateway, eliminating the need to set it up individually on each user's machine or application. This significantly simplifies the management process.
-
Centralized access control
Since all connections route through the gateway, access can be governed or revoked from a single location for all users.
| Data Gateway |
Local ODBC
data source
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Simple configuration | ||
| Installation | Single machine | Per machine |
| Connectivity | Local and remote | Local only |
| Connections limit | Limited by License | Unlimited |
| Central data access | ||
| Central access control | ||
| More flexible cost |
If you need any of these requirements, you will have to create a data source in Data Gateway to connect to CSV, and to create an ODBC data source to connect to Data Gateway in Python.
Let's not wait and get going!
Creating CSV data source in Gateway
In this section we will create a data source for CSV in Data Gateway. Let's follow these steps to accomplish that:
-
Search for
gatewayin Windows Start Menu and open ZappySys Data Gateway Configuration:
-
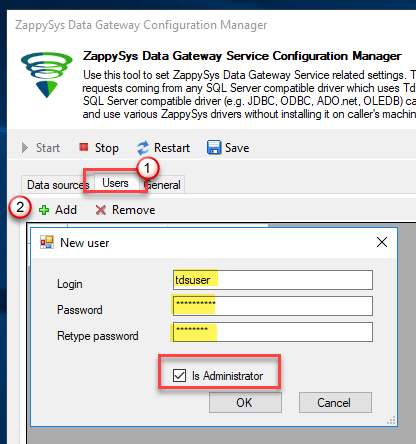
Go to Users tab and follow these steps to add a Data Gateway user:
- Click Add button
-
In Login field enter username, e.g.,
john - Then enter a Password
- Check Is Administrator checkbox
- Click OK to save
-
Now we are ready to add a data source:
- Click Add button
- Give Datasource a name (have it handy for later)
- Then select Native - ZappySys CSV Driver
- Finally, click OK
CsvDSNZappySys CSV Driver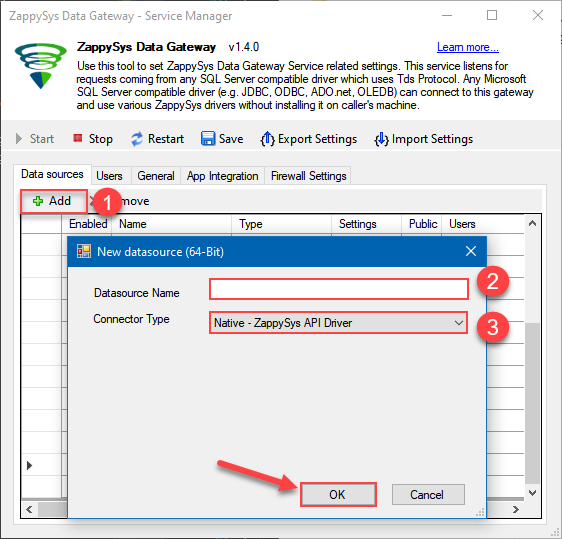
-
When the ZappySys CSV Driver configuration window opens, configure the Data Source the same way you configured it in ODBC Data Sources (64-bit), in the beginning of this article.
-
Very important step. Now, after creating or modifying the data source make sure you:
- Click the Save button to persist your changes.
- Hit Yes, once asked if you want to restart the Data Gateway service.
This will ensure all changes are properly applied:
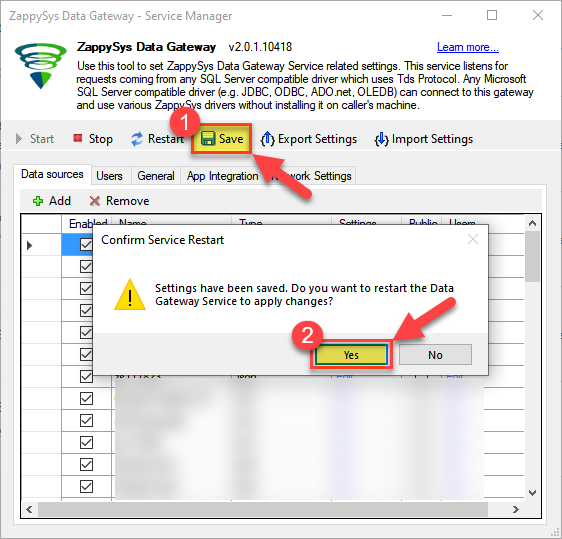 Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Skipping this step may result in the new settings not taking effect and, therefore you will not be able to connect to the data source.
