MongoDB Native Query Language
Many features supported by MongoDB query engine is not implemented in our light weight SQL Style query language for MongoDB. In that case you can always use
Native MongoDB query syntax for full capability found in
db.collection.find(...).
When you use SQL Query for MongoDB Source it generates native query behind the scene. Syntax for using Native query is below. Below syntax has two parts. First part includes Table name, projection field names (optional) and row limit (optional). Second part includes actual native query document ( first argument of
db.collection.find(...) method goes here).
MongoDB Native query support
many query operators (see below).
Syntax for MongoDB native query inside SSIS MongoDB Source:
{
Table:YourTableName
[,Method: Find|Aggregate|Distinct]
[,MaxRows: N]
[,Columns: column1|column2...columnN]
[,AllowCursor: true|false]
[,AllowDiskUse: true|false]
[,Timeout: N]
[,Comment: your_comment_without_comma]
[,Hint: indexed_column_name1=1|-1;indexed_column_name2=1|-1...]
[,CursorType:NonTailable|Tailable|TailableAwait]
[,NoCursorTimeout=true|false]
[,AllowPartialResults=true|false]
[,BypassDocumentValidation=true|false]
}
{
<MongoDB-Query-OR-Pipeline-Goes-Here>
}
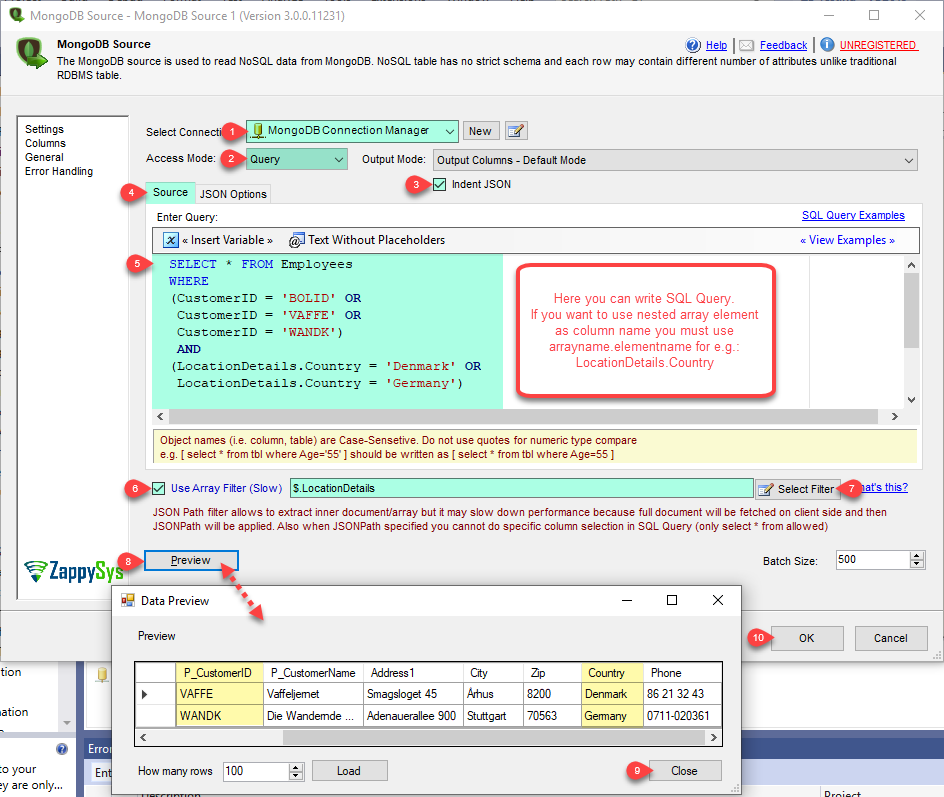
Example : MongoDB native query (use of Query operators)
See below example of using native query inside MongoDB Source (MaxRows and Columns are optional. If you omit them all rows and all columns returned).