Creating ODBC data source for Data Gateway
In this part we will create ODBC data source to connect to Data Gateway from Python. To achieve that, let's perform these steps:
-
Open ODBC Data Sources (x64):

-
Create a User data source (User DSN) based on ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server:
ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server If you don't see ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version driver.
If you don't see ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server driver in the list, choose a similar version driver. -
Then set a Name of the data source (e.g.
Gateway) and the address of the Data Gateway:GatewayDSNlocalhost,5000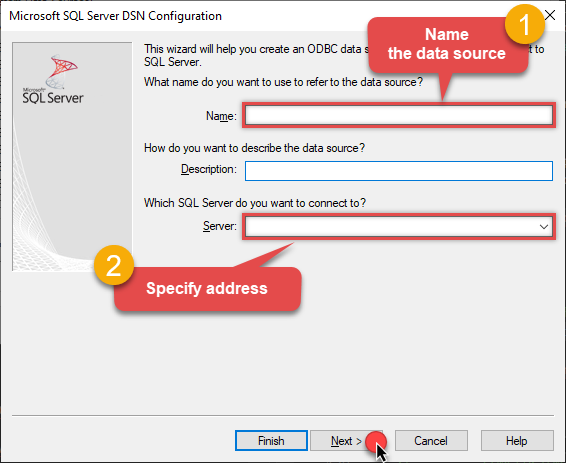 Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.
Make sure you separate the hostname and port with a comma, e.g.localhost,5000. -
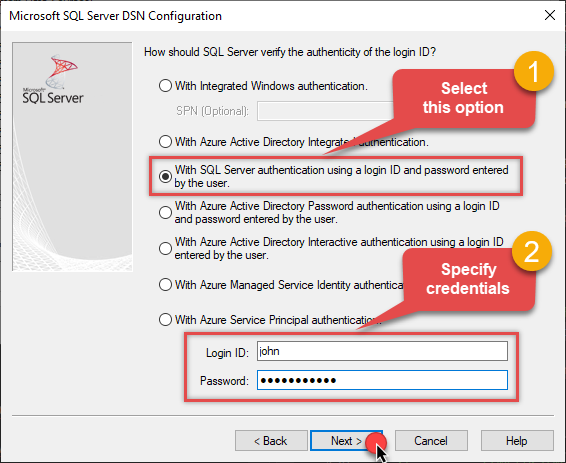
Proceed with authentication part:
- Select SQL Server authentication
-
In Login ID field enter the user name you used in Data Gateway, e.g.,
john - Set Password to the one you configured in Data Gateway
-
Then set the default database property to
CsvDSN(the one we used in Data Gateway):CsvDSN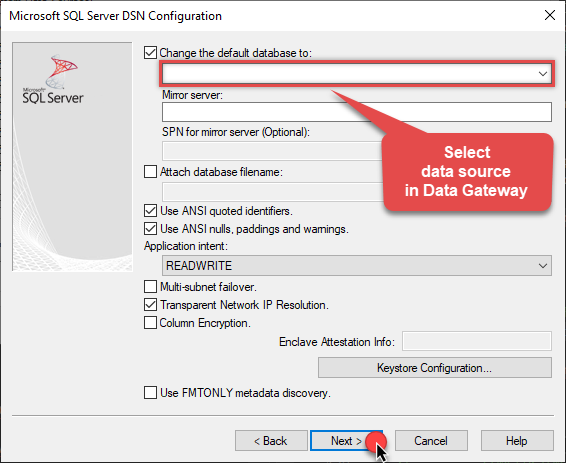
-
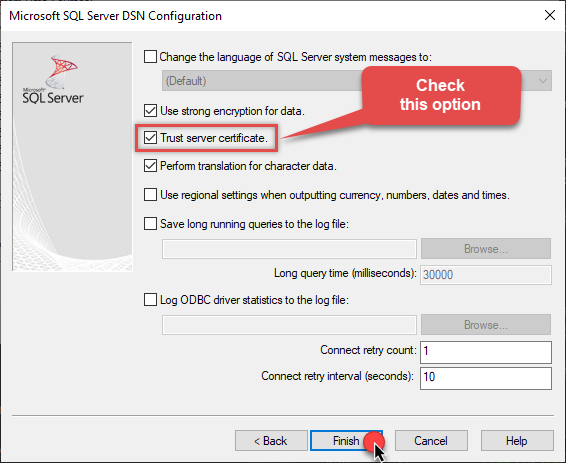
Continue by checking Trust server certificate option:
-
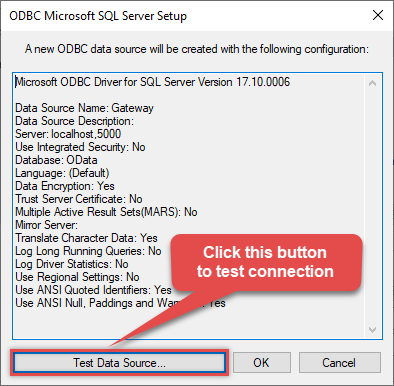
Once you do that, test the connection:
-
If connection is successful, everything is good:
-
Done!