{Table:Customer, MaxRows: 2, Columns:"Age|CustomerID"}
{
"$and":
[
{"$or":
[{"CustomerID": "ALFKI"},
{"CustomerID": "BOLID"}
]},
{"$or":
[{"Age": 1},
{"Age": 2},
{"Age": 3}
]}
]
}
| Option |
Description |
| Table (Required) |
Collection name on which you want to perform Aggregation.
|
| Method (Optional) |
Supported methods Find (Default), Aggregation and Distinct. If you specify Method: Aggregation then you must specify pipeline attribute in query body. If you specify Distinct then you must specify Columns: YourColumnName.
|
| MaxRows |
(Optional - Valid for=Find|Aggregate|Distinct) Default=0 (i.e. no limit). Maximum number of rows you want to output (Similar as select top N from collection) |
| AllowDiskUse |
(Optional - Valid for=Find|Aggregate) Default=True. This option allow to exceed 100MB RAM limitation for pipeline. When set to true, aggregation operations can write data to the _tmp subdirectory in the dbPath directory |
| AllowCursor (For Older version) |
(Optional - Valid for=Find|Aggregate) Default=True. This option enables cursor which fetch data in batch. See BatchSize property of component to control size of batch. If you have large documents then reduce size of Batch so all records together is less than 16MB limit of single batch. You may sometimes get error aggregation result exceeds maximum document size (16MB). In that case reduce Batch size until error goes away. |
| Timeout |
(Optional - Valid for=Find|Aggregate|Distinct). Timeout for command in seconds. This option specify how long single command can execute before throwing timeout error (Max time server is allowed to execute the specified query). |
| Comment (For new version only) |
(Optional - Valid for=Find|Aggregate|Distinct) String to describe your query (Useful for logging purpose). Do not use comma in the string. |
| Hint (For new version only) |
(Optional - Valid for=Find|Aggregate|Distinct) Specifies hint to use one or more indexed columns. Syntax: indexed_column1[=1|-1][,indexed_column2=[1|-1]]...[,indexed_columnN=[1|-1]]. 1 mean Ascending and -1 means Descending order index. |
| CursorType (For new version only) |
(Optional - Valid for=Find) Specifies cursor type to use. |
| NoCursorTimeout (For new version only) |
(Optional - Valid for=Find) Do not time out of cursor is idle. |
| AllowPartialResults (For new version only) |
(Optional - Valid for=Find) Allow partial result if shard not available. |
| BypassDocumentValidation (For new version only) |
(Optional - Valid for=Aggregate) Allow partial result if shard not available. |
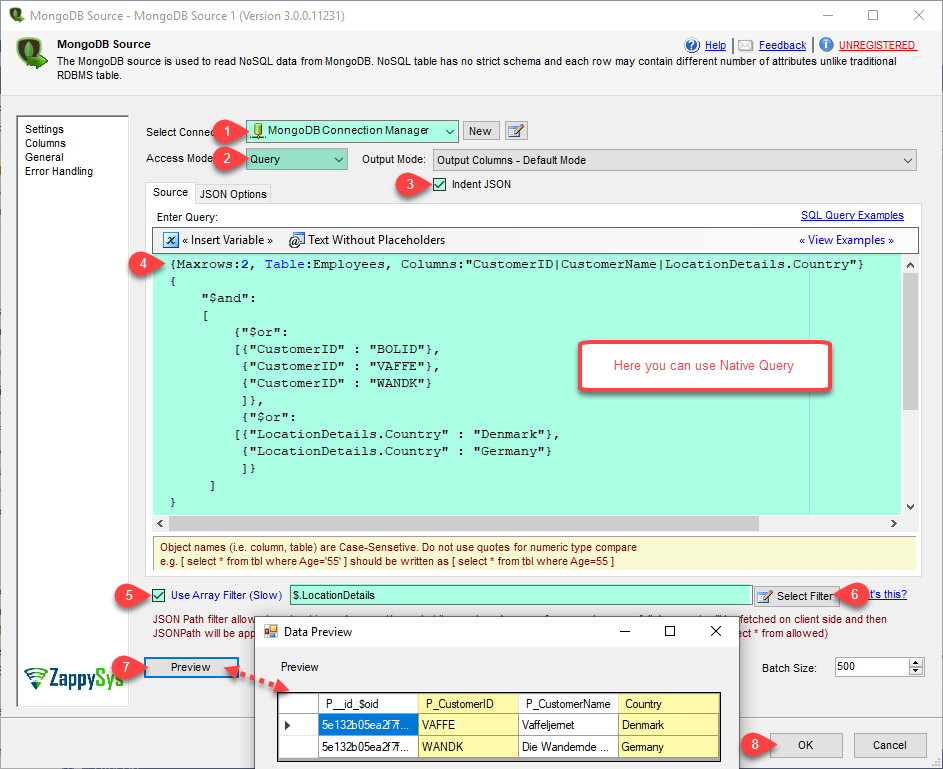
Above code is same as below SQL query
SELECT TOP 2 Age, CustomerID FROM Customer WHERE (CustomerID='ALFKI' OR CustomerID='BOLID') AND (Age=1 OR Age=2 OR Age=3)
MongoDB Aggregation Framework (Group by)
If you want to write aggregation queries in MongoDB (similar to Group By query in SQL language) then you must use Native query language because custom SQL Query language of MongoDB Source doesn't support Group By construct.To learn more about aggregation framework and pipeline operators check below links.
SQL vs MongoDB Aggregation Comparison
Aggregation framework pipeline operators
db.collection.aggregate()
Aggregation Pipeline Process
Here is syntax of Aggregation query syntax in MongoDB Source
{Table:YourTableName
,Method:aggregate
[,AllowCursor: true|false]
[,AllowDiskUse: true|false]
[,Timeout: N]
[,Comment: your_comment_without_comma]
[,Hint: column1=1|-1;column2=1|-1...]
}
{
pipeline: [
[ <pipeline-stage1-more-info>]
[,<pipeline-stage2-more-info>]
...
...
[,<pipeline-stageN-more-info>]
]
}
Performance tuning / Handling large documents / Buffers
Many times you may face slow queries. In that case make sure following few things.
- Make sure you have proper index defined on the necessary column used in query. Example if you searching based on PartNumber make sure its indexed.
- If you have large documents make sure BatchSize is set correctly to avoid 16MB limit error. Each batch cannot exceed
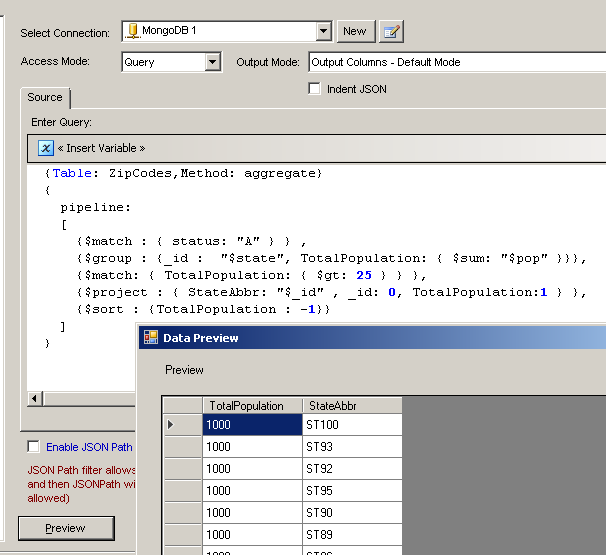
Example : MongoDB native query using aggregation framework (Group By)
Here is an example of group by query using MongoDB Source. Notice how we arranged various pipeline stages in specific order under pipeline:[ {..},{..},{..} ] just like how you write SQL query in specific way (SELECT..FROM..WHERE..GROUP BY..HAVING..ORDER BY). MongoDB Aggregation Pipeline has similar concepts (e.g. $match, $group, $projection, $sort). Its not exact same way as SQL but you get an idea how to do aggregation in MongoDB. Notice that $match operator is used for filter (e.g. WHERE and HAVING both) in above example. If $match appears before $group stage then it acts as WHERE clause else HAVING clause (see below). To read more about various pipeline operators
check this link
{Table: ZipCodes,Method: aggregate}
{
pipeline:
[
{$match : { status: "A" } } ,
{$group : {_id : "$state", TotalPopulation: { $sum: "$pop" }}},
{$match: { TotalPopulation: { $gt: 25 } } },
{$project : { StateAbbr: "$_id" , _id: 0, TotalPopulation:1 } },
{$sort : {TotalPopulation : -1}}
]
}
Above MongoDB query is same as below relational SQL query
SELECT State as StateAbbr,SUM(population) as TotalPopulation
FROM ZipCodes
WHERE status='Active'
HAVING SUM(population) > 25
Order By TotalPopulation DESC
Example : Getting distinct values in MongoDB Source
If you want to fetch distinct values for specific field using MongoDB Source then write following Native query.