We are ready to move to the final step. Let's do it!
Accessing data in Python via Data Gateway
Finally, we are ready to read data from CSV in Python via Data Gateway. Follow these final steps:
-
Go back to Python.
-
Use this code snippet to read the data using
GatewayDSNdata source:GatewayDSN')
-
Read the data the same way we discussed at the beginning of this article.
-
That's it!
Now you can connect to CSV data in Python via the Data Gateway.
john and your password.
Configuring pagination in the CSV Driver
ZappySys CSV Driver equips users with powerful tools for seamless data extraction and management from REST APIs, leveraging advanced pagination methods for enhanced efficiency. These options are designed to handle various types of pagination structures commonly used in APIs. Below are the detailed descriptions of these options:
Page-based Pagination: This method works by retrieving data in fixed-size pages from the Rest API. It allows you to specify the page size and navigate through the results by requesting different page numbers, ensuring that you can access all the data in a structured manner.
Offset-based Pagination: With this approach, you can extract data by specifying the starting point or offset from which to begin retrieving data. It allows you to define the number of records to skip and fetch subsequent data accordingly, providing precise control over the data extraction process.
Cursor-based Pagination: This technique involves using a cursor or a marker that points to a specific position in the dataset. It enables you to retrieve data starting from the position indicated by the cursor and proceed to subsequent segments, ensuring that you capture all the relevant information without missing any records.
Token-based Pagination: In this method, a token serves as a unique identifier for a specific data segment. It allows you to access the next set of data by using the token provided in the response from the previous request. This ensures that you can systematically retrieve all the data segments without duplication or omission.
Utilizing these comprehensive pagination features in the ZappySys CSV Driver facilitates efficient data management and extraction from REST APIs, optimizing the integration and analysis of extensive datasets.
For more detailed steps, please refer to this link: How to do REST API Pagination in SSIS / ODBC Drivers
Authentication
ZappySys offers various authentication methods to securely access data from various sources. These authentication methods include OAuth, Basic Authentication, Token-based Authentication, and more, allowing users to connect to a wide range of data sources securely.
ZappySys Authentication is a robust system that facilitates secure access to data from a diverse range of sources. It includes a variety of authentication methods tailored to meet the specific requirements of different data platforms and services. These authentication methods may involve:
OAuth: ZappySys supports OAuth for authentication, which allows users to grant limited access to their data without revealing their credentials. It's commonly used for applications that require access to user account information.
Basic Authentication: This method involves sending a username and password with every request. ZappySys allows users to securely access data using this traditional authentication approach.
Token-based Authentication: ZappySys enables users to utilize tokens for authentication. This method involves exchanging a unique token with each request to authenticate the user's identity without revealing sensitive information.
By implementing these authentication methods, ZappySys ensures the secure and reliable retrieval of data from various sources, providing users with the necessary tools to access and integrate data securely and efficiently. For more comprehensive details on the authentication process, please refer to the official ZappySys documentation or reach out to their support team for further assistance.
For more details, please refer to this link: ZappySys Connections
Conclusion
In this article we showed you how to connect to CSV in Python and integrate data without any coding, saving you time and effort.
We encourage you to download CSV Connector for Python and see how easy it is to use it for yourself or your team.
If you have any questions, feel free to contact ZappySys support team. You can also open a live chat immediately by clicking on the chat icon below.
Download CSV Connector for Python Documentation