{Table: ZipCodes,Method: distinct, Columns:'State'}
{
}
Above query is same as below SQL
SELECT DISTINCT state FROM ZipCodes
--OR-- Use some filter like below
{Table: ZipCodes,Method: distinct, Columns:'State'}
{
$and: { status:'A', country:'USA' }
}
Above query is same as below SQL
SELECT DISTINCT state FROM ZipCodes WHERE status='A' AND country='USA'
Example : MongoDB native query (use of $where expression)
Here is another powerful use of
$where query operator. $where support expressions and javascript functions for advanced query. However only use this operator if you cant use other operators such as (
comparison operators and
logical operators) because when you javascript in $where it may not use index defined on columns in your collection.
Use the $where operator to pass either a string containing a JavaScript expression or a full JavaScript function to the query system. The $where provides greater flexibility, but requires that the database processes the JavaScript expression or function for each document in the collection. Reference the document in the JavaScript expression or function using either this or obj .
{Table:Customer}
{ $where: "this.credits == this.debits" }
MongoDB SQL Query Language
If you work with traditional RDBMS and you recently come to NoSQL world you will quickly realize that most of NoSQL database vendors including
MongoDB is missing familiar SQL query language. But no worry we got you covered. We have implemented custom query parser which will do hard work for you so you don't have to spend time learning new query language for MongoDB. Our query engine will
convert SQL query to Native MongoDB query language.
SQL Grammar for MongoDB:
<Select Statement> ::= SELECT [{TOP Clause}] {Column List} {From Clause} [{Where Clause}] [{OrderBy Clause}]
<TOP Clause> ::= TOP IntegerLiteral
<Column List> ::= * | IDENTIFIER [ [,IDENTIFIER] [,IDENTIFIER] ... ]
<From Clause> ::= FROM IDENTIFIER
<Where Clause> ::= WHERE <Expression List>
<OrderBy Clause>::= ORDER BY IDENTIFIER [ASC|DESC] [[,IDENTIFIER [ASC|DESC] [,IDENTIFIER [ASC|DESC] ... ]
! =============================================================================
! Expressions
! =============================================================================
! Nesting AND, OR supported using Multiple conditions
<Expression List> ::= <Expression>
| <Expression> AND <Expression>
| <Expression> AND (<Expression List>)
| <Expression> OR <Expression>
| <Expression> OR (<Expression List>)
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER = <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER != <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER <> <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER > <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER >= <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER < <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER <= <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER IN (<Value> [[, <Value>] [, <Value>] ...])
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER BETWEEN <Value> AND <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER LIKE <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER NOT LIKE <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER NOT LIKE <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER CONTAINS <Value>
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER IS NULL
<Expression> ::= IDENTIFIER IS NOT NULL
<Value> ::= IntegerLiteral | StringLiteral
Supported Operators:
- AND
- OR
- IN
- NOT IN
- IS NULL
- IS NOT NULL
- LIKE (Only % allowed)
- NOT LIKE
- BETWEEN
- NOT BETWEEN
- = (Equal)
- !=, <> (Not Equal)
- < (Less than)
- > (Greater than)
- <= (Less than or equal to)
- >= (Greater than or equal to)
Searching for text patterns (Use of Regular Expressions):
To search text pattern you may use simple wild card (i.e. % ) in your LIKE clause or specify REGX hint. Your text pattern can end with search hints. To specify search hints use vertical bar and then one or more following options
select * from mytable where column LIKE 'some-pattern|[i][r][x][m][s]'
where options are as below
Searching for text (case-sensitive mode - this is default):
by default text pattern search is case-sensitive so no option needed.
select * from customers where password LIKE 'P@ss'
Searching for text patterns (case-insensitive mode):
by default text pattern search is case-sensitive. If you want to perform case in-sensitive search then you must provide option [i] at the end after vertical bar.
select * from customers where City LIKE 'New%|i'
Searching for text patterns using Regular Expression:
select * from customers where phone LIKE '\d\d\d|r'
Using multiple options:
select * from customers where notes LIKE '^ABC\d(.*)|rm'
MongoDB SQL query language examples:
-- Selecting all columns
select * from CustomerTest
-- Selecting multiple columns
select CustomerID,CompanyName from CustomerTest
-- Selecting multiple columns, where some attribute name has space in it
select CustomerID,[Contact Title] from CustomerTest
-- Using Where clause with simple condition, select all columns
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID='ALC3R'
-- Query ISO Date attribute
select * from Orders Where OrderDate='DATE(2015-01-31)'
-- Using ORDER BY on single column
select * from CustomerTest Order By CustomerID
-- Using muliple columns in ORDER BY
select * from CustomerTest Order By CustomerID ASC,Country DESC
-- Using CONTAINS to do substring search
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID CONTAINS 'C3'
-- Using LIKE to do substring search (Only % allowed as wildcard character)
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID LIKE '%C3%'
-- Using NOT LIKE: Return all records where CustomerID doesnt contain substring 'C3'
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID NOT LIKE '%C%'
-- Using LIKE to search for starts with: search all record where ContactName starts with Maria
select * from CustomerTest Where ContactName LIKE 'Maria%'
-- Limiting records returned from query using TOP clause (Similar as LIMIT found inn some RDBMS query engine)
select top 7 * from CustomerTest
-- Using IN with String Values: select all records where CustomerID is 'ALFKI' or 'BOLID' or 'C3' (String values)
select * from CustomerTest where CustomerID IN ('ALFKI', 'BOLID','C3')
-- Using IN with Numeric Values: select all records where Age is 5 or 7 (Numeric values)
select * from CustomerTest where Age IN (5,7)
-- Using OR
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID = 'ALFKI' OR CustomerID = 'BOLID'
-- Using OR
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID = 'ALFKI' OR CustomerID = 'BOLID'
-- Mixing OR / AND
select * from CustomerTest Where (CustomerID = 'ALFKI' OR CustomerID='BOLID') AND (Age =1 OR Age =2 OR Age =3)
-- Using IS NOT NULL: Get all records where Age attribute is present and set to some value other than NULL
select * from CustomerTest Where Age IS NOT NULL
-- Using IS NULL: Get all records where Age attribute is either MISSING or is set to null
select * from CustomerTest Where Age IS NULL
-- Using comparision operators
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID <> 'ALFKI'
select * from CustomerTest Where CustomerID != 'ALFKI'
select * from CustomerTest Where Age > 5
select * from CustomerTest Where Age >= 5
select * from CustomerTest Where Age < 5
select * from CustomerTest Where Age = 5 AND CustomerID = 'C5'
-- Using BETWEEN for range compare
select * from CustomerTest Where Age Between 5 AND 10
-- Using NOT BETWEEN for range compare
select * from CustomerTest Where Age Not Between 5 AND 10
-- Mixing conditions
select * from CustomerTest Where (Age >= 1 OR Age <= 10) AND (CustomerID ='C7' Or CustomerID ='C9' )
select * from CustomerTest Where (CustomerID = 'ALFKI' OR (CustomerID = 'BOLID' OR (CustomerID = 'C1')))